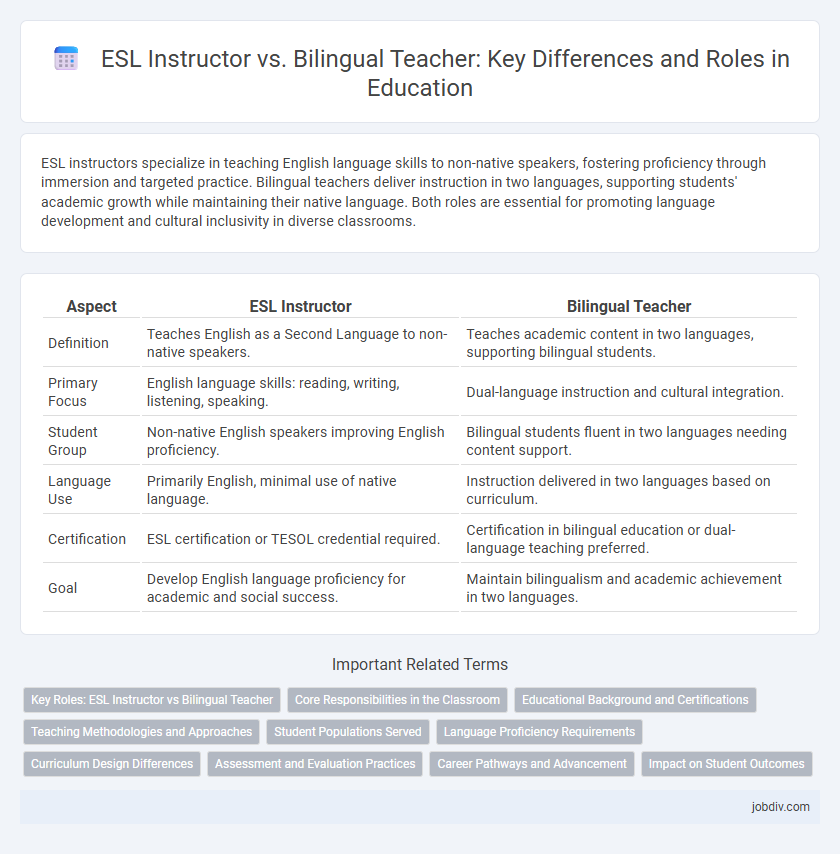
ESL instructors specialize in teaching English language skills to non-native speakers, fostering proficiency through immersion and targeted practice. Bilingual teachers deliver instruction in two languages, supporting students' academic growth while maintaining their native language. Both roles are essential for promoting language development and cultural inclusivity in diverse classrooms.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | ESL Instructor | Bilingual Teacher |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Teaches English as a Second Language to non-native speakers. | Teaches academic content in two languages, supporting bilingual students. |
| Primary Focus | English language skills: reading, writing, listening, speaking. | Dual-language instruction and cultural integration. |
| Student Group | Non-native English speakers improving English proficiency. | Bilingual students fluent in two languages needing content support. |
| Language Use | Primarily English, minimal use of native language. | Instruction delivered in two languages based on curriculum. |
| Certification | ESL certification or TESOL credential required. | Certification in bilingual education or dual-language teaching preferred. |
| Goal | Develop English language proficiency for academic and social success. | Maintain bilingualism and academic achievement in two languages. |
Key Roles: ESL Instructor vs Bilingual Teacher
ESL instructors specialize in teaching English language skills to non-native speakers, focusing on grammar, vocabulary, pronunciation, and listening comprehension to facilitate language acquisition. Bilingual teachers deliver instruction in two languages, supporting students' content learning while fostering proficiency in both their native language and English. Both roles aim to enhance language development but differ in instructional methods and linguistic integration within the classroom.
Core Responsibilities in the Classroom
ESL instructors concentrate on developing English language proficiency through specialized instruction in grammar, vocabulary, and conversational skills tailored for non-native speakers. Bilingual teachers deliver content in two languages, supporting students' academic achievement while maintaining and enhancing their native language skills. Both roles require adapting teaching strategies to diverse linguistic backgrounds to foster comprehension and participation.
Educational Background and Certifications
ESL instructors typically hold a bachelor's degree in education, linguistics, or TESOL, accompanied by certifications such as the TESOL Certificate or CELTA to specialize in teaching English to non-native speakers. Bilingual teachers often possess a degree in bilingual education or a related field, along with state-specific bilingual or dual language teaching credentials that authorize instruction in two languages. Both roles require knowledge of second language acquisition, but bilingual teachers are certified to deliver curriculum content in multiple languages, emphasizing proficiency in the target language and cultural competence.
Teaching Methodologies and Approaches
ESL instructors primarily utilize immersion and scaffolding techniques tailored to non-native English speakers, emphasizing language acquisition through contextualized communication and cultural integration. Bilingual teachers incorporate translanguaging and dual-language instruction models, enabling students to develop proficiency in both their native language and English simultaneously. Both methodologies prioritize differentiated instruction but vary in language use intensity and cognitive demand to support diverse learner needs.
Student Populations Served
ESL instructors primarily serve students learning English as a second language, focusing on language acquisition and proficiency for non-native speakers. Bilingual teachers support students who are fluent in two languages, providing academic instruction in both languages to promote bilingualism and biliteracy. Both educators address diverse linguistic needs but differ in their instructional approaches tailored to English learners versus bilingual students.
Language Proficiency Requirements
ESL instructors typically require proficiency in English and specialized training in teaching English as a second language, emphasizing skills in language acquisition and cultural adaptation. Bilingual teachers must demonstrate fluency in both English and a second language, often meeting state certification standards that verify their ability to instruct content in two languages. Language proficiency assessments for bilingual educators include evaluating reading, writing, speaking, and listening skills in both languages to ensure effective communication and academic support for diverse student populations.
Curriculum Design Differences
ESL instructors tailor curriculum to enhance English language acquisition through focused grammar, pronunciation, and vocabulary lessons, often emphasizing communicative competence for non-native speakers. Bilingual teachers design curricula that integrate content instruction in two languages, supporting cognitive development and academic achievement while fostering bilingual proficiency and cultural identity. The primary difference lies in ESL focusing on language development in isolation, whereas bilingual education balances language instruction with subject matter learning across languages.
Assessment and Evaluation Practices
ESL instructors specialize in assessing language proficiency through tailored tools like the WIDA ACCESS and CELDT, emphasizing speaking, listening, reading, and writing skills for non-native English speakers. Bilingual teachers utilize dual-language assessments to evaluate both students' native language and English abilities, ensuring balanced academic development across subjects. Effective evaluation practices in both roles involve ongoing formative assessments and culturally responsive feedback to support diverse learner needs.
Career Pathways and Advancement
ESL instructors typically focus on developing specialized language acquisition skills to support non-native English speakers, positioning them for roles in language centers, international schools, or higher education institutions. Bilingual teachers possess dual-language proficiency and cultural competency, allowing for broader career opportunities in dual-language immersion programs, special education, or administrative leadership in diverse school districts. Advancement for both careers often involves earning advanced certifications, such as TESOL or bilingual education credentials, and pursuing roles in curriculum development, educational consulting, or school administration.
Impact on Student Outcomes
ESL instructors specialize in teaching English language learners, improving language proficiency and academic performance through targeted language acquisition strategies. Bilingual teachers support students by delivering curriculum in both the native language and English, fostering cognitive development and cultural continuity while enhancing comprehension and engagement. Research indicates that bilingual instruction often leads to higher academic achievement and stronger identity formation compared to ESL-only programs.
ESL Instructor vs Bilingual Teacher Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com