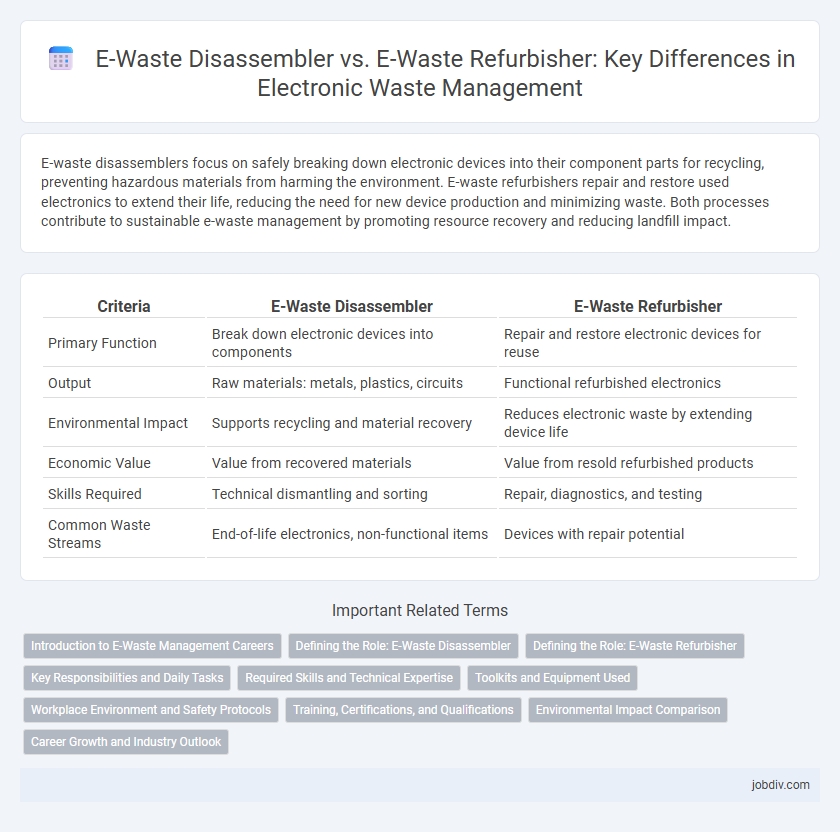
E-waste disassemblers focus on safely breaking down electronic devices into their component parts for recycling, preventing hazardous materials from harming the environment. E-waste refurbishers repair and restore used electronics to extend their life, reducing the need for new device production and minimizing waste. Both processes contribute to sustainable e-waste management by promoting resource recovery and reducing landfill impact.
Table of Comparison
| Criteria | E-Waste Disassembler | E-Waste Refurbisher |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Break down electronic devices into components | Repair and restore electronic devices for reuse |
| Output | Raw materials: metals, plastics, circuits | Functional refurbished electronics |
| Environmental Impact | Supports recycling and material recovery | Reduces electronic waste by extending device life |
| Economic Value | Value from recovered materials | Value from resold refurbished products |
| Skills Required | Technical dismantling and sorting | Repair, diagnostics, and testing |
| Common Waste Streams | End-of-life electronics, non-functional items | Devices with repair potential |
Introduction to E-Waste Management Careers
E-waste disassemblers specialize in systematically dismantling electronic devices to extract valuable materials like metals and plastics for recycling, reducing environmental harm. E-waste refurbishers focus on testing, repairing, and restoring used electronics for resale, extending product life and minimizing landfill contributions. Both careers are essential in the e-waste management industry, offering sustainable solutions and opportunities in environmental conservation and resource recovery.
Defining the Role: E-Waste Disassembler
An E-Waste Disassembler specializes in breaking down electronic devices into individual components for safe recycling and material recovery. This role involves systematically separating hazardous materials, such as lead and mercury, from valuable parts like gold and copper to prevent environmental contamination. Their expertise ensures that recyclable elements are efficiently extracted, minimizing landfill waste and supporting sustainable resource management.
