Exhibit designers specialize in creating engaging, interactive displays that communicate specific messages or stories within museums, galleries, or trade shows. Environmental designers focus on shaping outdoor and indoor physical spaces, integrating architecture, landscape, and urban planning to enhance user experience and sustainability. Both roles require a strong understanding of spatial design, but exhibit designers emphasize narrative and visitor interaction, while environmental designers prioritize functionality and environmental impact.
Table of Comparison
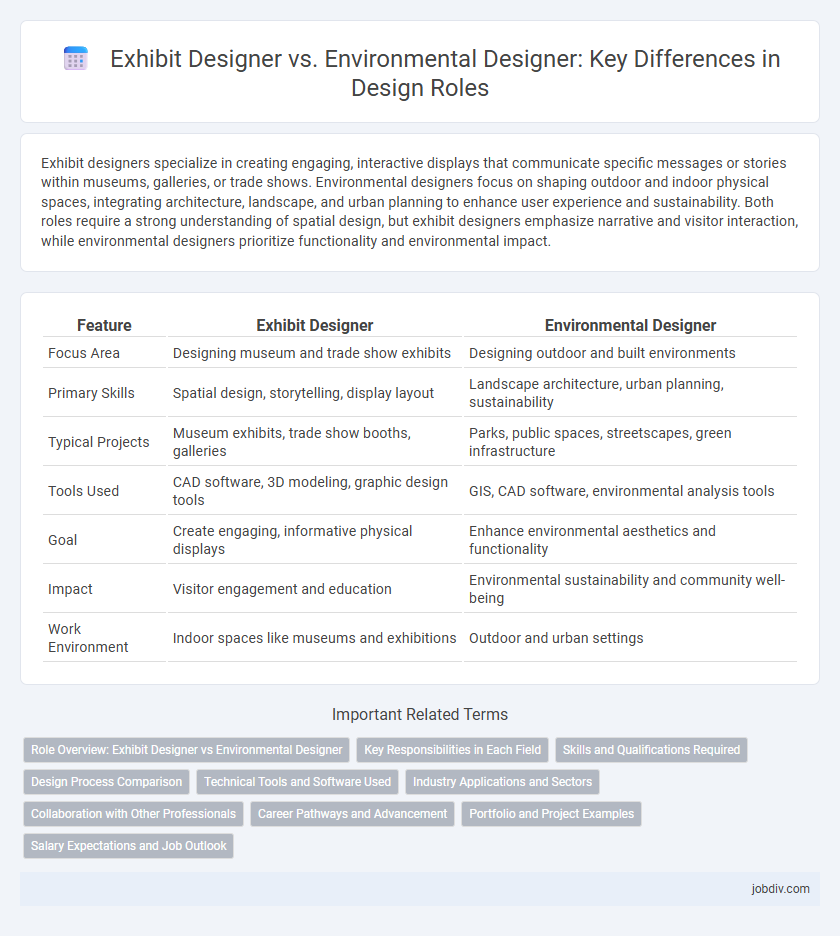
| Feature | Exhibit Designer | Environmental Designer |
|---|---|---|
| Focus Area | Designing museum and trade show exhibits | Designing outdoor and built environments |
| Primary Skills | Spatial design, storytelling, display layout | Landscape architecture, urban planning, sustainability |
| Typical Projects | Museum exhibits, trade show booths, galleries | Parks, public spaces, streetscapes, green infrastructure |
| Tools Used | CAD software, 3D modeling, graphic design tools | GIS, CAD software, environmental analysis tools |
| Goal | Create engaging, informative physical displays | Enhance environmental aesthetics and functionality |
| Impact | Visitor engagement and education | Environmental sustainability and community well-being |
| Work Environment | Indoor spaces like museums and exhibitions | Outdoor and urban settings |
Role Overview: Exhibit Designer vs Environmental Designer
Exhibit designers specialize in creating engaging, visually compelling displays for museums, galleries, and trade shows, emphasizing storytelling through spatial arrangements and interactive elements. Environmental designers focus on the broader physical environment, integrating architecture, landscape, and interior elements to enhance user experience and sustainability in public and private spaces. Both roles require strong design skills, but exhibit designers hone in on temporary, curated presentations, while environmental designers address long-term spatial interactions and functionality.
