A water meter reader manually records water consumption data from individual meters to ensure accurate billing and detect leaks or abnormalities. A water usage analyst interprets this data using advanced tools to identify consumption patterns, optimize water use, and support sustainable resource management. Both roles contribute to effective water management but differ in their approach, with readers focusing on data collection and analysts on data interpretation and strategy.
Table of Comparison
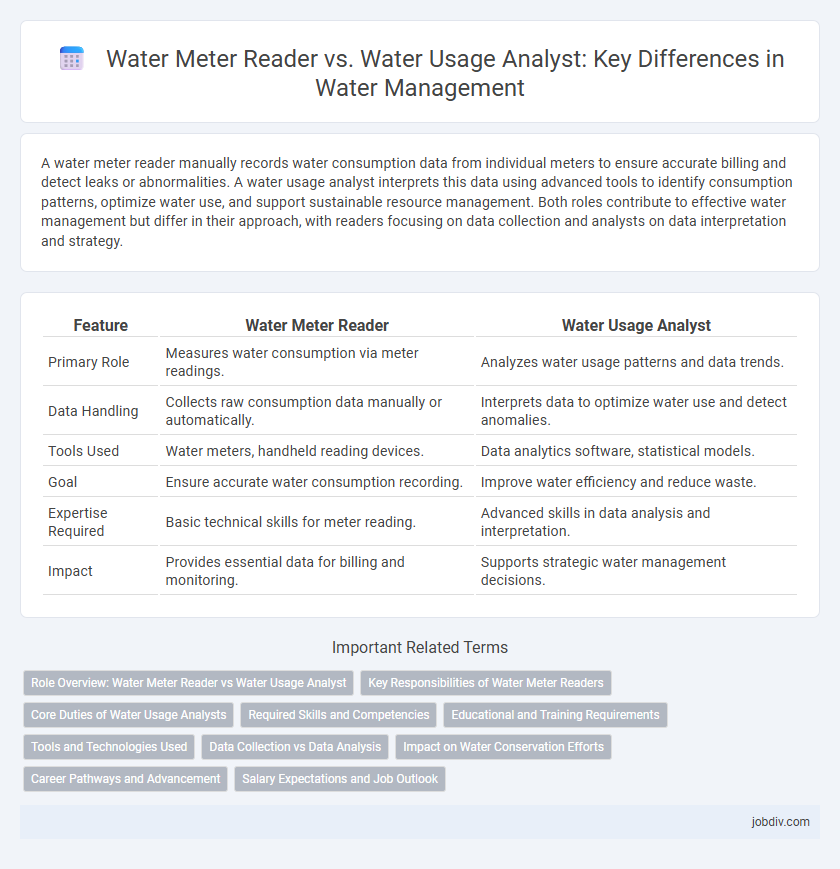
| Feature | Water Meter Reader | Water Usage Analyst |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Measures water consumption via meter readings. | Analyzes water usage patterns and data trends. |
| Data Handling | Collects raw consumption data manually or automatically. | Interprets data to optimize water use and detect anomalies. |
| Tools Used | Water meters, handheld reading devices. | Data analytics software, statistical models. |
| Goal | Ensure accurate water consumption recording. | Improve water efficiency and reduce waste. |
| Expertise Required | Basic technical skills for meter reading. | Advanced skills in data analysis and interpretation. |
| Impact | Provides essential data for billing and monitoring. | Supports strategic water management decisions. |
Role Overview: Water Meter Reader vs Water Usage Analyst
A Water Meter Reader is responsible for physically collecting data by reading water meters to record accurate consumption, ensuring billing accuracy and detecting irregularities. A Water Usage Analyst interprets water consumption data, identifying usage patterns, forecasting demand, and recommending efficiency improvements for resource management. Both roles contribute to water resource management but differ in hands-on data collection versus analytical evaluation.
