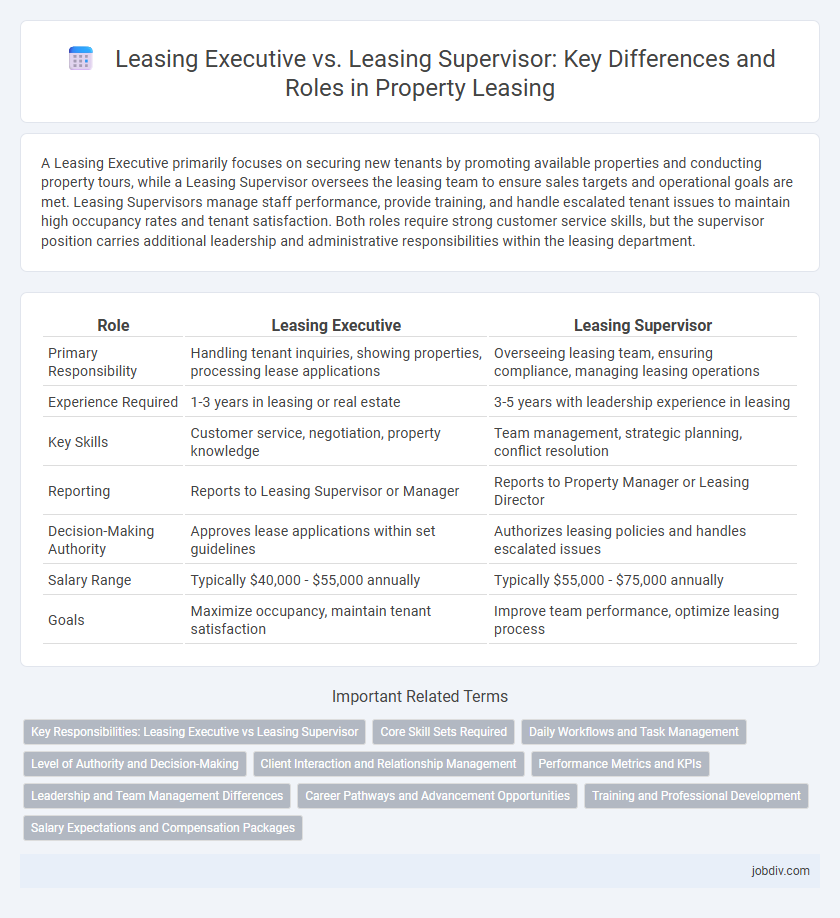
A Leasing Executive primarily focuses on securing new tenants by promoting available properties and conducting property tours, while a Leasing Supervisor oversees the leasing team to ensure sales targets and operational goals are met. Leasing Supervisors manage staff performance, provide training, and handle escalated tenant issues to maintain high occupancy rates and tenant satisfaction. Both roles require strong customer service skills, but the supervisor position carries additional leadership and administrative responsibilities within the leasing department.
Table of Comparison
| Role | Leasing Executive | Leasing Supervisor |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Responsibility | Handling tenant inquiries, showing properties, processing lease applications | Overseeing leasing team, ensuring compliance, managing leasing operations |
| Experience Required | 1-3 years in leasing or real estate | 3-5 years with leadership experience in leasing |
| Key Skills | Customer service, negotiation, property knowledge | Team management, strategic planning, conflict resolution |
| Reporting | Reports to Leasing Supervisor or Manager | Reports to Property Manager or Leasing Director |
| Decision-Making Authority | Approves lease applications within set guidelines | Authorizes leasing policies and handles escalated issues |
| Salary Range | Typically $40,000 - $55,000 annually | Typically $55,000 - $75,000 annually |
| Goals | Maximize occupancy, maintain tenant satisfaction | Improve team performance, optimize leasing process |
Key Responsibilities: Leasing Executive vs Leasing Supervisor
A Leasing Executive manages client interactions, property showings, lease documentation, and tenant screening to drive occupancy rates. A Leasing Supervisor oversees the leasing team, enforces company policies, ensures compliance with leasing regulations, and monitors performance metrics to achieve business targets. Both roles require strong communication skills, but the supervisor emphasizes leadership and operational oversight while the executive focuses on direct tenant engagement.
