Information librarians specialize in organizing, managing, and curating physical and digital information resources, ensuring accessibility and accuracy for diverse user needs. Digital librarians focus primarily on managing digital content, including electronic databases, digital archives, and online resources, employing advanced technologies to facilitate digital preservation and user interaction. Both roles require expertise in information organization but differ in their emphasis on physical versus digital information environments.
Table of Comparison
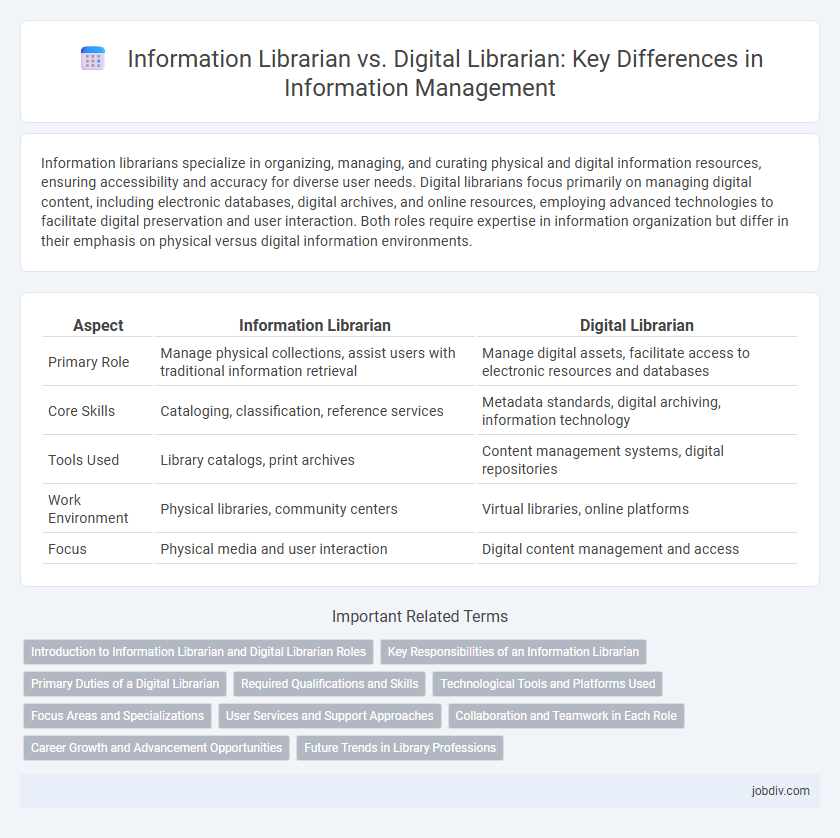
| Aspect | Information Librarian | Digital Librarian |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Manage physical collections, assist users with traditional information retrieval | Manage digital assets, facilitate access to electronic resources and databases |
| Core Skills | Cataloging, classification, reference services | Metadata standards, digital archiving, information technology |
| Tools Used | Library catalogs, print archives | Content management systems, digital repositories |
| Work Environment | Physical libraries, community centers | Virtual libraries, online platforms |
| Focus | Physical media and user interaction | Digital content management and access |
Introduction to Information Librarian and Digital Librarian Roles
Information librarians specialize in managing traditional library resources such as books, periodicals, and archival materials, focusing on cataloging, classification, and user reference services. Digital librarians prioritize the acquisition, organization, and preservation of digital content, including e-books, databases, and multimedia files, ensuring easy access through online platforms and digital repositories. Both roles require expertise in information retrieval, user support, and resource management, but digital librarians emphasize technological skills and digital information systems.
Key Responsibilities of an Information Librarian
An Information Librarian specializes in managing and organizing physical and digital information resources, ensuring accurate cataloging, classification, and retrieval of data. Key responsibilities include maintaining library collections, assisting users with research queries, and developing information literacy programs. Proficiency in metadata standards, database management, and user services is essential for effective information dissemination and resource accessibility.
Primary Duties of a Digital Librarian
A Digital Librarian primarily manages and curates digital collections, ensuring accessibility and preservation of electronic resources such as e-books, databases, and multimedia files. They develop and maintain digital cataloging systems, implement metadata standards like Dublin Core, and optimize user interfaces for efficient information retrieval. Their role also involves collaborating with IT professionals to troubleshoot digital platform issues and safeguard digital content against data loss or cyber threats.
Required Qualifications and Skills
Information Librarians require a master's degree in library science (MLS) or information studies with strong organizational, reference, and cataloging skills. Digital Librarians need advanced expertise in digital technologies, metadata standards, and digital asset management, often combined with knowledge of information systems and digital preservation. Both roles demand proficiency in information retrieval, data analysis, and user-centric service delivery to support diverse research and knowledge management needs.
Technological Tools and Platforms Used
Information librarians primarily utilize integrated library systems (ILS), cataloging software, and metadata standards like MARC and Dublin Core to manage physical and digital collections efficiently. Digital librarians focus on advanced technological tools such as digital asset management systems (DAMS), content management systems (CMS), and specialized platforms like DSpace and Omeka for curating, preserving, and providing access to electronic resources. Both roles leverage emerging technologies including cloud computing, linked data, and artificial intelligence to enhance information retrieval and user experience.
Focus Areas and Specializations
Information librarians specialize in organizing, managing, and curating physical and digital information resources within traditional library settings, emphasizing cataloging, reference services, and user education. Digital librarians focus on electronic resources, metadata standards, digital preservation, and information retrieval technologies to enhance access to digital collections and online databases. Both roles require expertise in information science, but digital librarians prioritize technological proficiency and digital content management systems.
User Services and Support Approaches
Information librarians specialize in personalized user services by offering tailored research assistance and reference support, enhancing information retrieval through direct interaction. Digital librarians focus on providing remote access to digital resources, utilizing virtual help desks, online tutorials, and automated tools to support users in navigating electronic databases. Both roles prioritize user-centric approaches but differ in their methods, with information librarians emphasizing face-to-face guidance and digital librarians leveraging technology for wider accessibility.
Collaboration and Teamwork in Each Role
Information librarians excel in fostering collaboration through traditional research support, coordinating with academic staff and patrons to curate physical and digital collections. Digital librarians emphasize teamwork using advanced digital tools and platforms, enabling seamless integration of electronic resources and online databases for remote users. Both roles require strong communication skills and a collaborative approach to enhance information accessibility and user experience.
Career Growth and Advancement Opportunities
Information librarians often have strong foundations in cataloging, metadata management, and reference services, which provide steady career growth within traditional library environments. Digital librarians specialize in digital asset management, data curation, and emerging technologies, positioning themselves for rapid advancement in tech-driven sectors and interdisciplinary roles. Career growth for digital librarians is frequently tied to skills in digital preservation, data analytics, and information system integration, offering broader opportunities compared to traditional information librarian roles.
Future Trends in Library Professions
Information librarians increasingly integrate artificial intelligence and data analytics to enhance user access and resource management, while digital librarians focus on managing electronic resources, digital archives, and virtual services. Emerging trends emphasize skills in digital preservation, cybersecurity, and user experience design to meet evolving patron demands and technological advancements. Collaboration between these roles will drive innovation in information organization, access, and dissemination across hybrid library environments.
Information Librarian vs Digital Librarian Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com