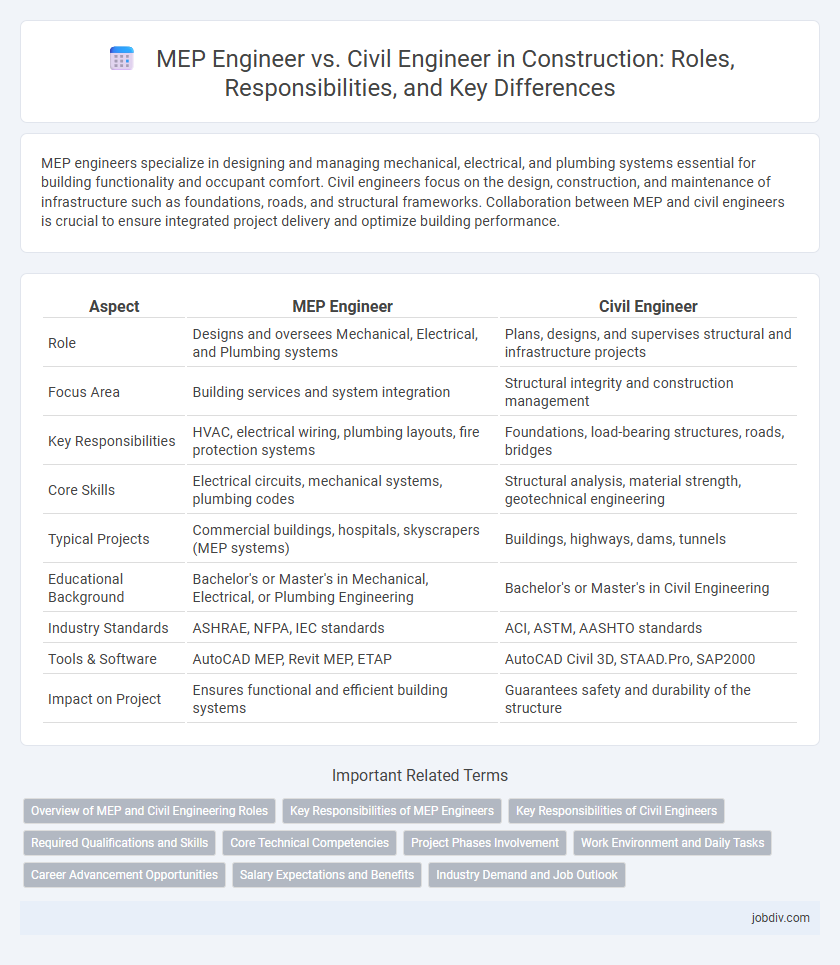
MEP engineers specialize in designing and managing mechanical, electrical, and plumbing systems essential for building functionality and occupant comfort. Civil engineers focus on the design, construction, and maintenance of infrastructure such as foundations, roads, and structural frameworks. Collaboration between MEP and civil engineers is crucial to ensure integrated project delivery and optimize building performance.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | MEP Engineer | Civil Engineer |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Designs and oversees Mechanical, Electrical, and Plumbing systems | Plans, designs, and supervises structural and infrastructure projects |
| Focus Area | Building services and system integration | Structural integrity and construction management |
| Key Responsibilities | HVAC, electrical wiring, plumbing layouts, fire protection systems | Foundations, load-bearing structures, roads, bridges |
| Core Skills | Electrical circuits, mechanical systems, plumbing codes | Structural analysis, material strength, geotechnical engineering |
| Typical Projects | Commercial buildings, hospitals, skyscrapers (MEP systems) | Buildings, highways, dams, tunnels |
| Educational Background | Bachelor's or Master's in Mechanical, Electrical, or Plumbing Engineering | Bachelor's or Master's in Civil Engineering |
| Industry Standards | ASHRAE, NFPA, IEC standards | ACI, ASTM, AASHTO standards |
| Tools & Software | AutoCAD MEP, Revit MEP, ETAP | AutoCAD Civil 3D, STAAD.Pro, SAP2000 |
| Impact on Project | Ensures functional and efficient building systems | Guarantees safety and durability of the structure |
Overview of MEP and Civil Engineering Roles
MEP engineers specialize in mechanical, electrical, and plumbing systems essential for building functionality, focusing on HVAC, electrical wiring, and water supply networks. Civil engineers design and oversee infrastructure projects such as foundations, roads, and structural frameworks, ensuring safety and compliance with building codes. Both roles collaborate closely to integrate structural integrity with essential building services for successful construction projects.
