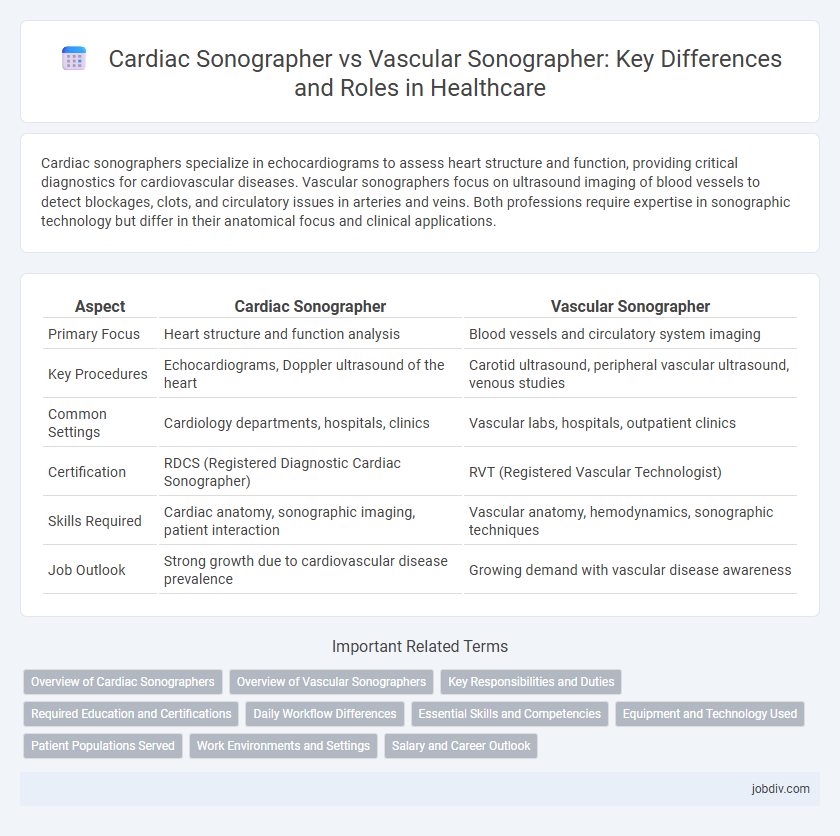
Cardiac sonographers specialize in echocardiograms to assess heart structure and function, providing critical diagnostics for cardiovascular diseases. Vascular sonographers focus on ultrasound imaging of blood vessels to detect blockages, clots, and circulatory issues in arteries and veins. Both professions require expertise in sonographic technology but differ in their anatomical focus and clinical applications.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Cardiac Sonographer | Vascular Sonographer |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Heart structure and function analysis | Blood vessels and circulatory system imaging |
| Key Procedures | Echocardiograms, Doppler ultrasound of the heart | Carotid ultrasound, peripheral vascular ultrasound, venous studies |
| Common Settings | Cardiology departments, hospitals, clinics | Vascular labs, hospitals, outpatient clinics |
| Certification | RDCS (Registered Diagnostic Cardiac Sonographer) | RVT (Registered Vascular Technologist) |
| Skills Required | Cardiac anatomy, sonographic imaging, patient interaction | Vascular anatomy, hemodynamics, sonographic techniques |
| Job Outlook | Strong growth due to cardiovascular disease prevalence | Growing demand with vascular disease awareness |
Overview of Cardiac Sonographers
Cardiac sonographers specialize in performing echocardiograms to assess heart function and diagnose cardiovascular conditions, using ultrasound technology to create detailed images of the heart's chambers, valves, and vessels. They often work closely with cardiologists, providing critical data to detect abnormalities such as valve defects, heart failure, and congenital heart disease. Expertise in cardiac anatomy and pathophysiology is essential for accurately conducting and interpreting these diagnostic tests, which play a vital role in patient treatment planning.
Overview of Vascular Sonographers
Vascular sonographers specialize in using ultrasound technology to evaluate blood flow and identify vascular conditions such as blood clots, blockages, and arterial diseases. They perform non-invasive diagnostic procedures to assess veins and arteries, aiding in the detection of peripheral artery disease, deep vein thrombosis, and aneurysms. Vascular sonographers work closely with cardiologists and vascular surgeons to provide critical imaging data that guides treatment plans and interventions.