Core Skill Sets Required
Leasing Executives require strong customer service, negotiation, and communication skills to effectively secure tenants and manage lease agreements. Leasing Supervisors need advanced leadership abilities, strategic problem-solving, and team management expertise to oversee leasing staff and ensure operational efficiency. Both roles demand a deep understanding of property leasing regulations, market trends, and CRM software proficiency for optimal performance.
Daily Workflows and Task Management
Leasing Executives primarily handle direct customer interactions, managing property tours, processing applications, and coordinating lease agreements to maximize occupancy rates. Leasing Supervisors focus on overseeing the leasing team's daily workflows, ensuring adherence to compliance standards, and implementing strategies to improve operational efficiency. Both roles require meticulous task management, but Supervisors emphasize performance monitoring and staff development while Executives concentrate on client engagement and transaction execution.
Level of Authority and Decision-Making
Leasing Executives manage daily tenant interactions and lease agreements with limited decision-making authority, primarily following established guidelines. Leasing Supervisors oversee a team of leasing executives, hold higher authority in lease negotiations, and make critical decisions regarding tenant approvals and policy enforcement. The supervisor role involves strategic oversight and escalated problem-solving responsibilities compared to the executive level.
Client Interaction and Relationship Management
Leasing Executives typically handle direct client interaction by guiding prospective tenants through property tours, answering inquiries, and facilitating lease agreements to ensure a smooth onboarding process. Leasing Supervisors oversee the leasing team's client interactions, providing strategic guidance to enhance relationship management and ensuring consistent, high-quality tenant experiences. Both roles prioritize building and maintaining strong client relationships, but Supervisors also focus on team performance and process improvements to optimize tenant satisfaction.
Performance Metrics and KPIs
Leasing Executives primarily focus on individual performance metrics such as lease conversion rates, tenant retention percentages, and the number of property viewings conducted weekly, which directly impact revenue generation. Leasing Supervisors oversee broader KPIs including team leasing targets, average lease cycle time, and overall portfolio occupancy rates, ensuring alignment with organizational goals. Both roles rely on monitoring customer satisfaction scores and lease renewal rates to optimize leasing outcomes and tenant experience.
Leadership and Team Management Differences
Leasing Executives primarily focus on individual client engagement, driving lease negotiations, and achieving personal sales targets, showcasing strong interpersonal skills but limited leadership responsibilities. Leasing Supervisors oversee the entire leasing team, coordinating daily operations, providing mentorship, and implementing strategic processes to improve team performance and tenant satisfaction. Effective leadership in leasing supervision demands advanced conflict resolution abilities and performance management, distinguishing it from the more transactional role of a Leasing Executive.
Career Pathways and Advancement Opportunities
Leasing Executives primarily focus on direct tenant relations, lease negotiations, and client acquisition, serving as the frontline representatives of property management companies. Leasing Supervisors oversee a team of Leasing Executives, ensuring performance targets are met, implementing leasing strategies, and coordinating training and development programs. Career advancement often progresses from Leasing Executive to Leasing Supervisor, with further opportunities in property management, regional leasing roles, or portfolio management, leveraging experience in tenant relations and leasing operations.
Training and Professional Development
Leasing Executives undergo foundational training focused on customer service, property management software, and lease agreement fundamentals to optimize tenant acquisition and retention. Leasing Supervisors receive advanced professional development targeting leadership skills, team management, and conflict resolution to enhance team performance and operational efficiency. Continuous education programs for both roles emphasize market trends, legal compliance, and sales strategies to maintain competitive leasing operations.
Salary Expectations and Compensation Packages
Leasing Executives typically earn a base salary ranging from $40,000 to $55,000 annually, with commissions and bonuses tied to lease agreements enhancing overall compensation. Leasing Supervisors command higher salaries, usually between $55,000 and $75,000, reflecting their managerial responsibilities and experience, often complemented by performance-based incentives and comprehensive benefits packages. Compensation for Leasing Supervisors frequently includes health insurance, retirement plans, and additional perks, positioning their total rewards above those of Leasing Executives.
Leasing Executive vs Leasing Supervisor Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com