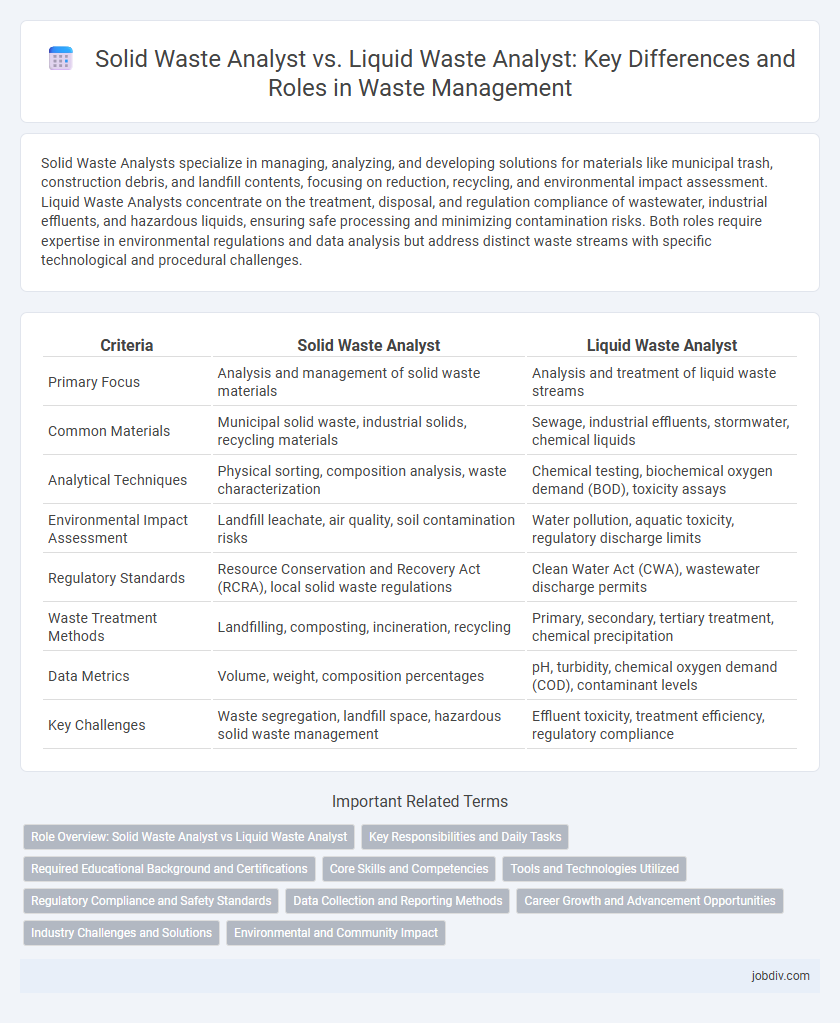
Solid Waste Analysts specialize in managing, analyzing, and developing solutions for materials like municipal trash, construction debris, and landfill contents, focusing on reduction, recycling, and environmental impact assessment. Liquid Waste Analysts concentrate on the treatment, disposal, and regulation compliance of wastewater, industrial effluents, and hazardous liquids, ensuring safe processing and minimizing contamination risks. Both roles require expertise in environmental regulations and data analysis but address distinct waste streams with specific technological and procedural challenges.
Table of Comparison
| Criteria | Solid Waste Analyst | Liquid Waste Analyst |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Analysis and management of solid waste materials | Analysis and treatment of liquid waste streams |
| Common Materials | Municipal solid waste, industrial solids, recycling materials | Sewage, industrial effluents, stormwater, chemical liquids |
| Analytical Techniques | Physical sorting, composition analysis, waste characterization | Chemical testing, biochemical oxygen demand (BOD), toxicity assays |
| Environmental Impact Assessment | Landfill leachate, air quality, soil contamination risks | Water pollution, aquatic toxicity, regulatory discharge limits |
| Regulatory Standards | Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA), local solid waste regulations | Clean Water Act (CWA), wastewater discharge permits |
| Waste Treatment Methods | Landfilling, composting, incineration, recycling | Primary, secondary, tertiary treatment, chemical precipitation |
| Data Metrics | Volume, weight, composition percentages | pH, turbidity, chemical oxygen demand (COD), contaminant levels |
| Key Challenges | Waste segregation, landfill space, hazardous solid waste management | Effluent toxicity, treatment efficiency, regulatory compliance |
Role Overview: Solid Waste Analyst vs Liquid Waste Analyst
A Solid Waste Analyst specializes in managing and analyzing non-liquid waste materials, focusing on waste composition, recycling rates, landfill use, and regulatory compliance for solid waste disposal. A Liquid Waste Analyst concentrates on the treatment and disposal of wastewater, industrial effluents, and hazardous liquid substances, ensuring adherence to environmental standards and optimizing liquid waste processing systems. Both roles require expertise in environmental regulations, data analysis, and waste management technologies, but their focus differs between solid waste streams and liquid waste treatment processes.