Key Responsibilities and Duties
Cardiac sonographers specialize in performing echocardiograms to assess heart structure and function, capturing real-time images crucial for diagnosing cardiovascular conditions. Vascular sonographers focus on imaging blood vessels to detect blockages, clots, or abnormalities in veins and arteries using Doppler ultrasound techniques. Both professionals collaborate with physicians by preparing detailed reports and ensuring accurate, high-quality imaging to support patient diagnosis and treatment plans.
Required Education and Certifications
Cardiac sonographers typically require an associate degree or a postsecondary certificate in diagnostic medical sonography, with specialized training in echocardiography and certification through the American Registry for Diagnostic Medical Sonography (ARDMS) in Adult Echocardiography (RDCS). Vascular sonographers usually obtain similar educational credentials but focus on vascular technology, earning certifications such as the Registered Vascular Technologist (RVT) credential from the American Registry for Diagnostic Medical Sonography (ARDMS) or Cardiovascular Credentialing International (CCI). Both roles demand clinical experience and ongoing education to maintain certification and ensure proficiency in cardiovascular ultrasound imaging.
Daily Workflow Differences
Cardiac Sonographers primarily perform echocardiograms to assess heart function, including heart chamber size, valve operation, and blood flow, often working closely with cardiologists in hospital or clinical settings. Vascular Sonographers focus on imaging blood vessels throughout the body to detect blockages, clots, or abnormalities, frequently conducting Doppler ultrasound studies in outpatient clinics or vascular labs. The daily workflow of cardiac sonographers centers on detailed heart imaging protocols, while vascular sonographers emphasize peripheral vascular assessments and arterial or venous evaluation.
Essential Skills and Competencies
Cardiac sonographers require expertise in echocardiography, proficient use of ultrasound equipment, and a deep understanding of cardiovascular anatomy and pathology to accurately assess heart function. Vascular sonographers must excel in Doppler ultrasound techniques, possess detailed knowledge of vascular anatomy and hemodynamics, and be skilled in detecting blood flow abnormalities and vascular diseases. Both roles demand strong analytical skills, patient communication abilities, and adherence to safety protocols to ensure precise diagnostic imaging.
Equipment and Technology Used
Cardiac Sonographers primarily use advanced echocardiography machines equipped with high-frequency transducers that provide detailed images of the heart's structures and blood flow, enabling precise diagnosis of cardiac conditions. Vascular Sonographers utilize Doppler ultrasound devices designed to assess blood flow and detect blockages or abnormalities within arteries and veins, often employing duplex ultrasound technology combining traditional and Doppler imaging. Both specialties rely on state-of-the-art imaging software that enhances image resolution and supports real-time analysis for accurate and efficient patient evaluations.
Patient Populations Served
Cardiac Sonographers primarily serve patients with heart-related conditions, performing echocardiograms to diagnose and monitor cardiovascular diseases, including heart valve disorders and congestive heart failure. Vascular Sonographers focus on patients with vascular system issues, using ultrasound technology to evaluate blood flow and detect abnormalities such as deep vein thrombosis, peripheral artery disease, and carotid artery stenosis. Both specialties play crucial roles in managing cardiovascular health but target different patient populations based on the anatomical systems involved.
Work Environments and Settings
Cardiac sonographers primarily work in hospital cardiac units, outpatient cardiology clinics, and specialized heart centers, conducting echocardiograms and monitoring heart conditions. Vascular sonographers are often employed in vascular labs, surgical centers, and diagnostic imaging facilities, focusing on blood flow and artery health assessments. Both roles may also perform duties in rehabilitation centers and mobile diagnostic services, tailored to specific cardiovascular diagnostic needs.
Salary and Career Outlook
Cardiac sonographers earn an average salary ranging from $65,000 to $85,000 annually, with a projected job growth rate of approximately 17% over the next decade due to increased demand for cardiovascular diagnostics. Vascular sonographers typically have a similar salary range, often between $60,000 and $80,000, but their career outlook is slightly stronger, with a growth estimate near 20% as vascular diseases rise in prevalence. Both specialties offer stable career opportunities within hospitals, outpatient clinics, and diagnostic imaging centers, driven by advancements in medical imaging technology and aging populations.
Cardiac Sonographer vs Vascular Sonographer Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com