An obstetrician specializes in pregnancy, childbirth, and postpartum care, ensuring both mother and baby remain healthy throughout the process. A gynecologist focuses on the overall female reproductive system, managing issues such as menstrual disorders, contraception, and menopause. Both specialists play crucial roles in women's health but address different stages and aspects of reproductive care.
Table of Comparison
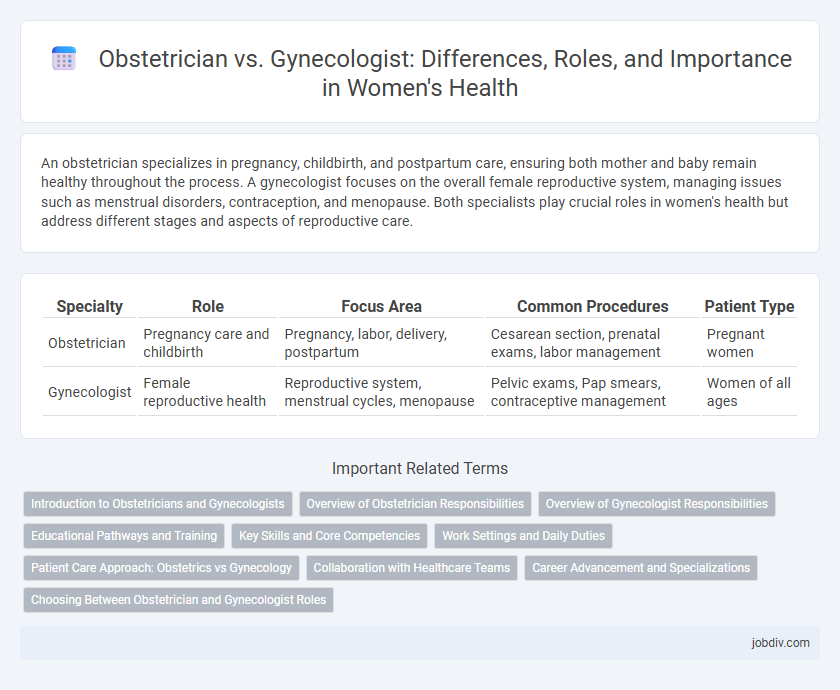
| Specialty | Role | Focus Area | Common Procedures | Patient Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Obstetrician | Pregnancy care and childbirth | Pregnancy, labor, delivery, postpartum | Cesarean section, prenatal exams, labor management | Pregnant women |
| Gynecologist | Female reproductive health | Reproductive system, menstrual cycles, menopause | Pelvic exams, Pap smears, contraceptive management | Women of all ages |
Introduction to Obstetricians and Gynecologists
Obstetricians specialize in pregnancy, childbirth, and postpartum care, managing both routine and high-risk pregnancies with expertise in labor and delivery. Gynecologists focus on the female reproductive system, diagnosing and treating conditions such as menstrual disorders, infertility, and reproductive cancers. Many doctors are dual specialists known as OB-GYNs, providing comprehensive care that spans both pregnancy and general women's health.
Overview of Obstetrician Responsibilities
Obstetricians specialize in managing pregnancy, childbirth, and postpartum care, ensuring the health and safety of both mother and baby throughout the gestation period. Their responsibilities include monitoring fetal development, performing prenatal screenings, managing labor and delivery, and addressing complications such as preeclampsia or gestational diabetes. Obstetricians also provide guidance on prenatal nutrition, birth plans, and postpartum recovery.
Overview of Gynecologist Responsibilities
Gynecologists specialize in the female reproductive system, diagnosing and treating conditions related to menstruation, fertility, and menopause. They perform routine screenings such as Pap smears, manage infections and hormonal disorders, and provide preventive care including contraceptive counseling. Gynecologists also offer care for sexually transmitted infections, pelvic pain, and cancers of the reproductive organs.
Educational Pathways and Training
Obstetricians complete medical school followed by a 4-year residency specializing in obstetrics and gynecology, with an emphasis on pregnancy, childbirth, and postpartum care. Gynecologists undergo the same initial training but focus more extensively on the female reproductive system, including diagnosis and treatment of disorders unrelated to pregnancy. Both specialties require board certification, but obstetricians receive additional training in surgical delivery techniques and prenatal management.
Key Skills and Core Competencies
Obstetricians specialize in prenatal care, labor, and delivery, requiring expertise in fetal monitoring, maternal health management, and emergency obstetric procedures. Gynecologists focus on female reproductive health, with core competencies in diagnosing and treating conditions like endometriosis, ovarian cysts, and cervical cancer. Both professionals must possess skills in patient communication, surgical techniques, and hormonal therapies to provide comprehensive women's healthcare.
Work Settings and Daily Duties
Obstetricians primarily work in hospitals, maternity wards, and birthing centers, focusing on prenatal care, labor, delivery, and postpartum management. Gynecologists typically operate in outpatient clinics or private practices, performing routine pelvic exams, screenings, and managing reproductive health issues such as menstrual disorders and menopause. Both specialists collaborate closely to provide comprehensive care for women's reproductive health across different stages.
Patient Care Approach: Obstetrics vs Gynecology
Obstetricians focus primarily on patient care during pregnancy, childbirth, and postpartum, ensuring both maternal and fetal health through monitoring, managing labor, and handling complications. Gynecologists specialize in the overall reproductive health of women, addressing issues such as menstrual disorders, hormonal imbalances, and preventive screenings like Pap smears and pelvic exams. Both specialties emphasize personalized care, but obstetrics centers on prenatal and delivery care, whereas gynecology revolves around maintaining long-term reproductive system health.
Collaboration with Healthcare Teams
Obstetricians and gynecologists collaborate closely with multidisciplinary healthcare teams to provide comprehensive care for women throughout pregnancy, childbirth, and reproductive health. Their teamwork with nurses, anesthesiologists, pediatricians, and nutritionists ensures optimized outcomes for both mother and baby by addressing medical, emotional, and nutritional needs. Effective communication within these healthcare teams enhances patient safety, facilitates timely interventions, and supports personalized treatment plans.
Career Advancement and Specializations
Obstetricians specialize in prenatal care, labor, and delivery, while gynecologists focus on the female reproductive system outside of pregnancy. Career advancement in obstetrics often involves sub-specializing in areas such as maternal-fetal medicine or reproductive endocrinology, enhancing expertise in high-risk pregnancies or fertility treatments. Gynecologists can pursue further specialization in gynecologic oncology or urogynecology, broadening their scope in cancer treatment and pelvic floor disorders.
Choosing Between Obstetrician and Gynecologist Roles
Choosing between an obstetrician and a gynecologist depends primarily on your healthcare needs; obstetricians specialize in pregnancy, childbirth, and prenatal care, while gynecologists focus on the female reproductive system, including menstrual issues, contraception, and menopause. Many physicians are trained as OB-GYNs, providing comprehensive care spanning both fields. For pregnancy-related concerns, selecting an obstetrician ensures expert monitoring, whereas gynecologists are ideal for routine reproductive health and preventative screenings.
Obstetrician vs Gynecologist Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com