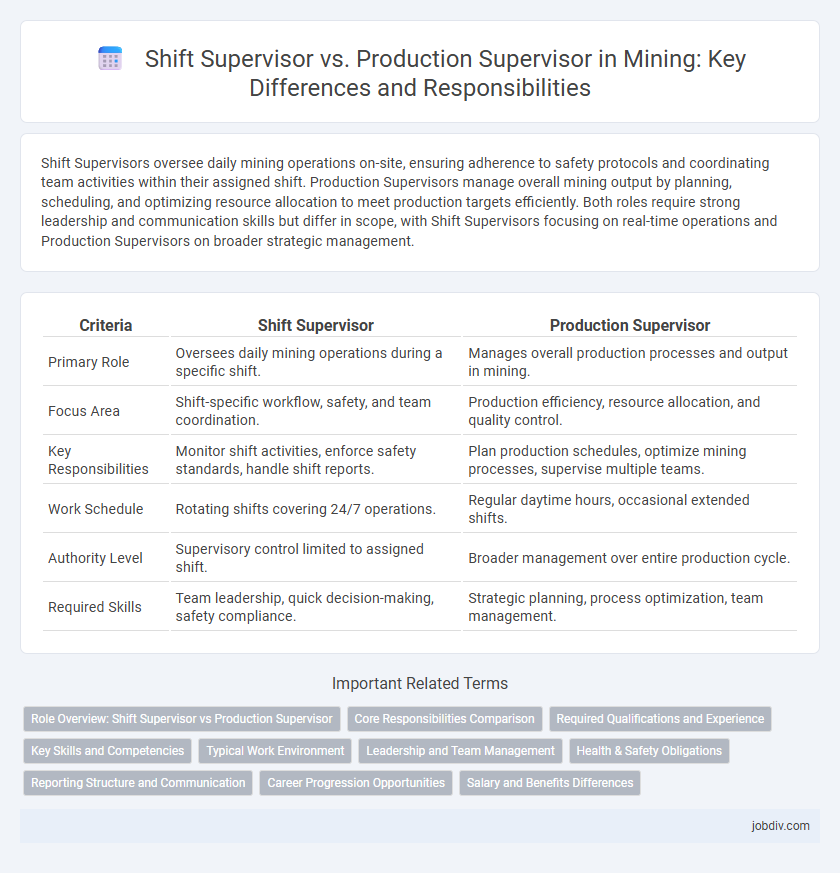
Shift Supervisors oversee daily mining operations on-site, ensuring adherence to safety protocols and coordinating team activities within their assigned shift. Production Supervisors manage overall mining output by planning, scheduling, and optimizing resource allocation to meet production targets efficiently. Both roles require strong leadership and communication skills but differ in scope, with Shift Supervisors focusing on real-time operations and Production Supervisors on broader strategic management.
Table of Comparison
| Criteria | Shift Supervisor | Production Supervisor |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Oversees daily mining operations during a specific shift. | Manages overall production processes and output in mining. |
| Focus Area | Shift-specific workflow, safety, and team coordination. | Production efficiency, resource allocation, and quality control. |
| Key Responsibilities | Monitor shift activities, enforce safety standards, handle shift reports. | Plan production schedules, optimize mining processes, supervise multiple teams. |
| Work Schedule | Rotating shifts covering 24/7 operations. | Regular daytime hours, occasional extended shifts. |
| Authority Level | Supervisory control limited to assigned shift. | Broader management over entire production cycle. |
| Required Skills | Team leadership, quick decision-making, safety compliance. | Strategic planning, process optimization, team management. |
Role Overview: Shift Supervisor vs Production Supervisor
The Shift Supervisor oversees mining operations during specific shifts, ensuring safety protocols and daily production targets are met, while managing real-time workforce coordination and equipment functionality. In contrast, the Production Supervisor holds broader responsibility for overall production efficiency, planning, and long-term resource allocation across multiple shifts. Both roles require expertise in operational management, but the Shift Supervisor concentrates on immediate operational control, whereas the Production Supervisor focuses on strategic production outcomes.
