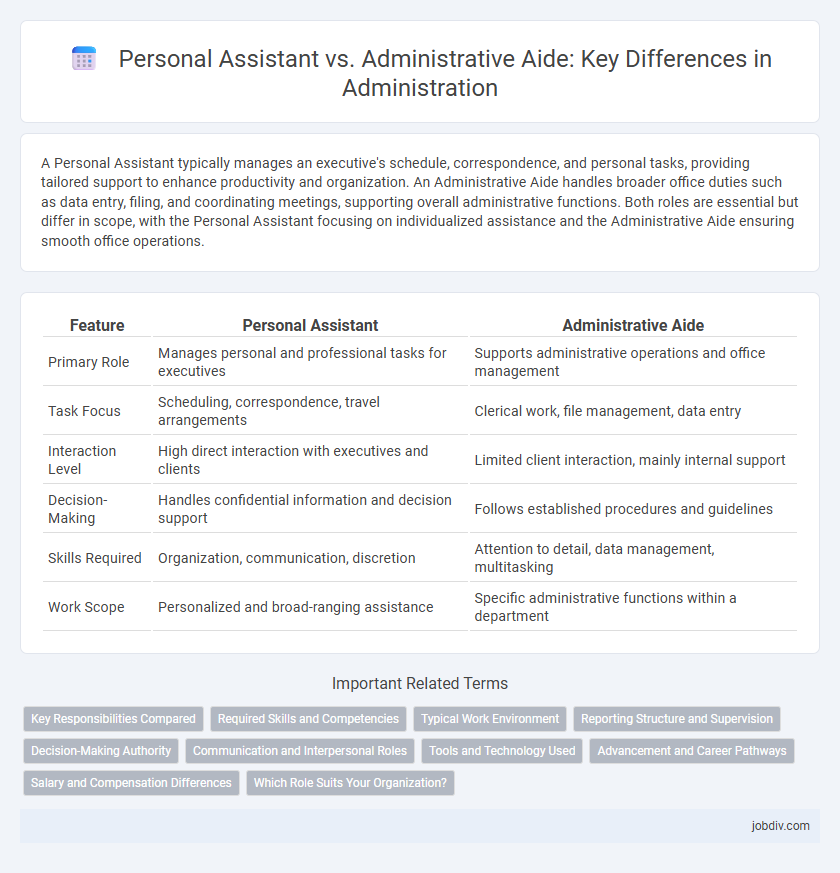
A Personal Assistant typically manages an executive's schedule, correspondence, and personal tasks, providing tailored support to enhance productivity and organization. An Administrative Aide handles broader office duties such as data entry, filing, and coordinating meetings, supporting overall administrative functions. Both roles are essential but differ in scope, with the Personal Assistant focusing on individualized assistance and the Administrative Aide ensuring smooth office operations.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Personal Assistant | Administrative Aide |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Manages personal and professional tasks for executives | Supports administrative operations and office management |
| Task Focus | Scheduling, correspondence, travel arrangements | Clerical work, file management, data entry |
| Interaction Level | High direct interaction with executives and clients | Limited client interaction, mainly internal support |
| Decision-Making | Handles confidential information and decision support | Follows established procedures and guidelines |
| Skills Required | Organization, communication, discretion | Attention to detail, data management, multitasking |
| Work Scope | Personalized and broad-ranging assistance | Specific administrative functions within a department |
Key Responsibilities Compared
Personal Assistants primarily manage executive schedules, coordinate meetings, and handle confidential communications to support high-level decision-making. Administrative Aides focus on clerical duties such as filing, data entry, and managing office supplies to ensure efficient office operations. Both roles require organizational skills but differ in scope, with Personal Assistants engaging in more strategic support and Administrative Aides concentrating on operational tasks.
Required Skills and Competencies
Personal Assistants require strong organizational skills, proficiency in calendar management, and excellent communication abilities to efficiently handle executives' schedules and correspondence. Administrative Aides must possess solid administrative skills, including data entry, file management, and familiarity with office software to support day-to-day office operations. Both roles demand attention to detail, time management, and adaptability to prioritize tasks in fast-paced environments.
Typical Work Environment
Personal Assistants often work in dynamic office settings, supporting executives directly with scheduling, correspondence, and personal tasks. Administrative Aides typically operate within structured environments such as government agencies or corporate departments, handling clerical duties, record keeping, and office management. Both roles require proficiency in office software, communication skills, and adaptability to fast-paced or routine workflows.
Reporting Structure and Supervision
Personal Assistants typically report directly to senior executives or high-level managers, providing dedicated support and handling confidential tasks, while Administrative Aides often report to department supervisors or office managers, assisting with a broader range of clerical and organizational duties. The supervision of Personal Assistants is usually more individualized and closely aligned with the specific needs of their employer, whereas Administrative Aides receive oversight within a team or departmental framework. Understanding the distinct reporting structures and supervision levels helps clarify role expectations and enhances workflow efficiency in administrative settings.
Decision-Making Authority
A Personal Assistant typically holds more decision-making authority, managing schedules, prioritizing tasks, and sometimes representing the executive in meetings. An Administrative Aide generally performs routine clerical duties with limited authority, supporting administrative functions without making high-level decisions. The distinct difference lies in the autonomy each role has in influencing workflow and organizational priorities.
Communication and Interpersonal Roles
Personal Assistants excel in managing high-level communication, coordinating schedules, and acting as primary liaisons for executives, ensuring seamless information flow and relationship management. Administrative Aides focus on supportive communication tasks such as handling correspondence, organizing meetings, and facilitating internal team interactions. Both roles require strong interpersonal skills, but Personal Assistants emphasize strategic communication while Administrative Aides prioritize operational support.
Tools and Technology Used
Personal Assistants utilize advanced scheduling software, communication platforms, and project management tools like Microsoft Outlook, Slack, and Trello to streamline workflow and enhance productivity. Administrative Aides often rely on document management systems, basic office software such as Microsoft Office Suite, and traditional filing tools to support administrative tasks efficiently. Both roles leverage technology to optimize organizational operations, though Personal Assistants typically engage with more dynamic and integrated digital solutions.
Advancement and Career Pathways
Personal Assistants often advance by specializing in executive support or project management roles, leveraging skills in calendar management, communication, and confidentiality to move into senior administrative or office management positions. Administrative Aides typically follow a career path that includes gaining expertise in office systems, data management, and clerical functions, with potential growth into administrative coordinator or operations support roles. Both roles benefit from continuing education and certifications such as Certified Administrative Professional (CAP) to enhance career progression opportunities.
Salary and Compensation Differences
Personal Assistants typically earn higher salaries than Administrative Aides due to their specialized skills in managing executive schedules, handling confidential information, and providing personalized support. The median annual salary for Personal Assistants ranges from $45,000 to $65,000, while Administrative Aides average between $30,000 and $45,000, reflecting differences in responsibilities and expertise. Compensation packages for Personal Assistants often include bonuses and benefits that are less common for Administrative Aides, aligning with their critical role in executive support.
Which Role Suits Your Organization?
Choosing between a Personal Assistant and an Administrative Aide depends on your organization's specific needs and workflow complexity. Personal Assistants provide tailored support to executives, handling scheduling, communication, and confidential tasks, ideal for leadership requiring focused, high-level assistance. Administrative Aides manage broader office functions, including clerical duties, data management, and general support, fitting organizations seeking versatile help across multiple departments.
Personal Assistant vs Administrative Aide Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com