A commercial leasing broker specializes in negotiating leases for office, retail, and industrial properties, focusing on complex terms and long-term agreements tailored to business needs. In contrast, a residential leasing broker handles rental agreements for apartments, houses, and condos, emphasizing tenant preferences and short-term lease terms. Both brokers navigate regulatory compliance, but their expertise differs according to property type and client requirements.
Table of Comparison
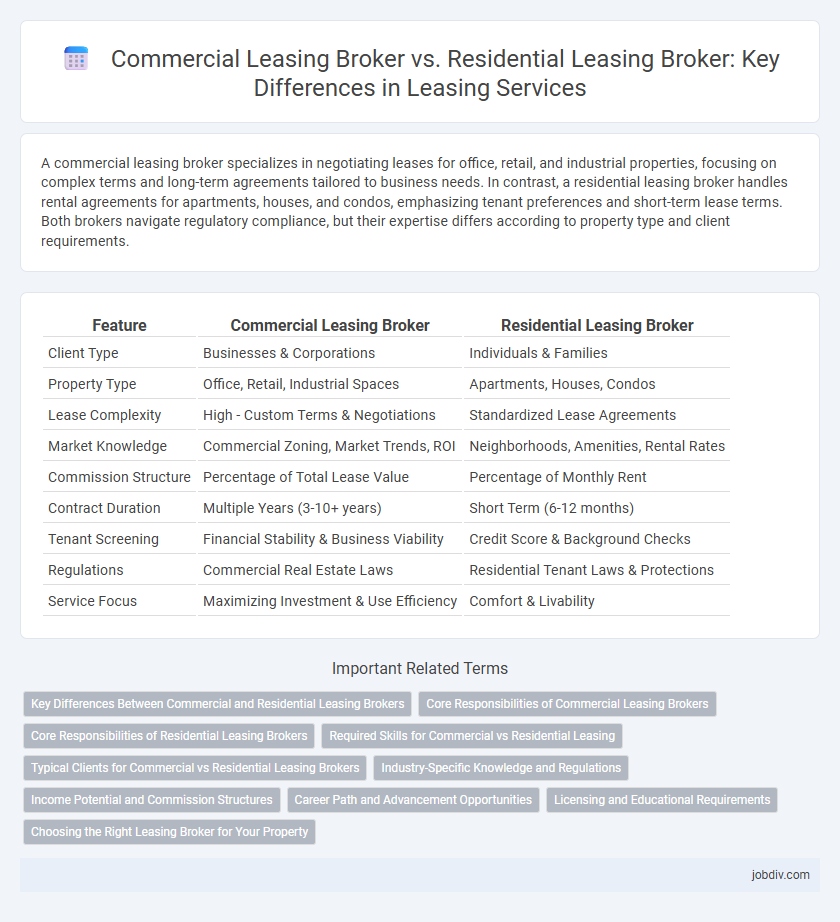
| Feature | Commercial Leasing Broker | Residential Leasing Broker |
|---|---|---|
| Client Type | Businesses & Corporations | Individuals & Families |
| Property Type | Office, Retail, Industrial Spaces | Apartments, Houses, Condos |
| Lease Complexity | High - Custom Terms & Negotiations | Standardized Lease Agreements |
| Market Knowledge | Commercial Zoning, Market Trends, ROI | Neighborhoods, Amenities, Rental Rates |
| Commission Structure | Percentage of Total Lease Value | Percentage of Monthly Rent |
| Contract Duration | Multiple Years (3-10+ years) | Short Term (6-12 months) |
| Tenant Screening | Financial Stability & Business Viability | Credit Score & Background Checks |
| Regulations | Commercial Real Estate Laws | Residential Tenant Laws & Protections |
| Service Focus | Maximizing Investment & Use Efficiency | Comfort & Livability |
Key Differences Between Commercial and Residential Leasing Brokers
Commercial leasing brokers specialize in negotiating leases for retail, office, and industrial properties, requiring expertise in complex contracts and market analysis tailored to business needs. Residential leasing brokers focus on individual or family housing, emphasizing tenant screenings, rental agreements, and local housing regulations. The primary distinctions lie in the property types handled, the complexity of lease terms, and the client base served, with commercial brokers dealing in larger-scale transactions and longer lease durations compared to residential brokers.
