Environmental Technicians specialize in monitoring and managing waste to ensure compliance with environmental regulations, often collecting samples and conducting site inspections to prevent pollution. Waste Auditors analyze waste management practices within facilities to identify inefficiencies and recommend improvements for reducing waste generation and disposal costs. Both roles play crucial parts in promoting sustainable waste management but focus on different stages of waste control and assessment.
Table of Comparison
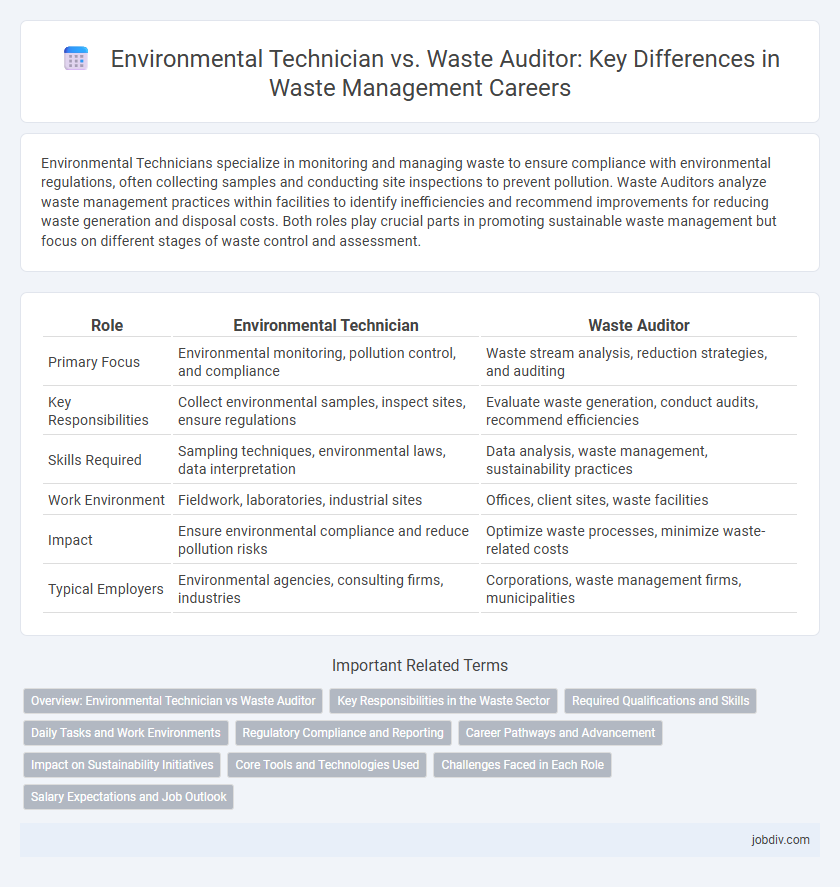
| Role | Environmental Technician | Waste Auditor |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Environmental monitoring, pollution control, and compliance | Waste stream analysis, reduction strategies, and auditing |
| Key Responsibilities | Collect environmental samples, inspect sites, ensure regulations | Evaluate waste generation, conduct audits, recommend efficiencies |
| Skills Required | Sampling techniques, environmental laws, data interpretation | Data analysis, waste management, sustainability practices |
| Work Environment | Fieldwork, laboratories, industrial sites | Offices, client sites, waste facilities |
| Impact | Ensure environmental compliance and reduce pollution risks | Optimize waste processes, minimize waste-related costs |
| Typical Employers | Environmental agencies, consulting firms, industries | Corporations, waste management firms, municipalities |
Overview: Environmental Technician vs Waste Auditor
Environmental Technicians specialize in monitoring and managing pollution and hazardous materials to ensure compliance with environmental regulations, often collecting samples and conducting field inspections. Waste Auditors focus on analyzing waste streams, identifying inefficiencies, and recommending strategies to improve waste reduction and recycling efforts within organizations. Both roles contribute to sustainable environmental management but differ in their core responsibilities and areas of expertise.
