Dairy farmers focus on raising cows for milk production, managing herd health, and optimizing lactation cycles to maximize yield. Poultry farmers specialize in breeding and raising chickens or other fowl primarily for meat and egg production, emphasizing biosecurity and feed efficiency. Both require careful attention to animal welfare, but the equipment, facilities, and daily management practices differ significantly between the two farming types.
Table of Comparison
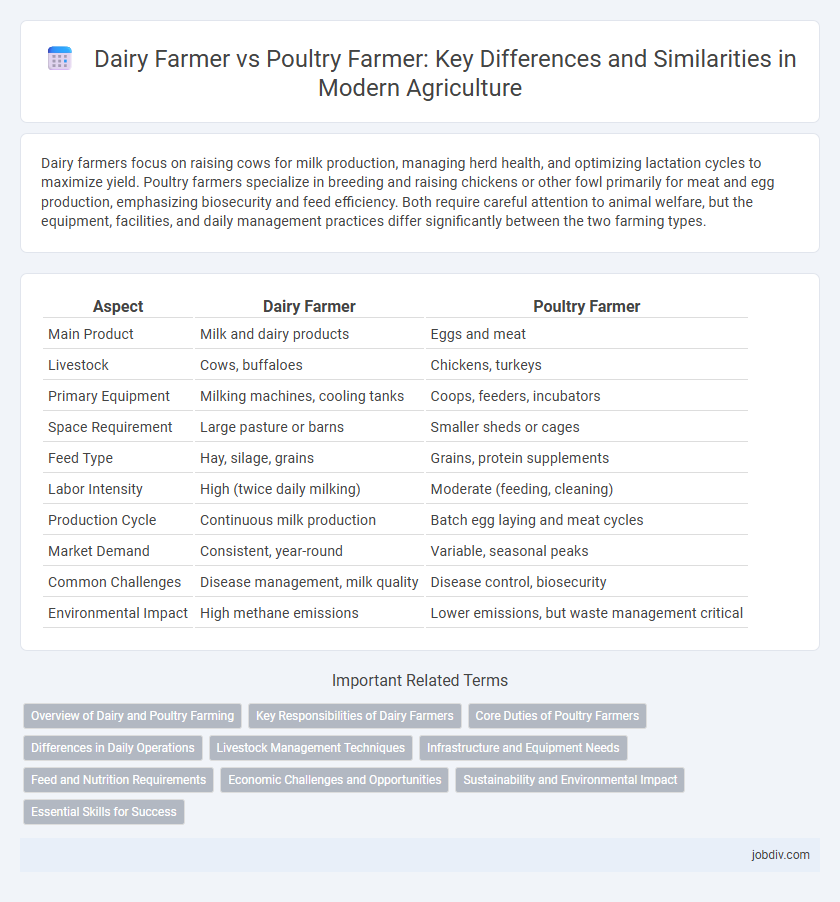
| Aspect | Dairy Farmer | Poultry Farmer |
|---|---|---|
| Main Product | Milk and dairy products | Eggs and meat |
| Livestock | Cows, buffaloes | Chickens, turkeys |
| Primary Equipment | Milking machines, cooling tanks | Coops, feeders, incubators |
| Space Requirement | Large pasture or barns | Smaller sheds or cages |
| Feed Type | Hay, silage, grains | Grains, protein supplements |
| Labor Intensity | High (twice daily milking) | Moderate (feeding, cleaning) |
| Production Cycle | Continuous milk production | Batch egg laying and meat cycles |
| Market Demand | Consistent, year-round | Variable, seasonal peaks |
| Common Challenges | Disease management, milk quality | Disease control, biosecurity |
| Environmental Impact | High methane emissions | Lower emissions, but waste management critical |
Overview of Dairy and Poultry Farming
Dairy farming involves the breeding and management of cows specifically for milk production, focusing on maintaining herd health and maximizing milk yield through proper nutrition and milking techniques. Poultry farming centers on raising domesticated birds like chickens and turkeys primarily for meat and egg production, emphasizing feed efficiency, disease control, and housing conditions. Both sectors require specialized knowledge of animal husbandry, biosecurity measures, and sustainable practices to ensure profitability and product quality in agriculture.