Core Responsibilities of Commercial Leasing Brokers
Commercial leasing brokers specialize in negotiating lease agreements for office spaces, retail locations, and industrial properties, requiring in-depth knowledge of zoning laws, property valuation, and market trends. They analyze financial metrics such as net operating income and cap rates to advise clients on investment viability and lease terms. Their core responsibilities include facilitating complex lease negotiations, structuring contracts to protect client interests, and coordinating with legal, financial, and property management professionals.
Core Responsibilities of Residential Leasing Brokers
Residential leasing brokers specialize in connecting tenants with suitable residential properties, managing lease negotiations, and ensuring compliance with local housing laws. They conduct market analysis to set competitive rental rates and facilitate tenant screenings to secure reliable occupants. Their core responsibilities also include drafting lease agreements and coordinating move-in inspections to maintain property standards.
Required Skills for Commercial vs Residential Leasing
Commercial leasing brokers require strong negotiation skills, a deep understanding of market trends, and expertise in complex lease structures to manage office, retail, or industrial properties effectively. Residential leasing brokers excel in customer service, tenant screening, and local market knowledge to match renters with suitable living spaces efficiently. Both roles demand strong communication skills, but commercial brokers prioritize analytical abilities, while residential brokers emphasize interpersonal engagement.
Typical Clients for Commercial vs Residential Leasing Brokers
Commercial leasing brokers typically serve business owners, investors, and corporations seeking office, retail, or industrial spaces. Residential leasing brokers primarily assist individual renters, families, and landlords looking for apartments, houses, or condos. The client base for commercial brokers is driven by business needs and investment goals, while residential brokers focus on personal living arrangements and tenant-landlord relationships.
Industry-Specific Knowledge and Regulations
Commercial leasing brokers possess in-depth knowledge of complex zoning laws, environmental regulations, and market trends affecting business properties, enabling them to negotiate favorable terms for retail, office, or industrial spaces. Residential leasing brokers specialize in tenant rights, lease agreements, fair housing laws, and local housing ordinances to ensure compliance and protect both landlords and renters in multifamily or single-family dwellings. Each broker type must stay updated on industry-specific regulations and contract stipulations to effectively serve their distinct client base within the leasing market.
Income Potential and Commission Structures
Commercial leasing brokers typically earn higher commissions, often ranging from 3% to 6% of the lease value, with deals involving larger property spaces and longer lease terms, resulting in greater income potential. Residential leasing brokers usually receive commissions of about 5% to 7% of the annual rent, but since residential leases tend to be shorter and involve smaller properties, their overall earnings are generally lower than those of commercial brokers. The commission structure in commercial leasing often includes split arrangements and performance bonuses, whereas residential brokers mostly rely on straightforward commission percentages per lease secured.
Career Path and Advancement Opportunities
Commercial leasing brokers typically engage with larger, more complex transactions involving office, retail, or industrial properties, which often leads to higher commissions and faster career advancement through specialized sectors such as corporate real estate or investment firms. Residential leasing brokers usually manage apartment and single-family property rentals, providing a steadier but less lucrative career path often limited to local markets and smaller-scale property management roles. Advancement opportunities for commercial brokers frequently include positions like leasing manager, portfolio manager, or commercial real estate analyst, while residential brokers might progress toward property management or real estate sales roles.
Licensing and Educational Requirements
Commercial leasing brokers must typically obtain a real estate license with specialized certifications in commercial property, often requiring advanced coursework in property management, finance, and contract law. Residential leasing brokers usually hold a standard real estate license with mandatory training focused on residential tenant rights, fair housing laws, and lease agreements. While both professionals need to pass state licensing exams, commercial brokers face more rigorous educational prerequisites due to the complexity and higher value of commercial transactions.
Choosing the Right Leasing Broker for Your Property
Choosing the right leasing broker is crucial for maximizing property returns, with commercial leasing brokers specializing in office, retail, and industrial spaces, while residential leasing brokers focus on apartment and single-family homes. Commercial brokers have expertise in longer lease terms, complex contracts, and tenant creditworthiness, whereas residential brokers prioritize speed of occupancy and market rent analysis. Understanding the property type and tenant profile ensures selection of a leasing broker who aligns with your investment goals and local market dynamics.
Commercial Leasing Broker vs Residential Leasing Broker Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com