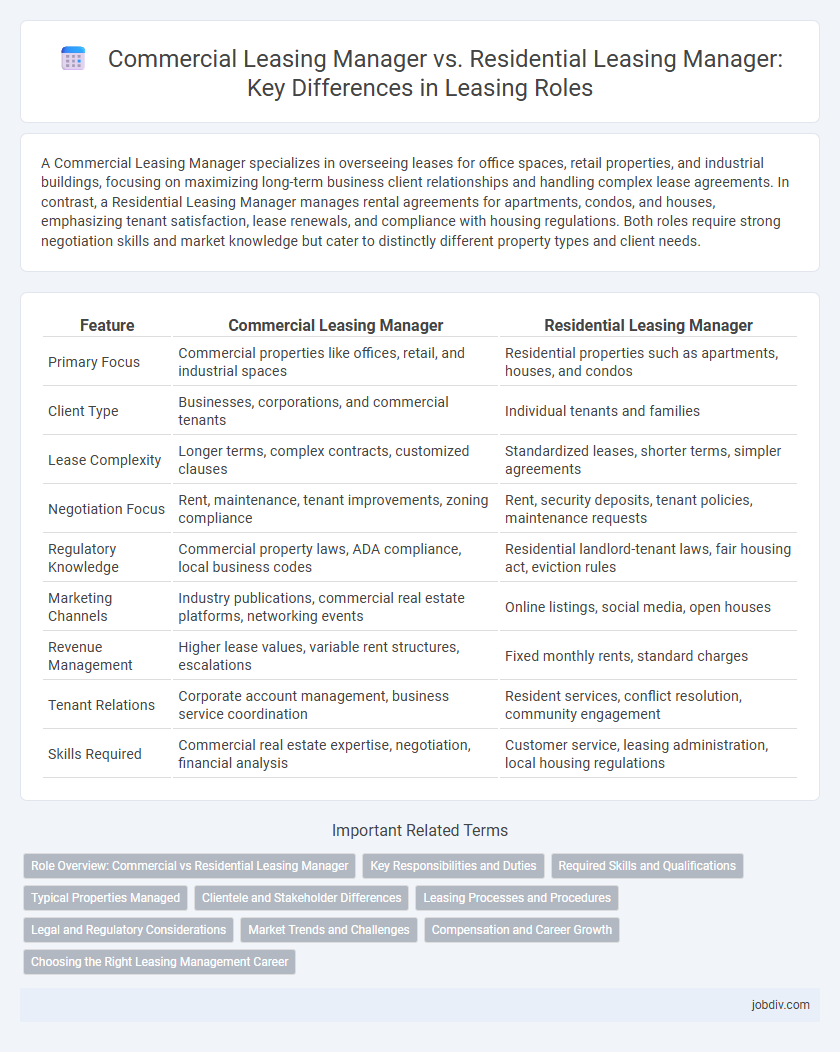
A Commercial Leasing Manager specializes in overseeing leases for office spaces, retail properties, and industrial buildings, focusing on maximizing long-term business client relationships and handling complex lease agreements. In contrast, a Residential Leasing Manager manages rental agreements for apartments, condos, and houses, emphasizing tenant satisfaction, lease renewals, and compliance with housing regulations. Both roles require strong negotiation skills and market knowledge but cater to distinctly different property types and client needs.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Commercial Leasing Manager | Residential Leasing Manager |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Commercial properties like offices, retail, and industrial spaces | Residential properties such as apartments, houses, and condos |
| Client Type | Businesses, corporations, and commercial tenants | Individual tenants and families |
| Lease Complexity | Longer terms, complex contracts, customized clauses | Standardized leases, shorter terms, simpler agreements |
| Negotiation Focus | Rent, maintenance, tenant improvements, zoning compliance | Rent, security deposits, tenant policies, maintenance requests |
| Regulatory Knowledge | Commercial property laws, ADA compliance, local business codes | Residential landlord-tenant laws, fair housing act, eviction rules |
| Marketing Channels | Industry publications, commercial real estate platforms, networking events | Online listings, social media, open houses |
| Revenue Management | Higher lease values, variable rent structures, escalations | Fixed monthly rents, standard charges |
| Tenant Relations | Corporate account management, business service coordination | Resident services, conflict resolution, community engagement |
| Skills Required | Commercial real estate expertise, negotiation, financial analysis | Customer service, leasing administration, local housing regulations |
Role Overview: Commercial vs Residential Leasing Manager
Commercial Leasing Managers oversee leasing agreements for business properties such as office buildings, retail spaces, and industrial warehouses, focusing on negotiation, tenant relations, and market analysis to maximize income. Residential Leasing Managers handle leasing for housing units including apartments and single-family homes, emphasizing tenant screening, lease administration, and property maintenance coordination. Both roles require expertise in contract management and compliance but differ in target markets and lease complexity.