Key Responsibilities of Dairy Farmers
Dairy farmers are responsible for managing the health and nutrition of dairy cows, ensuring optimal milk production through proper feeding, milking, and disease prevention. They monitor the cleanliness and maintenance of milking equipment and facilities to comply with hygiene standards. Additionally, dairy farmers record production data and manage breeding programs to improve herd quality and productivity.
Core Duties of Poultry Farmers
Poultry farmers manage the breeding, raising, and health care of chickens, turkeys, and other domesticated birds primarily for meat and egg production. Key responsibilities include maintaining optimal living conditions, monitoring feed quality, and preventing disease outbreaks through vaccinations and biosecurity measures. Unlike dairy farmers who focus on milking cattle and managing dairy production, poultry farmers emphasize flock management and efficient egg or meat yield.
Differences in Daily Operations
Dairy farmers manage daily tasks including milking cows, monitoring animal health, and maintaining milking equipment, emphasizing consistent schedules for milk production. Poultry farmers focus on feeding, egg collection, and regulating environment controls such as temperature and ventilation for chickens or turkeys. Both farmers prioritize biosecurity and disease prevention, but their routine operations differ significantly due to the distinct biological needs of livestock versus poultry.
Livestock Management Techniques
Dairy farmers employ specialized milking routines, nutrient-rich feed formulations, and climate-controlled barns to maximize milk production and maintain herd health. Poultry farmers focus on brooding management, controlled lighting schedules, and biosecurity measures to enhance egg yield and prevent disease outbreaks. Both livestock management techniques prioritize animal welfare, efficient feeding systems, and disease control tailored to species-specific needs.
Infrastructure and Equipment Needs
Dairy farmers require specialized infrastructure such as milking parlors, cooling tanks, and storage facilities to maintain milk quality and hygiene, while poultry farmers need controlled-environment poultry houses with ventilation systems, feeders, and automated egg collection equipment. The equipment for dairy farming includes milking machines, bulk milk cooling tanks, and manure management systems, whereas poultry farming relies on brooders, incubators, and feed dispensers designed for high-density bird populations. Investment in infrastructure varies significantly, as dairy farming demands robust water supply and waste treatment systems, contrasting with the biosecurity measures essential for preventing disease spread in poultry operations.
Feed and Nutrition Requirements
Dairy farmers prioritize high-quality forage, balanced rations rich in energy, protein, vitamins, and minerals to maximize milk yield and maintain cow health. Poultry farmers focus on nutrient-dense feeds formulated with optimal levels of protein, calcium, and essential amino acids to support rapid growth, egg production, and overall bird vitality. Understanding specific feed formulations and nutritional needs is crucial for efficiency and productivity in both dairy and poultry farming systems.
Economic Challenges and Opportunities
Dairy farmers face economic challenges such as fluctuating milk prices, high feed costs, and significant investment in milking equipment, while opportunities include value-added products like cheese and yogurt. Poultry farmers contend with volatile feed prices and disease management expenses but benefit from faster production cycles and growing demand for poultry meat and eggs. Both sectors must navigate regulatory pressures and market competition to optimize profitability and sustainability.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Dairy farmers often face challenges related to methane emissions, water usage, and land management, which significantly impact sustainability efforts in agriculture. Poultry farming typically exhibits a lower carbon footprint per unit of protein produced due to more efficient feed conversion and less methane output. Sustainable practices in both sectors include optimizing resource use, implementing waste management systems, and adopting renewable energy sources to reduce environmental impact.
Essential Skills for Success
Dairy farmers require expertise in animal husbandry, milking technology, and nutritional management to maintain herd health and milk quality. Poultry farmers must excel in biosecurity measures, flock management, and disease control to optimize egg and meat production. Both professions demand strong problem-solving abilities and knowledge of farm machinery to ensure operational efficiency.
Dairy Farmer vs Poultry Farmer Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com