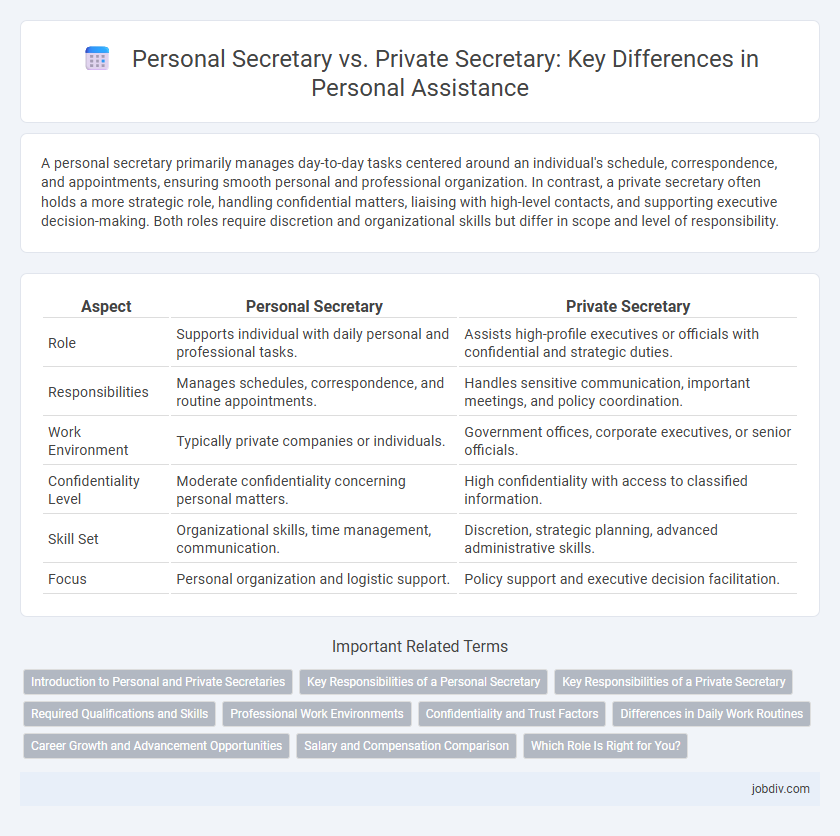
A personal secretary primarily manages day-to-day tasks centered around an individual's schedule, correspondence, and appointments, ensuring smooth personal and professional organization. In contrast, a private secretary often holds a more strategic role, handling confidential matters, liaising with high-level contacts, and supporting executive decision-making. Both roles require discretion and organizational skills but differ in scope and level of responsibility.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Personal Secretary | Private Secretary |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Supports individual with daily personal and professional tasks. | Assists high-profile executives or officials with confidential and strategic duties. |
| Responsibilities | Manages schedules, correspondence, and routine appointments. | Handles sensitive communication, important meetings, and policy coordination. |
| Work Environment | Typically private companies or individuals. | Government offices, corporate executives, or senior officials. |
| Confidentiality Level | Moderate confidentiality concerning personal matters. | High confidentiality with access to classified information. |
| Skill Set | Organizational skills, time management, communication. | Discretion, strategic planning, advanced administrative skills. |
| Focus | Personal organization and logistic support. | Policy support and executive decision facilitation. |
Introduction to Personal and Private Secretaries
Personal secretaries manage an individual's daily administrative tasks, including scheduling appointments, handling correspondence, and organizing meetings to enhance personal efficiency. Private secretaries typically support high-level executives or officials by overseeing confidential information, coordinating complex schedules, and acting as a liaison between the principal and external parties. Both roles require strong organizational skills, discretion, and the ability to prioritize tasks effectively within a personal or professional context.
Key Responsibilities of a Personal Secretary
A Personal Secretary primarily manages daily scheduling, correspondence, and communication for an individual, ensuring efficient time management and organization. They handle confidential information, coordinate meetings, and prepare documents tailored to the employer's personal and professional needs. Expertise in administrative tasks, attention to detail, and discretion are essential skills for a Personal Secretary's key responsibilities.
Key Responsibilities of a Private Secretary
A Private Secretary manages high-level scheduling, confidential communications, and crucial correspondence for executives or government officials, ensuring seamless daily operations. They coordinate meetings, prepare briefing materials, and act as a gatekeeper to prioritize tasks and maintain organizational efficiency. Their role requires discretion, excellent organizational skills, and the ability to handle sensitive information with utmost professionalism.
Required Qualifications and Skills
A Personal Secretary requires strong organizational skills, multitasking ability, and proficiency in office software to manage schedules and correspondence efficiently. A Private Secretary demands advanced communication skills, discretion, and often specialized knowledge in legal or executive support to handle confidential matters and high-level coordination. Both roles necessitate attention to detail and time management, but a Private Secretary typically needs higher qualifications, including experience with complex administrative functions.
Professional Work Environments
A personal secretary typically manages the daily schedules, correspondence, and administrative tasks for an individual in various professional work environments, emphasizing personalized support. In contrast, a private secretary often operates within more formal settings, handling confidential documents, coordinating executive communications, and liaising between top-level management and other departments. Both roles require strong organizational skills, but private secretaries tend to engage in higher-level strategic duties within corporate or governmental institutions.
Confidentiality and Trust Factors
A Personal Secretary manages everyday tasks with a focus on general organizational support, while a Private Secretary handles high-level confidential matters requiring enhanced trust and discretion. Confidentiality is paramount for Private Secretaries, as they often access sensitive information and influence critical decisions within executive operations. Trust factors emphasize the Private Secretary's close professional relationship with senior leaders, ensuring confidentiality and reliability beyond routine administrative duties.
Differences in Daily Work Routines
A Personal Secretary manages the daily schedule, handles correspondence, and coordinates personal tasks for an individual, often blending both professional and personal responsibilities. A Private Secretary focuses primarily on organizing official engagements, preparing documents, and managing communications within a formal business or governmental setting. The Personal Secretary's routine is more flexible and personalized, while the Private Secretary's work follows structured protocols and formal deadlines.
Career Growth and Advancement Opportunities
A Personal Secretary primarily supports an individual by managing schedules, correspondence, and daily tasks, offering limited exposure to higher-level management functions. A Private Secretary often engages directly with senior executives or government officials, coordinating complex projects and strategic communications, which provides broader opportunities for career growth and advancement. Mastery of organizational, communication, and decision-making skills in the role of a Private Secretary typically leads to faster promotion potential and access to leadership roles.
Salary and Compensation Comparison
Personal Secretaries typically earn an average salary ranging from $40,000 to $60,000 per year, influenced by experience and industry. Private Secretaries often receive higher compensation, with salaries between $60,000 and $85,000 annually, reflecting their more specialized responsibilities. Benefits packages for Private Secretaries frequently include bonuses and incentives tied to executive performance, enhancing total compensation.
Which Role Is Right for You?
Choosing between a Personal Secretary and a Private Secretary depends on your specific needs and work environment. A Personal Secretary primarily manages personal tasks, schedules, and correspondence, ideal for individuals seeking help with daily life organization. A Private Secretary, often employed in corporate or government settings, handles confidential information, executive communications, and complex administrative duties, suited for professionals requiring high-level support and discretion.
Personal Secretary vs Private Secretary Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com