Key Responsibilities of MEP Engineers
MEP engineers specialize in designing, installing, and maintaining mechanical, electrical, and plumbing systems within a building, ensuring optimal functionality and safety. They conduct HVAC system layout, electrical power distribution, fire protection systems, and plumbing designs that meet code compliance and energy efficiency standards. Collaboration with civil engineers is essential for integrating building infrastructure while maintaining project timelines and budget constraints.
Key Responsibilities of Civil Engineers
Civil Engineers are primarily responsible for designing, constructing, and maintaining infrastructure such as roads, bridges, and buildings, ensuring structural integrity and compliance with safety standards. They conduct site analysis, manage project schedules, and coordinate with other engineering disciplines to oversee the physical framework of construction projects. Key responsibilities also include soil testing, foundation design, and supervising construction activities to guarantee project quality and durability.
Required Qualifications and Skills
MEP Engineers require expertise in mechanical, electrical, and plumbing systems, with proficiency in AutoCAD, Revit, and HVAC design software, alongside strong analytical and problem-solving skills. Civil Engineers must possess knowledge in structural analysis, geotechnical engineering, and construction materials, complemented by skills in software such as STAAD Pro, AutoCAD Civil 3D, and project management. Both roles demand a bachelor's degree in engineering, strong communication abilities, and a commitment to safety standards and regulatory compliance.
Core Technical Competencies
MEP engineers specialize in mechanical, electrical, and plumbing systems, requiring expertise in HVAC design, electrical circuit analysis, and plumbing layout coordination, ensuring building systems operate efficiently. Civil engineers focus on structural integrity, site grading, foundation design, and infrastructure development, utilizing skills in structural analysis, material strength assessment, and soil mechanics. Both roles demand proficiency in AutoCAD and Building Information Modeling (BIM), but MEP engineers emphasize system integration, while civil engineers prioritize load-bearing structures and earthworks.
Project Phases Involvement
MEP engineers primarily engage during the design development and construction phases, focusing on mechanical, electrical, and plumbing systems to ensure building functionality and compliance with standards. Civil engineers are involved from the initial site investigation and planning phases through construction and project closeout, overseeing structural integrity, earthworks, and infrastructure development. Both roles collaborate during project coordination and commissioning to align MEP systems with structural frameworks for successful project delivery.
Work Environment and Daily Tasks
MEP Engineers primarily operate inside buildings or on-site managing mechanical, electrical, and plumbing systems, ensuring HVAC, wiring, and piping align with design specifications and safety standards. Civil Engineers work outdoors on construction sites, focusing on infrastructure development like roads, bridges, and foundations, conducting surveys, soil testing, and overseeing structural integrity. Both roles involve collaboration with architects and contractors, but MEP Engineers concentrate on system installations while Civil Engineers handle groundwork and structural frameworks.
Career Advancement Opportunities
MEP Engineers often advance by specializing in systems design and project management, leading to roles such as senior engineer or consultant in mechanical, electrical, and plumbing systems. Civil Engineers typically progress through roles in structural design, site supervision, and infrastructure planning, advancing to project manager or civil engineering director positions. Career growth for both requires strong technical expertise, certifications like PMP or PE, and experience in large-scale construction projects.
Salary Expectations and Benefits
MEP engineers typically command salaries ranging from $65,000 to $110,000 annually, reflecting specialized skills in mechanical, electrical, and plumbing systems within construction projects. Civil engineers often earn between $70,000 and $120,000, with higher pay linked to expertise in structural design, infrastructure development, and project management. Benefits for both roles commonly include health insurance, retirement plans, and performance bonuses, with MEP engineers sometimes receiving additional allowances for industry certifications and technical training.
Industry Demand and Job Outlook
MEP engineers are increasingly in demand due to the rising complexity of building systems, with a job growth projected at 4% over the next decade, driven by the emphasis on energy-efficient and sustainable designs. Civil engineers maintain strong demand, projected at 8% growth, fueled by infrastructure development and urban expansion projects worldwide. Employers prioritize civil engineers for large-scale construction and public works, while MEP engineers are critical for specialized mechanical, electrical, and plumbing systems integration in modern buildings.
MEP Engineer vs Civil Engineer Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com