Key Responsibilities and Duties
A Commercial Leasing Manager oversees leasing for office buildings, retail spaces, and industrial properties, focusing on negotiating lease terms, managing tenant relations, and ensuring compliance with commercial lease agreements. A Residential Leasing Manager handles rental of apartments, houses, and residential complexes, emphasizing tenant screening, lease administration, rent collection, and maintenance coordination. Both roles require strong communication skills and market knowledge but differ in tenant type, lease complexity, and property management priorities.
Required Skills and Qualifications
Commercial Leasing Managers require strong negotiation skills, deep understanding of commercial property laws, and expertise in market analysis to secure high-value tenants and manage complex lease agreements. Residential Leasing Managers need excellent customer service abilities, knowledge of residential real estate regulations, and proficiency in tenant screening processes to maintain tenant satisfaction and occupancy rates. Both roles demand strong communication skills and experience with lease documentation, but commercial roles emphasize financial analysis while residential roles prioritize tenant relations.
Typical Properties Managed
Commercial Leasing Managers typically oversee office buildings, retail spaces, industrial warehouses, and mixed-use developments, focusing on properties that cater to business operations and commercial activities. Residential Leasing Managers handle apartment complexes, single-family homes, condominiums, and multi-family housing units, emphasizing tenant relations and residential living amenities. Both roles require expertise in property-specific market trends, lease negotiations, and compliance with relevant regulations tailored to commercial or residential sectors.
Clientele and Stakeholder Differences
Commercial Leasing Managers primarily engage with business clients, including corporations, retail chains, and industrial tenants, focusing on negotiating leases that accommodate business operations and growth. Residential Leasing Managers interact mainly with individual tenants or families, emphasizing personal living conditions and community compliance. Stakeholders in commercial leasing typically involve property investors and commercial developers, while residential leasing stakeholders often include homeowners' associations and local housing authorities.
Leasing Processes and Procedures
Commercial Leasing Managers oversee complex lease negotiations involving longer terms, higher financial stakes, and detailed contract clauses tailored for business use, requiring advanced knowledge of zoning laws and commercial real estate market trends. Residential Leasing Managers focus on shorter lease durations, standard rental agreements, tenant screening, and compliance with housing laws designed to protect individual renters, streamlining tenant onboarding and renewals. The leasing process in commercial properties demands comprehensive financial analysis and customization, whereas residential leasing emphasizes efficient turnover and tenant satisfaction through standardized procedures.
Legal and Regulatory Considerations
Commercial Leasing Managers navigate complex legal frameworks involving zoning laws, environmental regulations, and compliance with the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA), often dealing with longer lease terms and customized contract clauses. Residential Leasing Managers focus on tenant rights under local landlord-tenant laws, fair housing regulations, and habitability standards, ensuring compliance with security deposit limits and eviction procedures specific to residential properties. Both roles require updated knowledge of state and federal regulations, but Commercial Leasing Managers handle more varied and industry-specific legal risks compared to the more standardized and tenant-protective regulations faced by Residential Leasing Managers.
Market Trends and Challenges
Commercial Leasing Managers face fluctuating demand influenced by economic cycles and remote work trends, requiring adaptability to changing workspace needs and longer vacancy periods. Residential Leasing Managers contend with rising housing costs and increased tenant turnover driven by urbanization and demographic shifts. Both roles must navigate regulatory changes and technology adoption to optimize lease management and tenant relations in competitive markets.
Compensation and Career Growth
Commercial Leasing Managers typically earn higher salaries than Residential Leasing Managers due to the larger value and complexity of commercial properties, with average annual compensation ranging from $70,000 to $120,000 compared to $50,000 to $80,000 for residential roles. Career growth for Commercial Leasing Managers often leads to senior management positions such as Director of Leasing or Real Estate Asset Manager, while Residential Leasing Managers may advance to Regional Property Manager or Leasing Director roles within residential portfolios. Both roles benefit from strong negotiation skills and market knowledge, but commercial leasing experience is valued for higher strategic impact and earning potential.
Choosing the Right Leasing Management Career
Choosing the right leasing management career depends on industry preferences and skill alignment. Commercial Leasing Managers oversee office, retail, and industrial properties, requiring expertise in contract negotiation, market analysis, and tenant relations for high-value leases. Residential Leasing Managers focus on multifamily or single-family properties, emphasizing tenant screening, leasing compliance, and community engagement to enhance tenant retention.
Commercial Leasing Manager vs Residential Leasing Manager Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com