Wholesalers purchase pet products in bulk and store inventory, enabling retailers to buy at discounted prices with faster shipping times. Drop shippers act as intermediaries who list products without holding stock, relying on suppliers to ship directly to customers, which minimizes upfront costs but may increase delivery times. Choosing between wholesaling and drop shipping hinges on inventory control preferences, capital investment capacity, and desired fulfillment speed.
Table of Comparison
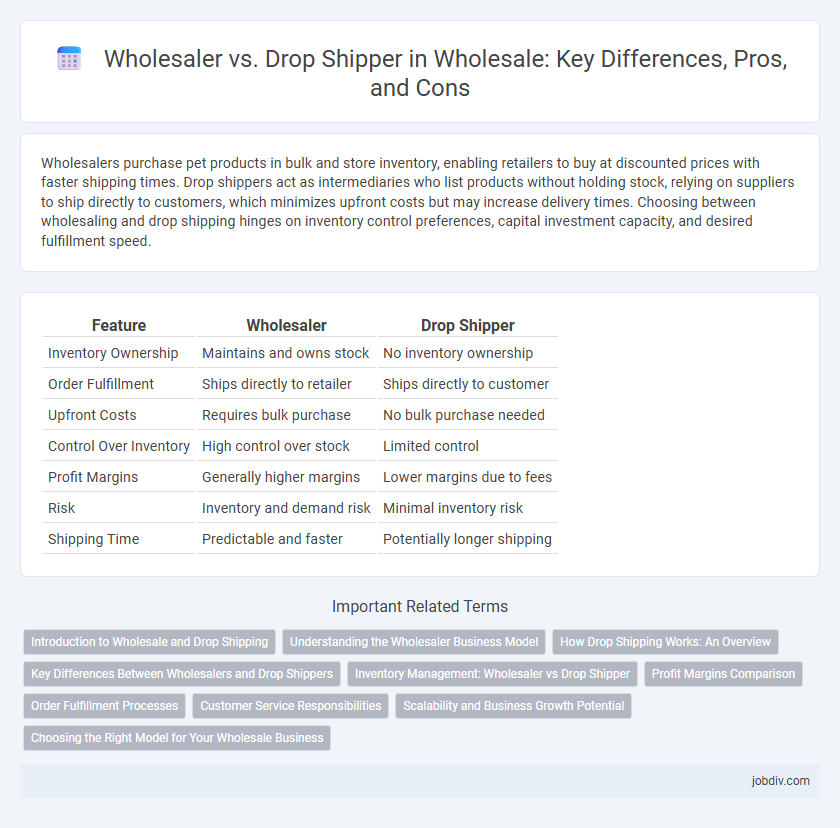
| Feature | Wholesaler | Drop Shipper |
|---|---|---|
| Inventory Ownership | Maintains and owns stock | No inventory ownership |
| Order Fulfillment | Ships directly to retailer | Ships directly to customer |
| Upfront Costs | Requires bulk purchase | No bulk purchase needed |
| Control Over Inventory | High control over stock | Limited control |
| Profit Margins | Generally higher margins | Lower margins due to fees |
| Risk | Inventory and demand risk | Minimal inventory risk |
| Shipping Time | Predictable and faster | Potentially longer shipping |
Introduction to Wholesale and Drop Shipping
Wholesale involves purchasing large quantities of products directly from manufacturers or distributors at discounted rates to resell them at a profit, ensuring inventory control and faster shipping. Drop shipping eliminates the need for inventory by allowing sellers to forward customer orders directly to suppliers, who then ship products on their behalf. Both models have unique advantages in wholesaling, balancing upfront investment, risk, and logistical responsibilities.
Understanding the Wholesaler Business Model
Wholesalers purchase large quantities of products directly from manufacturers and sell them in bulk to retailers or other businesses, enabling lower per-unit costs and streamlined inventory management. Unlike drop shippers who handle inventory and shipping logistics indirectly, wholesalers maintain physical stock and control distribution channels, offering faster fulfillment and the ability to negotiate volume-based pricing. This traditional wholesale business model supports supply chain efficiency and provides retailers with consistent product availability and reduced procurement costs.
How Drop Shipping Works: An Overview
Drop shipping operates by allowing retailers to sell products without holding inventory, as suppliers directly ship items to customers upon order placement. This process reduces upfront costs and minimizes storage requirements compared to traditional wholesalers who purchase and stock bulk inventory. Retailers act as intermediaries, managing product listings and customer service while suppliers handle fulfillment and shipping logistics.
Key Differences Between Wholesalers and Drop Shippers
Wholesalers hold inventory in bulk and sell products directly to retailers or businesses, enabling faster shipping and lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Drop shippers, in contrast, do not stock products but forward customer orders to suppliers who handle storage, packaging, and delivery, reducing upfront investment and inventory risk. The key differences include inventory ownership, order fulfillment responsibility, and the level of control over shipping times and product quality.
Inventory Management: Wholesaler vs Drop Shipper
Wholesalers maintain large inventories in warehouses, allowing for bulk order fulfillment and faster shipping times, which enhances supply chain reliability. Drop shippers rely on third-party suppliers to hold and manage inventory, eliminating the need for physical storage but often resulting in longer delivery periods and less control over stock availability. Efficient inventory management in wholesale requires balancing inventory holding costs with customer demand forecasting, whereas drop shipping prioritizes flexibility and reduced upfront investment.
Profit Margins Comparison
Wholesalers typically offer higher profit margins due to bulk purchasing discounts and inventory control, enabling retailers to set competitive prices while maintaining substantial markups. Drop shippers often experience lower profit margins because they avoid inventory costs but face higher per-unit expenses and less pricing flexibility. Understanding these margin differences is crucial for businesses choosing between inventory-heavy wholesale models and inventory-light drop shipping strategies.
Order Fulfillment Processes
Wholesalers typically purchase goods in bulk, store inventory, and manage the entire order fulfillment process from packaging to shipping, ensuring control over stock levels and delivery times. Drop shippers, on the other hand, do not hold inventory; instead, they transfer customer orders directly to manufacturers or wholesalers who then handle storage and shipment. This fundamental difference impacts shipping speed, inventory risk, and fulfillment costs in wholesale operations.
Customer Service Responsibilities
Wholesalers manage inventory, packing, and shipping, ensuring quality control and fast delivery to maintain customer satisfaction. Drop shippers handle order processing and customer inquiries but rely on third-party suppliers to fulfill shipments, limiting direct control over product quality and delivery times. Effective customer service in wholesaling demands proactive communication, timely issue resolution, and transparent order tracking to build trust and loyalty.
Scalability and Business Growth Potential
Wholesalers offer greater scalability by allowing businesses to purchase inventory in bulk, ensuring consistent stock levels and better control over product quality, which supports long-term business growth. Drop shippers have lower upfront costs but face limited scalability due to dependency on third-party suppliers, leading to potential stock shortages and reduced profit margins. Investing in wholesale models provides stronger business growth potential through enhanced inventory management and expanded market reach.
Choosing the Right Model for Your Wholesale Business
Selecting the right wholesale model involves understanding the core differences between wholesalers and drop shippers; wholesalers typically require inventory investment and offer lower per-unit costs, while drop shippers eliminate inventory risks by fulfilling orders directly from suppliers. Consider factors such as upfront capital, control over inventory, order fulfillment speed, and customer service when deciding. Analyzing market demand, logistic capabilities, and profit margin expectations ensures a strategic match to your business goals.
Wholesaler vs Drop Shipper Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com