Key Responsibilities in Each Field
Exhibit designers specialize in creating engaging, visually compelling displays for museums, galleries, and trade shows, focusing on spatial layout, storytelling, and visitor interaction to enhance the exhibit experience. Environmental designers concentrate on integrating architectural elements with natural surroundings, emphasizing sustainability, user experience, and ecological impact in public spaces, landscapes, and urban environments. Both roles require proficiency in design software, collaboration with multidisciplinary teams, and a strong understanding of materials and construction methods to realize their concepts effectively.
Skills and Qualifications Required
Exhibit designers require strong skills in spatial planning, visual storytelling, and proficiency with 3D modeling software like SketchUp and AutoCAD to create engaging displays that enhance visitor experience. Environmental designers focus on integrating sustainable practices, knowledge of landscape architecture, and expertise in environmental impact assessments to develop functional, eco-friendly spaces. Both roles demand creativity, project management abilities, and collaboration skills, but exhibit design emphasizes aesthetics and interaction while environmental design prioritizes ecological balance and community well-being.
Design Process Comparison
Exhibit designers focus on creating immersive, interactive displays that engage visitors within specific spaces, emphasizing storytelling and user experience through detailed layout planning and multimedia integration. Environmental designers approach projects with a broader perspective, prioritizing sustainable, functional, and aesthetic solutions that enhance public spaces and built environments by integrating ecological, social, and cultural factors. Both disciplines utilize iterative design processes but differ in scale, stakeholder involvement, and the balance between technical feasibility and experiential impact.
Technical Tools and Software Used
Exhibit designers primarily utilize 3D modeling software like SketchUp, AutoCAD, and Rhino to create detailed spatial layouts and interactive displays, emphasizing visitor engagement and storytelling. Environmental designers employ GIS software, Revit, and sustainable design tools such as Ecotect and Sefaira to analyze site-specific data, optimize natural light, and ensure eco-friendly integration. Both roles rely on Adobe Creative Suite for visual presentations but diverge in their technical focus--exhibit designers prioritize immersive experiences, while environmental designers emphasize environmental impact and spatial functionality.
Industry Applications and Sectors
Exhibit designers specialize in creating engaging, interactive displays primarily for museums, trade shows, and retail spaces, enhancing visitor experience through storytelling and spatial arrangement. Environmental designers focus on large-scale projects such as urban planning, landscape architecture, and public spaces, integrating ecological sustainability and human interaction within the built environment. Both roles serve distinct industry sectors, with exhibit designers targeting cultural institutions and commercial events, while environmental designers collaborate with government agencies, real estate developers, and environmental organizations.
Collaboration with Other Professionals
Exhibit designers collaborate closely with curators, fabricators, and lighting specialists to create immersive, engaging displays that effectively communicate narratives and brand identity. Environmental designers work alongside urban planners, architects, and sustainability experts to develop spaces that enhance user experience while addressing ecological and social impacts. Both roles require seamless teamwork across disciplines to integrate aesthetics, functionality, and innovation in public and private environments.
Career Pathways and Advancement
Exhibit designers specialize in creating immersive displays for museums, trade shows, and galleries, focusing on storytelling through spatial arrangement and interactive elements. Environmental designers integrate architecture, landscape, and interior design to craft sustainable, user-centered public and private spaces with ecological considerations. Career advancement for exhibit designers often leads to roles in creative direction or museum curation, while environmental designers progress toward urban planning, sustainability consulting, or architectural design leadership.
Portfolio and Project Examples
Exhibit designers showcase portfolios highlighting interactive displays, museum installations, and trade show booths emphasizing user engagement and narrative flow. Environmental designers present project examples involving urban planning, sustainable landscapes, and built environments focused on ecological impact and spatial harmony. Both portfolios require detailed visual documentation of design processes, materials, and client outcomes to demonstrate specialized expertise.
Salary Expectations and Job Outlook
Exhibit designers typically earn a median salary of around $55,000 to $75,000 annually, with job growth projected at 3% due to steady demand in museums and trade shows. Environmental designers, with a broader scope including urban planning and sustainable spaces, command higher salaries often ranging from $65,000 to $90,000 and experience faster job growth of approximately 6%, driven by increasing emphasis on eco-friendly and human-centered design solutions. Both careers offer diverse opportunities, but environmental design generally provides enhanced salary potential and stronger employment prospects.
Exhibit Designer vs Environmental Designer Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com