Riparian Specialists focus on managing and restoring areas adjacent to streams and rivers, promoting water quality, bank stability, and habitat diversity. Wetlands Foresters specialize in maintaining forested wetland ecosystems, balancing water levels, vegetation health, and wildlife support. Both roles require expertise in hydrology and ecology but differ in their primary landscape focus and management goals.
Table of Comparison
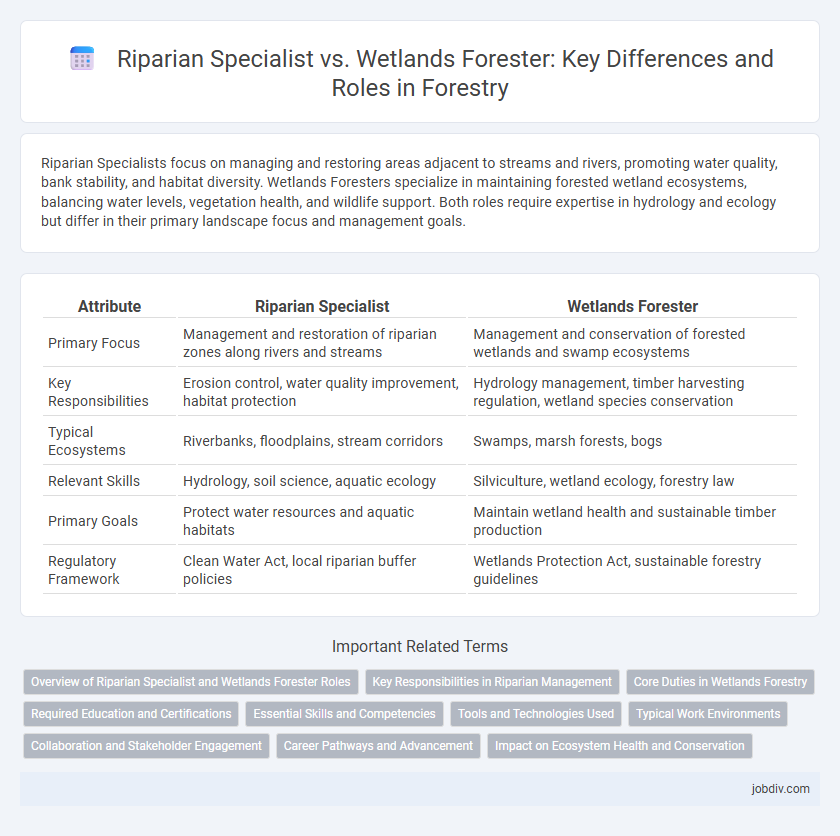
| Attribute | Riparian Specialist | Wetlands Forester |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Management and restoration of riparian zones along rivers and streams | Management and conservation of forested wetlands and swamp ecosystems |
| Key Responsibilities | Erosion control, water quality improvement, habitat protection | Hydrology management, timber harvesting regulation, wetland species conservation |
| Typical Ecosystems | Riverbanks, floodplains, stream corridors | Swamps, marsh forests, bogs |
| Relevant Skills | Hydrology, soil science, aquatic ecology | Silviculture, wetland ecology, forestry law |
| Primary Goals | Protect water resources and aquatic habitats | Maintain wetland health and sustainable timber production |
| Regulatory Framework | Clean Water Act, local riparian buffer policies | Wetlands Protection Act, sustainable forestry guidelines |
Overview of Riparian Specialist and Wetlands Forester Roles
Riparian Specialists focus on managing and restoring ecosystems adjacent to rivers and streams, ensuring water quality and habitat stability. Wetlands Foresters specialize in the sustainable management of forested wetland areas, balancing ecological health with timber production. Both roles require expertise in hydrology, soil science, and vegetation management to support biodiversity and watershed protection.
Key Responsibilities in Riparian Management
Riparian Specialists focus on protecting and restoring streamside vegetation to maintain water quality, enhance wildlife habitat, and stabilize banks, often implementing buffer zones and erosion control measures. Wetlands Foresters manage hydric soils and wetland ecosystems, emphasizing wetland delineation, hydrological assessments, and compliance with environmental regulations to sustain wetland health. Both roles collaborate on riparian management by integrating forest stand improvement with water resource conservation and habitat diversity.