Core Responsibilities Comparison
Shift Supervisors in mining oversee daily operational activities, worker safety, and equipment functionality during designated shifts to ensure continuous production flow. Production Supervisors focus on planning, coordinating, and optimizing overall mining production processes, resource allocation, and meeting production targets. Both roles require strong leadership, but Shift Supervisors emphasize real-time problem-solving on-site, while Production Supervisors manage broader production efficiency and strategic planning.
Required Qualifications and Experience
Shift Supervisors in mining typically require strong technical knowledge of operational processes, often demonstrated by several years of hands-on experience in mining or heavy machinery operation, alongside relevant certifications in safety and equipment handling. Production Supervisors demand extensive experience in overseeing overall production workflows, with qualifications often including a degree in mining engineering or industrial management combined with proven leadership skills and familiarity with compliance standards. Both roles emphasize safety management, yet Production Supervisors generally require deeper expertise in strategic planning and resource allocation to optimize mining productivity.
Key Skills and Competencies
Shift Supervisors in mining prioritize real-time operational oversight, emphasizing skills in team coordination, safety compliance, and quick decision-making under pressure. Production Supervisors focus on process optimization, resource management, and productivity analysis, requiring competencies in workflow planning, quality control, and reporting. Both roles demand strong leadership, communication abilities, and technical knowledge of mining equipment and procedures.
Typical Work Environment
Shift Supervisors in mining typically work onsite in operational areas such as underground tunnels or open pits, managing real-time production activities and ensuring safety compliance during their shifts. Production Supervisors often operate both onsite and in control rooms, overseeing broader production processes and coordinating between different departments to optimize output. Both roles require adaptability to variable environmental conditions, including exposure to dust, noise, and heavy machinery.
Leadership and Team Management
Shift Supervisors in mining oversee operational activities during specific shifts, ensuring workforce productivity and safety compliance on-site, while Production Supervisors manage overall production processes, coordinating multiple shifts and aligning output with company targets. Leadership for Shift Supervisors involves real-time decision-making and conflict resolution among frontline workers, whereas Production Supervisors emphasize strategic planning, resource allocation, and cross-department communication. Effective team management by Shift Supervisors centers on direct supervision and immediate performance feedback; Production Supervisors prioritize workforce development and long-term operational efficiency.
Health & Safety Obligations
Shift Supervisors in mining are directly responsible for enforcing health and safety protocols during their assigned shift, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards and immediate hazard mitigation. Production Supervisors oversee broader operational processes, integrating health and safety management with production goals to maintain a secure work environment throughout the mining site. Both roles require rigorous risk assessment, incident reporting, and the promotion of safety culture to minimize workplace accidents and occupational health risks.
Reporting Structure and Communication
In mining operations, the Shift Supervisor reports directly to the Production Supervisor, ensuring alignment of daily activities with overall production goals. Communication flows from the Shift Supervisor to frontline workers, facilitating real-time issue resolution and workflow adjustments. This reporting structure enhances operational efficiency by maintaining clear accountability and streamlined information exchange.
Career Progression Opportunities
Shift Supervisors in mining typically focus on overseeing day-to-day operations on-site, gaining hands-on experience with equipment and workforce management, which builds a strong operational foundation. Production Supervisors hold broader responsibilities that include strategic planning, resource allocation, and process optimization, positioning them for senior management roles. Career progression often sees Shift Supervisors advancing to Production Supervisor roles as they develop leadership skills and technical expertise within the mining sector.
Salary and Benefits Differences
Shift Supervisors in mining typically receive higher hourly wages compared to Production Supervisors due to the demanding nature of overseeing operations during non-standard hours and ensuring safety compliance on site. Production Supervisors may earn a slightly lower base salary but often benefit from superior health insurance plans, retirement contributions, and performance bonuses tied to overall production efficiency. Both roles offer distinct compensations aligned with their responsibilities, but Shift Supervisors generally command premium pay for shift differentials and hazard-related allowances.
Shift Supervisor vs Production Supervisor Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com