Key Responsibilities in the Waste Sector
Environmental Technicians monitor waste management systems by collecting samples, conducting site inspections, and ensuring compliance with environmental regulations. Waste Auditors analyze waste streams through data collection, waste characterization, and reporting to optimize recycling efforts and reduce landfill impact. Both roles collaborate to implement sustainable waste practices and improve overall environmental performance in the waste sector.
Required Qualifications and Skills
Environmental Technicians require a solid foundation in environmental science, typically holding an associate degree or relevant certification, with skills in sample collection, data analysis, and equipment maintenance. Waste Auditors demand expertise in waste management systems, often possessing a bachelor's degree in environmental studies or industrial engineering, alongside strong analytical abilities, attention to detail, and proficiency in auditing protocols. Both roles emphasize knowledge of environmental regulations and sustainability practices but differ in the technical competencies related to hands-on environmental monitoring versus comprehensive waste stream evaluation.
Daily Tasks and Work Environments
Environmental Technicians perform daily tasks such as collecting soil, water, and air samples to monitor pollution levels, maintaining equipment, and supporting environmental cleanup projects. They commonly work in field settings, laboratories, and industrial sites where environmental compliance is critical. Waste Auditors conduct waste stream analyses, prepare detailed reports on waste generation, and recommend waste reduction strategies while typically working in office environments, manufacturing plants, or municipal facilities.
Regulatory Compliance and Reporting
Environmental Technicians ensure regulatory compliance by conducting field inspections, sampling, and monitoring waste management practices to meet environmental standards set by agencies like the EPA. Waste Auditors focus on detailed analysis of waste generation, segregation, and disposal processes, preparing comprehensive reports to verify compliance with local, state, and federal waste regulations. Both roles are critical in maintaining accurate documentation and facilitating corrective actions to prevent regulatory violations and environmental harm.
Career Pathways and Advancement
Environmental Technicians primarily focus on monitoring and managing waste disposal processes, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations, and performing site inspections, which often leads to career advancement in environmental management or hazardous waste supervision. Waste Auditors analyze waste streams to identify reduction opportunities, improve recycling programs, and implement sustainability initiatives, paving the way for roles in waste consultancy or sustainability coordination. Both career paths offer progression into specialized environmental roles, with certifications and experience playing a crucial role in advancement within government agencies, private companies, or environmental organizations.
Impact on Sustainability Initiatives
Environmental Technicians play a crucial role in sustainability initiatives by conducting field inspections, collecting samples, and monitoring pollution levels to ensure compliance with environmental regulations, thereby directly reducing environmental hazards. Waste Auditors specialize in analyzing waste streams, identifying inefficiencies, and recommending waste reduction strategies that optimize resource use and minimize landfill contributions. Both positions significantly enhance sustainability efforts, with Environmental Technicians providing on-site environmental data and Waste Auditors offering actionable insights to improve waste management systems.
Core Tools and Technologies Used
Environmental Technicians primarily utilize air and water quality monitoring instruments, soil sampling tools, and environmental data analysis software to assess pollution levels and ensure regulatory compliance. Waste Auditors rely heavily on waste tracking systems, recycling sorting technologies, and data management platforms to evaluate waste streams and identify opportunities for waste reduction. Both roles incorporate Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and handheld digital devices for precise data collection and reporting, enhancing environmental and waste management efficiency.
Challenges Faced in Each Role
Environmental Technicians face challenges such as managing hazardous materials safely, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations, and maintaining equipment for monitoring pollution levels. Waste Auditors encounter difficulties in accurately assessing waste streams, identifying inefficiencies in waste management practices, and persuading organizations to adopt sustainable waste reduction strategies. Both roles require attention to detail and adaptability to evolving environmental standards and technologies.
Salary Expectations and Job Outlook
Environmental Technicians typically earn an average salary ranging from $40,000 to $55,000 annually, reflecting steady demand in sectors like pollution control and environmental protection. Waste Auditors, with specialized expertise in waste management and sustainability practices, can expect higher salaries averaging between $50,000 and $70,000, driven by increasing regulatory compliance and corporate sustainability initiatives. Both roles offer positive job outlooks, but Waste Auditors benefit from growing emphasis on waste reduction and resource optimization across industries.
Environmental Technician vs Waste Auditor Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com