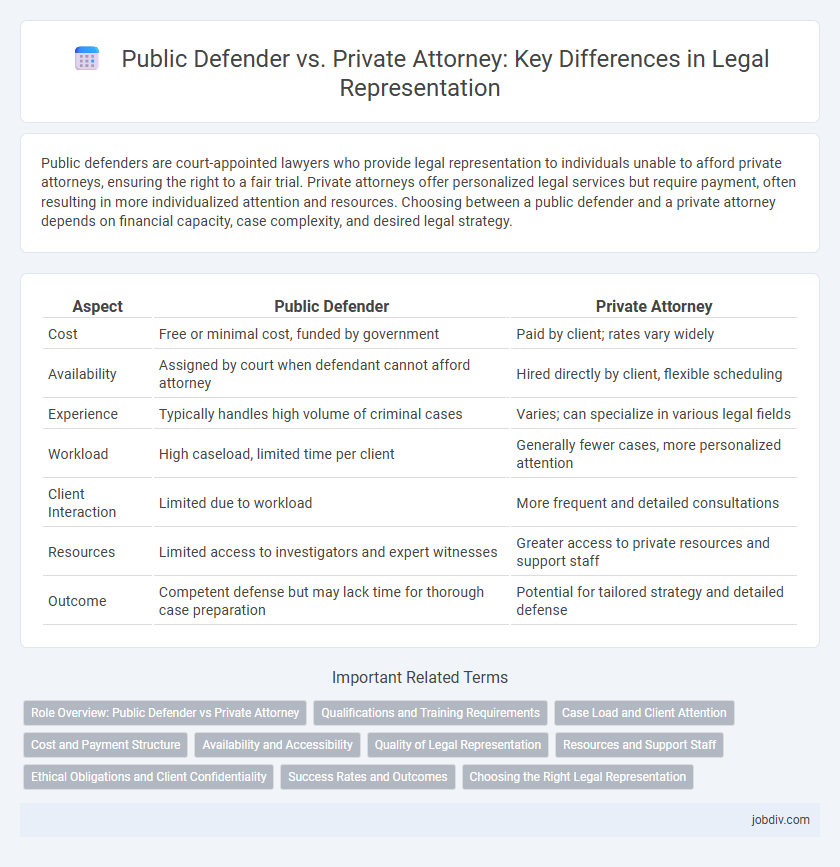
Public defenders are court-appointed lawyers who provide legal representation to individuals unable to afford private attorneys, ensuring the right to a fair trial. Private attorneys offer personalized legal services but require payment, often resulting in more individualized attention and resources. Choosing between a public defender and a private attorney depends on financial capacity, case complexity, and desired legal strategy.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Public Defender | Private Attorney |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Free or minimal cost, funded by government | Paid by client; rates vary widely |
| Availability | Assigned by court when defendant cannot afford attorney | Hired directly by client, flexible scheduling |
| Experience | Typically handles high volume of criminal cases | Varies; can specialize in various legal fields |
| Workload | High caseload, limited time per client | Generally fewer cases, more personalized attention |
| Client Interaction | Limited due to workload | More frequent and detailed consultations |
| Resources | Limited access to investigators and expert witnesses | Greater access to private resources and support staff |
| Outcome | Competent defense but may lack time for thorough case preparation | Potential for tailored strategy and detailed defense |
Role Overview: Public Defender vs Private Attorney
Public defenders are government-employed attorneys assigned to represent individuals who cannot afford private counsel, ensuring the constitutional right to legal defense in criminal cases. Private attorneys operate independently or within law firms, offering personalized legal services to clients who hire them directly, often providing broader case options beyond criminal defense. Both serve critical roles in the justice system, with public defenders managing high caseloads and limited resources, while private attorneys may provide more extensive client interaction and specialized expertise.
Qualifications and Training Requirements
Public defenders typically possess similar qualifications and training as private attorneys, including completing law school and passing the state bar exam. However, public defenders often undergo specialized training in criminal defense and trial procedures to handle high caseloads efficiently. Private attorneys may have more diverse practice areas with varying degrees of trial experience based on client needs and specialization.
Case Load and Client Attention
Public defenders often manage a significantly higher caseload compared to private attorneys, averaging hundreds of cases annually, which can limit the amount of individual client attention. Private attorneys typically handle fewer cases, allowing for more personalized time and tailored legal strategies for each client. This disparity in caseload directly impacts the quality and depth of legal representation provided in criminal defense.
Cost and Payment Structure
Public defenders provide legal representation at no cost to defendants who cannot afford an attorney, funded by government resources. Private attorneys charge clients based on various payment structures, including hourly rates, flat fees, or contingency fees, often resulting in significantly higher expenses than public defenders. Clients opting for private counsel should consider additional costs such as retainers and court fees, which are typically not covered by public defenders.
Availability and Accessibility
Public defenders are government-appointed lawyers primarily available to defendants who cannot afford private counsel, ensuring access to legal representation regardless of financial status. Private attorneys offer greater availability in terms of client choice and scheduling flexibility but often come with significant costs that limit accessibility for low-income individuals. The disparity in availability and accessibility highlights the critical role public defenders play in upholding the right to a fair trial under the Sixth Amendment.
Quality of Legal Representation
Public defenders often handle higher caseloads, which can limit the amount of time and resources dedicated to each case, potentially affecting the quality of legal representation. Private attorneys typically have more time to invest in case preparation, allowing for personalized strategies and comprehensive defense. Studies indicate that defendants with private attorneys frequently receive more favorable outcomes, highlighting discrepancies in resource availability and individualized attention.
Resources and Support Staff
Public defenders operate within government-funded agencies that often face budget constraints, resulting in limited access to support staff and investigative resources compared to private attorneys. Private attorneys typically have greater financial flexibility to hire paralegals, private investigators, and expert witnesses, enhancing their ability to build comprehensive defenses. The disparity in available resources and support staff can significantly impact case preparation and client representation quality in criminal defense.
Ethical Obligations and Client Confidentiality
Public defenders and private attorneys share strict ethical obligations to maintain client confidentiality, ensuring all communications remain protected under attorney-client privilege. Public defenders often handle higher caseloads, which requires diligent management to uphold confidentiality standards without compromising client trust. Private attorneys typically have more resources to implement advanced security measures for safeguarding sensitive client information.
Success Rates and Outcomes
Public defenders typically have lower success rates compared to private attorneys due to high caseloads and limited resources affecting case preparation. Private attorneys, benefiting from more time and specialized expertise, often achieve better outcomes such as reduced sentences or case dismissals. Statistical studies show private attorneys secure favorable verdicts in criminal defense cases approximately 20-30% more frequently than public defenders.
Choosing the Right Legal Representation
Selecting the right legal representation depends on factors such as case complexity, financial resources, and desired attorney availability. Public defenders provide cost-free services and handle high caseloads, often limiting personalized attention, while private attorneys offer dedicated focus with potential for specialized expertise at a higher cost. Evaluating these considerations ensures an informed choice between public defenders and private attorneys for effective legal defense.
Public Defender vs Private Attorney Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com