Core Duties in Wetlands Forestry
Riparian Specialists focus on managing and restoring streamside vegetation to protect water quality and aquatic habitats, emphasizing erosion control and buffer zone maintenance. Wetlands Foresters specialize in the sustainable management of forested wetlands, including hydrological monitoring, species selection adapted to saturated soils, and ensuring compliance with wetland protection regulations. Both roles require expertise in ecosystem functions but diverge in their primary focus areas within wetland forestry practices.
Required Education and Certifications
Riparian Specialists typically require a bachelor's degree in environmental science, forestry, or natural resource management, with certifications such as Certified Ecologist (CE) or Society of Wetland Scientists (SWS) Certified Wetland Professional enhancing their credentials. Wetlands Foresters generally need a degree in forestry or related fields, complemented by certifications like the Registered Professional Forester (RPF) license and Wetland Delineation Training to demonstrate expertise in wetland ecosystems. Both roles benefit from specialized training in hydrology, soil science, and ecosystem restoration to effectively manage and conserve riparian and wetland areas.
Essential Skills and Competencies
Riparian Specialists excel in hydrology, soil science, and aquatic ecosystem management, emphasizing bank stabilization and water quality protection to support healthy streamside environments. Wetlands Foresters possess expertise in wetland ecology, regulatory compliance, and habitat restoration, focusing on the sustainable management of forested wetlands and biodiversity conservation. Both roles require strong skills in GIS mapping, environmental assessment, and collaborative stakeholder engagement for effective natural resource stewardship.
Tools and Technologies Used
Riparian Specialists utilize GIS mapping, remote sensing, and drone technology to monitor water quality, vegetation health, and erosion along streambanks and river corridors. Wetlands Foresters rely on hydrological modeling software, GPS surveying tools, and soil moisture sensors to assess wetland boundaries, water regimes, and vegetation conditions critical for wetland ecosystem management. Both professionals harness advanced data analysis platforms to support restoration planning and regulatory compliance in forested aquatic environments.
Typical Work Environments
Riparian Specialists typically work in riverbanks, stream corridors, and adjacent upland areas, focusing on the health and management of ecosystems directly influenced by water bodies. Wetlands Foresters operate primarily in marshes, swamps, and bogs, managing forest resources within wetland habitats to preserve biodiversity and water quality. Both roles often involve fieldwork in sensitive ecological zones requiring specialized knowledge in hydrology, soil science, and vegetation management.
Collaboration and Stakeholder Engagement
Riparian Specialists and Wetlands Foresters collaborate closely to balance ecosystem health and land use, leveraging expertise in water quality, habitat restoration, and regulatory compliance. Engaging stakeholders such as landowners, government agencies, and conservation groups is critical for aligning project goals, facilitating permit processes, and ensuring long-term sustainability. Effective communication and coordinated management strategies enhance adaptive forestry practices in riparian and wetland environments.
Career Pathways and Advancement
Riparian Specialists focus on managing and restoring ecosystems adjacent to water bodies, often collaborating with environmental agencies to protect water quality and habitat health, while Wetlands Foresters specialize in the sustainable management of wetland forests, promoting biodiversity and timber production. Career advancement for Riparian Specialists typically involves roles in environmental consulting, government agencies, and nonprofit organizations, emphasizing hydrology and ecological restoration expertise. Wetlands Foresters advance by gaining certifications in forestry and wetland delineation, moving into higher management positions within forestry companies, conservation groups, or regulatory bodies.
Impact on Ecosystem Health and Conservation
Riparian Specialists focus on managing and restoring vegetation along waterways to stabilize banks, improve water quality, and enhance habitat for aquatic and terrestrial species, directly supporting biodiversity and ecosystem resilience. Wetlands Foresters concentrate on the conservation and sustainable management of wetland forests, promoting hydrological functions, carbon sequestration, and habitat diversity critical for flood control and nutrient cycling. Both roles play essential but distinct parts in ecosystem health by targeting different habitats with complementary conservation strategies that sustain landscape connectivity and ecological balance.
Riparian Specialist vs Wetlands Forester Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com