Key Responsibilities of Water Meter Readers
Water meter readers are responsible for accurately recording water consumption data by inspecting and reading residential or commercial meters on a scheduled basis. Their duties include identifying irregular water usage patterns and reporting meter malfunctions or leaks to ensure billing accuracy and early problem detection. This role supports effective water management by providing critical data used by water usage analysts for detailed consumption analysis and resource planning.
Core Duties of Water Usage Analysts
Water Usage Analysts specialize in examining consumption data to identify patterns, inefficiencies, and potential savings opportunities within residential, commercial, or industrial settings. They employ advanced analytical tools and software to interpret meter readings, forecast demand, and develop strategies for sustainable water management. Unlike Water Meter Readers who primarily collect raw data, Water Usage Analysts transform this information into actionable insights that guide decision-making and policy development.
Required Skills and Competencies
Water Meter Readers require proficiency in accurate data collection, physical stamina to access meters, and basic technical skills for using handheld devices. Water Usage Analysts demand advanced analytical abilities, expertise in data interpretation, and proficiency with software tools to identify consumption patterns and optimize water resources. Both roles benefit from strong attention to detail and knowledge of water distribution systems.
Educational and Training Requirements
Water Meter Readers typically require a high school diploma or equivalent along with on-the-job training for operating meter reading devices and understanding basic water distribution systems. Water Usage Analysts often hold a bachelor's degree in environmental science, engineering, or a related field and need advanced training in data analysis, hydrology, and water resource management. Proficiency in software tools and regulatory compliance is essential for Water Usage Analysts, while Water Meter Readers focus more on practical skills in fieldwork and equipment handling.
Tools and Technologies Used
Water meter readers primarily utilize handheld devices and mobile applications equipped with RFID or barcode scanners for efficient data collection at residential or commercial properties. Water usage analysts employ advanced software tools such as SCADA systems, Geographic Information Systems (GIS), and data analytics platforms to monitor, model, and optimize consumption patterns across large water distribution networks. Both roles leverage Internet of Things (IoT) sensors and real-time data integration technologies to enhance accuracy and enable proactive water management strategies.
Data Collection vs Data Analysis
A water meter reader specializes in the systematic collection of consumption data by physically recording water usage from meters at regular intervals. In contrast, a water usage analyst leverages this raw data to identify patterns, detect anomalies, and provide actionable insights that enhance water management efficiency. While data collection ensures accurate measurement, data analysis transforms these measurements into strategic decisions for conservation and operational improvements.
Impact on Water Conservation Efforts
Water Meter Readers collect precise consumption data directly from residential and commercial properties, enabling accurate billing and early detection of leaks that reduce water waste significantly. Water Usage Analysts interpret this data through advanced software to identify consumption patterns, forecast demand, and recommend strategic conservation measures, amplifying the effectiveness of sustainability initiatives. Together, these roles drive smarter water management, resulting in measurable reductions in water usage and enhanced conservation efforts in urban and rural settings.
Career Pathways and Advancement
Water meter readers primarily focus on collecting accurate data from residential or commercial water meters, serving as essential entry-level roles in the water management industry. Water usage analysts leverage this data to assess consumption patterns, identify inefficiencies, and support sustainable water resource planning, often requiring advanced skills in data analysis and environmental science. Career advancement from meter reader to usage analyst involves gaining technical expertise, analytical capabilities, and sometimes formal education, creating a clear pathway into more strategic and impactful water management positions.
Salary Expectations and Job Outlook
Water meter readers typically earn an average annual salary ranging from $30,000 to $45,000, reflecting entry-level skills focused on accurately recording water consumption data. Water usage analysts command higher salaries, often between $60,000 and $90,000, due to their expertise in data interpretation, system optimization, and water resource management. The job outlook for water usage analysts is stronger, driven by growing demand for sustainable water management and advanced analytics in municipal and environmental sectors.
Water Meter Reader vs Water Usage Analyst Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com