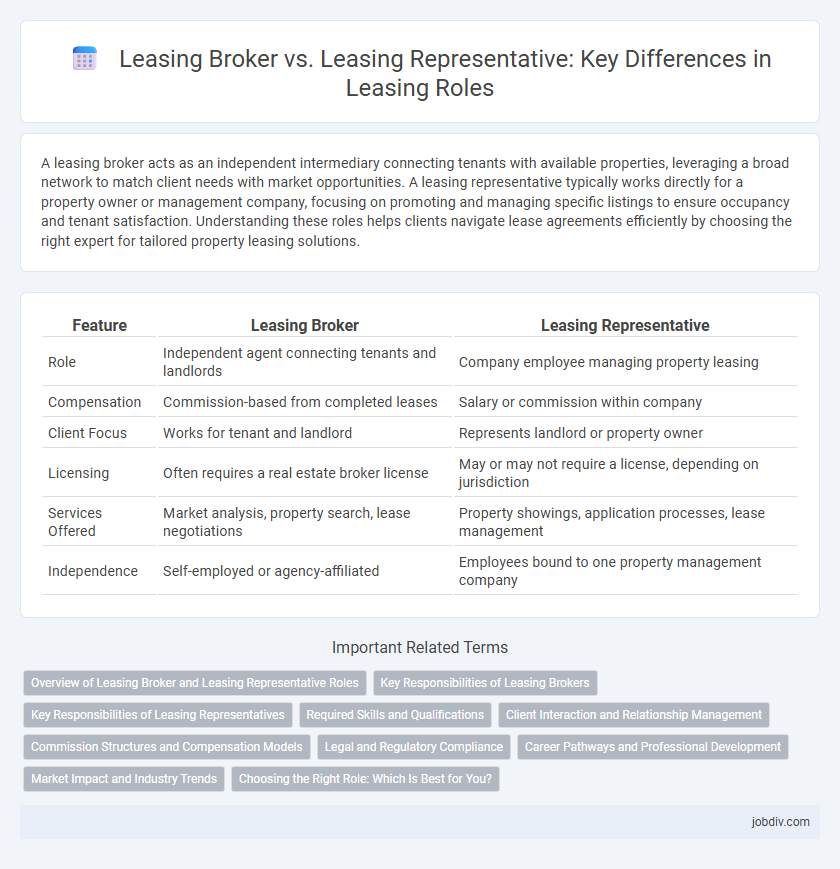
A leasing broker acts as an independent intermediary connecting tenants with available properties, leveraging a broad network to match client needs with market opportunities. A leasing representative typically works directly for a property owner or management company, focusing on promoting and managing specific listings to ensure occupancy and tenant satisfaction. Understanding these roles helps clients navigate lease agreements efficiently by choosing the right expert for tailored property leasing solutions.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Leasing Broker | Leasing Representative |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Independent agent connecting tenants and landlords | Company employee managing property leasing |
| Compensation | Commission-based from completed leases | Salary or commission within company |
| Client Focus | Works for tenant and landlord | Represents landlord or property owner |
| Licensing | Often requires a real estate broker license | May or may not require a license, depending on jurisdiction |
| Services Offered | Market analysis, property search, lease negotiations | Property showings, application processes, lease management |
| Independence | Self-employed or agency-affiliated | Employees bound to one property management company |
Overview of Leasing Broker and Leasing Representative Roles
Leasing brokers act as intermediaries between property owners and prospective tenants, facilitating lease agreements across residential and commercial real estate markets while often representing multiple landlords. Leasing representatives typically work directly for a specific property or management company, managing tenant relations, lease documentation, and property showings to ensure occupancy and compliance. Both roles require strong market knowledge and negotiation skills, but brokers provide broader market access, whereas representatives focus on the operational aspects of leasing individual properties.