Defining the Role: E-Waste Refurbisher
An E-Waste Refurbisher specializes in restoring used electronic devices to functional condition by repairing, replacing components, and upgrading software, extending product life cycles and reducing environmental impact. This role emphasizes quality testing and certification to ensure refurbished items meet safety and performance standards before resale or donation. Compared to disassemblers who primarily focus on material recovery and recycling, refurbishers prioritize reuse and circular economy principles in e-waste management.
Key Responsibilities and Daily Tasks
E-Waste Disassemblers specialize in safely breaking down electronic devices into primary components, focusing on hazardous material removal and sorting recyclable parts like metals, plastics, and circuit boards. E-Waste Refurbishers prioritize diagnosing and repairing defective electronics to restore functionality, performing tasks such as testing hardware, replacing faulty components, and upgrading systems. Both roles require strict adherence to environmental regulations and workplace safety protocols to minimize health risks and prevent toxic waste contamination.
Required Skills and Technical Expertise
E-waste disassemblers require proficiency in safely dismantling electronic devices, identifying hazardous components, and using specialized tools to separate recyclable materials without causing environmental harm. E-waste refurbishers need advanced technical expertise in diagnosing, repairing, and upgrading electronics to extend product lifespan while ensuring compliance with industry standards and quality control. Both roles demand knowledge of electronic circuitry, safety protocols, and environmental regulations to optimize recovery and reduce electronic waste impact.
Toolkits and Equipment Used
E-waste disassemblers use specialized hand tools, such as screwdrivers, pliers, and precision cutters, alongside safety gear like gloves and anti-static wristbands to carefully dismantle electronic devices for component separation. E-waste refurbishers employ diagnostic tools, soldering equipment, and software utilities to repair, test, and restore the functionality of used electronics before resale. Both roles require advanced equipment tailored to their unique processes, with disassemblers focusing on safe deconstruction and refurbishers on functional rehabilitation.
Workplace Environment and Safety Protocols
E-Waste disassemblers operate in environments with higher exposure to hazardous materials such as heavy metals and chemicals, requiring stringent safety protocols including protective gear and specialized ventilation systems. In contrast, E-Waste refurbishers generally work in controlled indoor settings where safety focuses more on electrical hazards and ergonomic measures to prevent repetitive strain injuries. Both industries mandate compliance with environmental regulations and worker safety standards, but disassembly demands more rigorous protective measures due to direct contact with toxic components.
Training, Certifications, and Qualifications
E-Waste disassemblers require specialized training in safe handling and dismantling techniques to prevent hazardous material exposure, often needing certifications like R2 or e-Stewards to ensure compliance with environmental standards. E-Waste refurbishers must possess technical qualifications in electronics repair, diagnostics, and quality control, with certifications such as CompTIA A+ or manufacturer-specific credentials to guarantee device functionality and marketability. Both roles prioritize safety and environmental management but differ in skill sets, with disassemblers focusing on material recovery and refurbishers on product restoration.
Environmental Impact Comparison
E-waste disassemblers primarily focus on breaking down electronic devices into reusable components, which reduces hazardous waste and prevents toxic materials like lead and mercury from contaminating soil and water. E-waste refurbishers extend the lifespan of electronics by repairing and upgrading devices, significantly lowering the demand for new products and conserving raw materials, thereby decreasing overall environmental strain. Both processes contribute to sustainable waste management, but disassemblers excel in resource recovery while refurbishers excel in reducing electronic consumption and waste generation.
Career Growth and Industry Outlook
E-waste disassemblers specialize in dismantling electronic devices to recover valuable components, with career growth driven by increasing global e-waste volume and stringent environmental regulations. E-waste refurbishers focus on repairing and upgrading electronics for resale, benefiting from rising demand for affordable, sustainable technology and circular economy initiatives. Both roles offer strong industry outlooks, but refurbishers may experience broader market opportunities due to growing consumer preference for refurbished products and tech sustainability.
E-Waste Disassembler vs E-Waste Refurbisher Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com