Tenant leasing prioritizes securing favorable terms and flexible lease durations that support business growth, ensuring predictable expenses and minimal disruption. Landlord leasing focuses on maximizing rental income and maintaining property value through long-term leases with reliable tenants. Both approaches require careful negotiation to balance financial goals and operational stability in the leasing agreement.
Table of Comparison
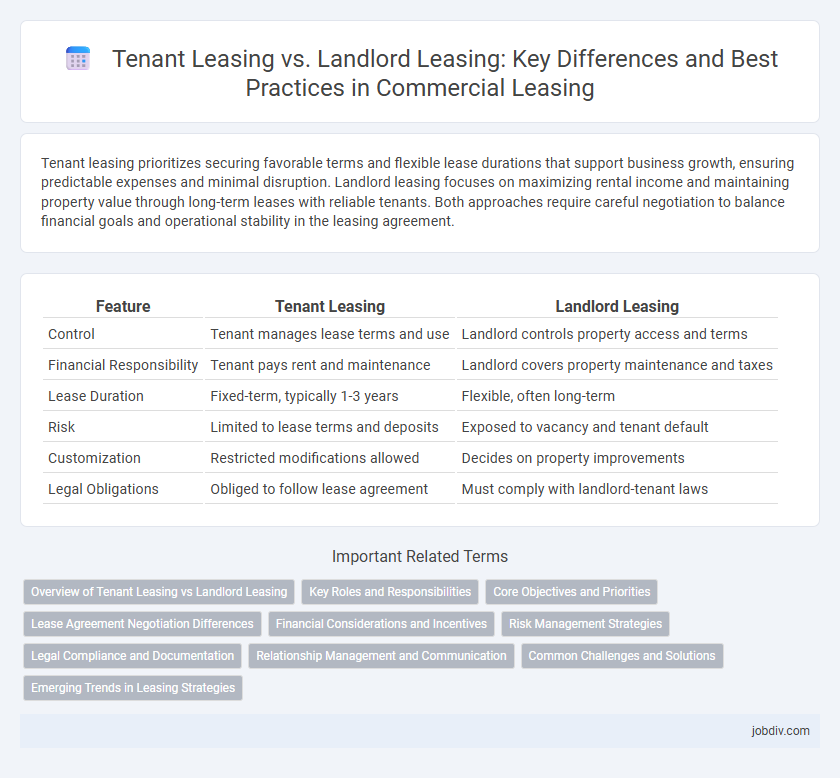
| Feature | Tenant Leasing | Landlord Leasing |
|---|---|---|
| Control | Tenant manages lease terms and use | Landlord controls property access and terms |
| Financial Responsibility | Tenant pays rent and maintenance | Landlord covers property maintenance and taxes |
| Lease Duration | Fixed-term, typically 1-3 years | Flexible, often long-term |
| Risk | Limited to lease terms and deposits | Exposed to vacancy and tenant default |
| Customization | Restricted modifications allowed | Decides on property improvements |
| Legal Obligations | Obliged to follow lease agreement | Must comply with landlord-tenant laws |
Overview of Tenant Leasing vs Landlord Leasing
Tenant leasing involves individuals or businesses securing rental agreements to occupy property, focusing on lease terms that protect their usage rights and allow flexibility. Landlord leasing centers on property owners managing rental agreements, emphasizing income generation, maintenance responsibilities, and enforcing lease compliance. Understanding the distinct priorities of each party enhances negotiation outcomes and lease management efficiency.
Key Roles and Responsibilities
Tenant leasing involves the tenant's role in selecting suitable properties, negotiating lease terms, and ensuring timely rent payments and property maintenance. Landlord leasing encompasses responsibilities such as marketing the property, screening tenants, managing lease agreements, and addressing repairs and legal compliance. Both parties must clearly understand their obligations to maintain a successful leasing relationship.
Core Objectives and Priorities
Tenant leasing focuses on securing flexible terms and favorable rental rates that align with the tenant's business needs and cash flow priorities. Landlord leasing prioritizes maximizing property income, maintaining high occupancy rates, and ensuring long-term lease stability through favorable contract conditions. Both parties aim to balance risk management and value optimization, but tenants emphasize operational flexibility while landlords emphasize asset performance.
Lease Agreement Negotiation Differences
Tenant leasing negotiations typically emphasize securing favorable lease terms such as rent price, maintenance responsibilities, and renewal options to protect tenant interests. Landlord leasing negotiations prioritize maximizing rental income, establishing tenant obligations, and including clauses that reduce vacancy risks and ensure property upkeep. Lease agreement negotiation differences hinge on the balance of risk allocation, with tenants seeking flexibility and cost control while landlords focus on asset protection and consistent revenue.
Financial Considerations and Incentives
Tenant leasing often prioritizes flexible lease terms and lower upfront costs to preserve cash flow, while landlord leasing emphasizes stable rental income and long-term asset value. Financial incentives for tenants may include rent abatements, tenant improvement allowances, and renewal options, whereas landlords might offer graduated rent increases and maintenance responsibilities to optimize property profitability. Understanding these financial considerations helps both parties negotiate favorable lease agreements that balance risk and return.
Risk Management Strategies
Tenant leasing prioritizes risk management through thorough credit assessments and negotiating lease terms that include rent escalation clauses to mitigate financial exposure. Landlord leasing involves implementing risk strategies such as requiring security deposits, insurance mandates, and enforcing strict lease compliance to protect property value and ensure steady income. Both parties benefit from clear communication and detailed contract provisions tailored to allocate risk appropriately and prevent disputes.
Legal Compliance and Documentation
Tenant leasing requires thorough legal compliance with lease agreements, zoning laws, and occupancy standards to protect tenant rights and avoid disputes. Landlord leasing demands meticulous documentation, including lease contracts, disclosures, and renewal terms, ensuring adherence to landlord-tenant laws and mitigating liability risks. Both parties must prioritize accurate record-keeping and timely compliance to facilitate smooth leasing transactions and prevent legal complications.
Relationship Management and Communication
Tenant leasing prioritizes transparent communication and proactive relationship management to ensure lease terms align with tenant needs, fostering long-term satisfaction and retention. Landlord leasing emphasizes regular updates, responsiveness, and conflict resolution to maintain property value and secure steady rental income. Effective mutual communication channels between tenants and landlords mitigate disputes and create a cooperative leasing environment.
Common Challenges and Solutions
Tenant leasing often faces challenges such as unclear lease terms, limited negotiation power, and unexpected maintenance costs, which can be addressed through thorough contract review, legal consultation, and clear communication with landlords. Landlord leasing encounters difficulties including tenant default risks, property damage, and vacancy periods, mitigated by stringent tenant screening, regular property inspections, and flexible lease terms. Both parties benefit from transparent agreements and proactive dispute resolution mechanisms to ensure a smooth leasing process.
Emerging Trends in Leasing Strategies
Tenant leasing strategies increasingly emphasize flexible lease terms and technology integration to enhance occupant experience, driving demand for smart building features and adaptive spaces. Landlord leasing trends focus on offering customizable lease packages, incorporating sustainability initiatives, and leveraging data analytics to optimize asset performance and tenant retention. Both parties prioritize collaboration and innovation to address evolving market demands and economic uncertainties.
Tenant Leasing vs Landlord Leasing Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com