Key Responsibilities of Leasing Brokers
Leasing brokers specialize in connecting tenants with landlords, managing property listings, conducting market analysis, and negotiating lease terms to secure favorable agreements for clients. They coordinate property showings, evaluate tenant needs, and facilitate communication between all parties to streamline the leasing process. Leasing brokers also assist with lease documentation, ensure compliance with local rental laws, and often provide strategic advice to maximize client benefits in competitive markets.
Key Responsibilities of Leasing Representatives
Leasing representatives handle tenant relations by managing lease agreements, conducting property tours, and processing applications to secure new tenants. They ensure compliance with leasing policies while addressing tenant inquiries and coordinating maintenance requests to maintain customer satisfaction. Their role emphasizes direct interaction with clients and property management, differentiating from leasing brokers who primarily focus on property marketing and client acquisition strategies.
Required Skills and Qualifications
Leasing brokers require strong negotiation skills, in-depth market knowledge, and licenses or certifications specific to real estate brokerage to represent multiple property owners independently. Leasing representatives focus on excellent customer service, communication skills, and often require experience in property management or real estate, with certifications like Certified Leasing Specialist enhancing credibility. Both roles demand proficiency in contract understanding and local leasing regulations to efficiently manage client needs and lease agreements.
Client Interaction and Relationship Management
Leasing brokers cultivate broad client networks by connecting prospective tenants with multiple property options, emphasizing personalized property matching and market expertise to optimize client satisfaction. Leasing representatives maintain direct, ongoing communication with clients on behalf of a single property owner or management company, focusing on detailed lease negotiation, tenant retention, and addressing tenant concerns promptly. Both roles require strong client interaction skills, but brokers prioritize diverse client acquisition, while representatives excel in sustained relationship management within specific property portfolios.
Commission Structures and Compensation Models
Leasing brokers typically earn commissions based on a percentage of the total lease value, often receiving a one-time fee upon signing the lease agreement. Leasing representatives usually work on a salary or hourly wage combined with smaller performance-based bonuses, reflecting their ongoing involvement in property management or tenant relations. Commission structures for brokers incentivize closing deals, while representatives benefit from consistent compensation tied to tenant retention and lease administration.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Leasing brokers operate under stringent legal and regulatory frameworks that often require specific licenses and adherence to state and federal consumer protection laws. Leasing representatives, typically employed by leasing companies, must comply with company policies and industry regulations but usually hold fewer independent legal obligations than brokers. Understanding these compliance distinctions is essential for risk management and ensuring lawful conduct within leasing transactions.
Career Pathways and Professional Development
Leasing brokers often work independently or with multiple agencies, developing diverse client networks and entrepreneurial skills that enable flexible career growth and potential business ownership. Leasing representatives typically advance within a single company, gaining specialized knowledge of property portfolios and client management, which supports upward mobility into senior leasing or property management roles. Both career pathways offer professional development through certifications like Certified Leasing Specialist (CLS) and opportunities to build expertise in real estate laws, negotiation, and market analysis.
Market Impact and Industry Trends
Leasing brokers drive market impact by connecting multiple landlords and tenants across regions, expanding access to diverse property portfolios and fostering competitive lease terms. Leasing representatives typically operate within specific property management firms, focusing on optimizing occupancy rates and tenant relations, which directly influence individual asset performance and localized market stability. Industry trends highlight a growing preference for brokers due to increased demand for market transparency and cross-sector expertise, while representatives are adapting through enhanced digital tools to improve tenant retention and lease administration efficiency.
Choosing the Right Role: Which Is Best for You?
Choosing between a leasing broker and a leasing representative depends on your goals and work style; brokers act independently to find the best property deals across multiple landlords, while representatives work directly for one property management company, focusing on available units within their portfolio. Leasing brokers often have access to a broader market and may earn commissions based on successful deals, appealing to those seeking flexibility and diverse opportunities. Leasing representatives benefit from steady income and comprehensive training provided by their employer, ideal for individuals who prefer stable work environments and in-depth knowledge of specific properties.
Leasing Broker vs Leasing Representative Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com