Key Responsibilities and Daily Tasks
Solid Waste Analysts focus on assessing, managing, and optimizing the treatment, disposal, and recycling of solid materials, including monitoring landfill operations, analyzing material composition, and ensuring regulatory compliance. Liquid Waste Analysts handle the testing, treatment, and disposal of wastewater and industrial effluents, performing routine sampling, chemical analysis, and process optimization to meet environmental standards. Both roles require expertise in environmental regulations and data interpretation but differ primarily in the physical state of the waste and specialized treatment technologies.
Required Educational Background and Certifications
Solid Waste Analysts typically require a background in environmental science, civil engineering, or waste management, with certifications such as the Certified Hazardous Materials Manager (CHMM) or Registered Environmental Manager (REM) enhancing their expertise. Liquid Waste Analysts often hold degrees in chemical engineering, environmental engineering, or chemistry and benefit from certifications like the Water Environment Federation's (WEF) Certified Operator or the National Association of Wastewater Technicians (NAWT) credentials. Both roles demand strong knowledge of regulatory compliance and environmental protection standards to effectively manage and analyze waste streams.
Core Skills and Competencies
Solid Waste Analysts specialize in waste characterization, landfill management, and recycling processes, requiring expertise in material composition analysis, regulatory compliance, and environmental impact assessment. Liquid Waste Analysts focus on wastewater treatment, chemical analysis, and effluent monitoring, demanding proficiency in fluid dynamics, contamination control, and water quality standards. Both roles necessitate strong data interpretation skills, knowledge of environmental regulations, and proficiency in specialized laboratory techniques tailored to solid or liquid waste streams.
Tools and Technologies Utilized
Solid Waste Analysts use Geographic Information Systems (GIS), waste characterization software, and landfill gas monitoring tools to assess and manage waste composition and landfill operations. Liquid Waste Analysts employ technologies such as spectrophotometers, COD (Chemical Oxygen Demand) analyzers, and advanced wastewater treatment modeling software to evaluate and control water pollution levels. Both roles integrate data analytics platforms to optimize waste management strategies and regulatory compliance.
Regulatory Compliance and Safety Standards
Solid Waste Analysts specialize in managing and analyzing non-liquid waste streams, ensuring compliance with regulations such as the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) and local landfill standards, while implementing safety protocols to minimize exposure to hazardous solids. Liquid Waste Analysts focus on monitoring effluent quality and treatment processes, adhering to the Clean Water Act (CWA) and EPA discharge permits, emphasizing chemical handling safety and spill prevention measures. Both roles require detailed knowledge of environmental regulations and safety standards, with distinct expertise tailored to the physical state of the waste they oversee.
Data Collection and Reporting Methods
Solid Waste Analysts primarily collect data through physical waste audits and spatial mapping, employing GIS technology to analyze landfill capacities and recycling rates. Liquid Waste Analysts focus on sampling and laboratory testing of effluents, utilizing sensors and real-time monitoring systems to track contaminant levels and flow rates. Reporting methods for solid waste emphasize volumetric and weight metrics, whereas liquid waste reporting highlights chemical composition and adherence to environmental discharge standards.
Career Growth and Advancement Opportunities
Solid Waste Analysts typically experience career growth by advancing into environmental consultancy, waste management planning, or regulatory compliance roles due to increasing municipal and industrial waste challenges. Liquid Waste Analysts often find advancement opportunities in water treatment facilities, chemical processing industries, and environmental remediation projects, driven by stringent wastewater regulations and sustainability initiatives. Both career paths offer specialization potential with rising demand for environmental engineers and policy experts focusing on sustainable waste management solutions.
Industry Challenges and Solutions
Solid Waste Analysts face challenges such as accurately categorizing heterogeneous materials and managing landfill capacity, while Liquid Waste Analysts must address contamination risks and complex treatment processes in industrial effluents. Both roles require advanced data analysis tools and sustainable technology implementation to optimize waste reduction and regulatory compliance. Industry solutions include adopting AI-driven monitoring systems and developing circular economy practices to mitigate environmental impact effectively.
Environmental and Community Impact
Solid Waste Analysts assess the environmental impact of landfill use, recycling processes, and solid waste disposal methods, crucial for reducing soil and groundwater contamination in communities. Liquid Waste Analysts evaluate the treatment and management of wastewater and industrial effluents to prevent water pollution and protect aquatic ecosystems affecting public health. Both roles contribute to sustainable waste management strategies that minimize environmental hazards and promote community well-being.
Solid Waste Analyst vs Liquid Waste Analyst Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com