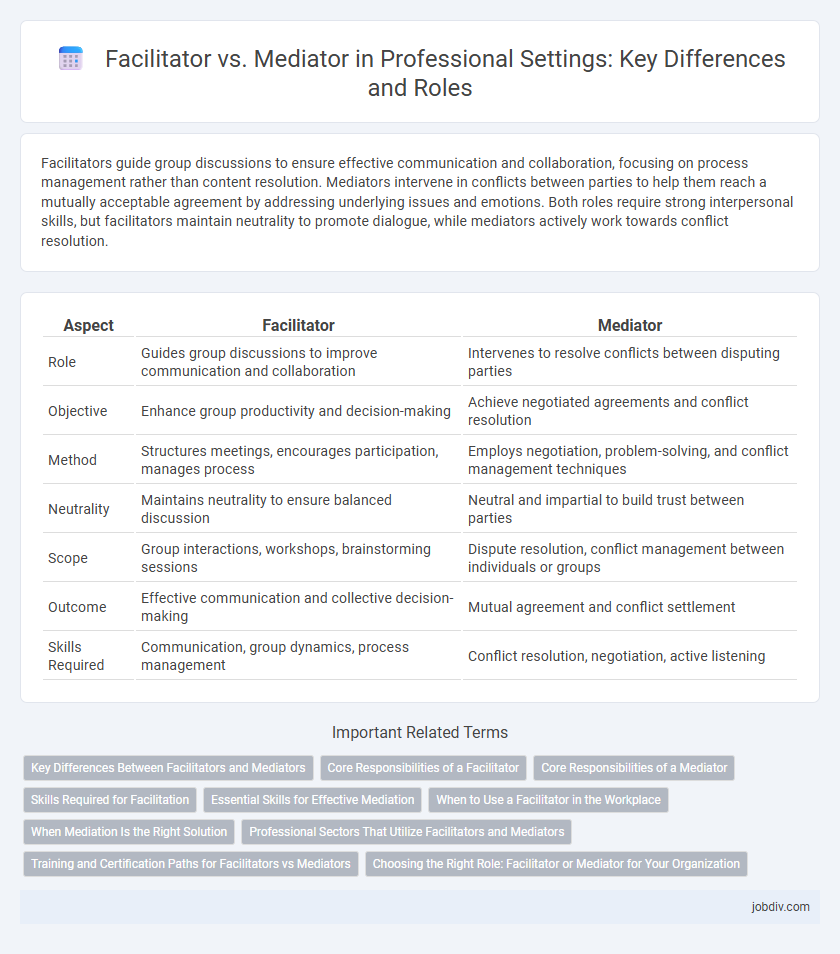
Facilitators guide group discussions to ensure effective communication and collaboration, focusing on process management rather than content resolution. Mediators intervene in conflicts between parties to help them reach a mutually acceptable agreement by addressing underlying issues and emotions. Both roles require strong interpersonal skills, but facilitators maintain neutrality to promote dialogue, while mediators actively work towards conflict resolution.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Facilitator | Mediator |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Guides group discussions to improve communication and collaboration | Intervenes to resolve conflicts between disputing parties |
| Objective | Enhance group productivity and decision-making | Achieve negotiated agreements and conflict resolution |
| Method | Structures meetings, encourages participation, manages process | Employs negotiation, problem-solving, and conflict management techniques |
| Neutrality | Maintains neutrality to ensure balanced discussion | Neutral and impartial to build trust between parties |
| Scope | Group interactions, workshops, brainstorming sessions | Dispute resolution, conflict management between individuals or groups |
| Outcome | Effective communication and collective decision-making | Mutual agreement and conflict settlement |
| Skills Required | Communication, group dynamics, process management | Conflict resolution, negotiation, active listening |
Key Differences Between Facilitators and Mediators
Facilitators guide group discussions to enhance collaboration and decision-making without imposing solutions, focusing on process management and communication flow. Mediators intervene in conflicts to negotiate agreements between disputing parties, often involving neutrality and conflict resolution techniques. While facilitators emphasize group dynamics and consensus-building, mediators prioritize resolving disagreements and achieving mutually acceptable outcomes.
Core Responsibilities of a Facilitator
A facilitator's core responsibilities include guiding group discussions to ensure balanced participation, maintaining a neutral stance to promote open communication, and structuring meetings to achieve clear objectives efficiently. Facilitators manage the process and dynamics within teams, helping to resolve conflicts by encouraging collaborative problem-solving rather than imposing solutions. Their role is distinct from mediators, whose primary focus is to intervene in disputes and negotiate resolutions between conflicting parties.
Core Responsibilities of a Mediator
A mediator's core responsibilities involve facilitating communication between disputing parties, promoting mutual understanding, and guiding negotiations toward a voluntary agreement. They remain neutral, create a confidential environment, and help identify underlying interests to find common ground. Unlike facilitators who focus on process management, mediators actively work to resolve conflicts and settle disputes through dialogue and compromise.
Skills Required for Facilitation
Effective facilitation requires skills such as active listening, clear communication, conflict management, and the ability to foster collaboration among diverse groups. Facilitators must also possess strong organizational abilities to guide discussions, keep meetings on track, and ensure balanced participation from all stakeholders. Unlike mediators, facilitators focus on process management rather than resolving disputes, emphasizing consensus-building techniques and group dynamics awareness.
Essential Skills for Effective Mediation
Effective mediation requires strong active listening, impartiality, and emotional intelligence to understand and address the underlying interests of all parties. Facilitators emphasize group communication and consensus-building skills, while mediators prioritize conflict resolution techniques and neutrality to guide parties toward mutually agreeable solutions. Mastery of negotiation strategies and the ability to manage power dynamics are essential skills distinguishing mediators in professional dispute resolution settings.
When to Use a Facilitator in the Workplace
A facilitator is ideal in the workplace when teams require structured guidance to improve collaboration, enhance communication, and achieve consensus on complex projects or meetings. Use a facilitator when the group needs to generate ideas, resolve process bottlenecks, or develop strategies without the presence of conflict. They play a crucial role in managing group dynamics, ensuring balanced participation, and maintaining focus on goals for effective decision-making.
When Mediation Is the Right Solution
Mediation is the right solution when parties seek a confidential, non-binding process to resolve disputes collaboratively, emphasizing mutual understanding and tailored agreements. Unlike facilitators, mediators possess specialized training in conflict resolution techniques that guide disputants toward consensus without imposing decisions. This approach is particularly effective in legal, workplace, and community conflicts where preserving relationships and achieving amicable settlements are priorities.
Professional Sectors That Utilize Facilitators and Mediators
Facilitators are extensively utilized in corporate sectors such as project management, strategic planning, and organizational development to guide group discussions and enhance collaborative decision-making. Mediators are predominantly employed in legal, healthcare, and labor relations sectors to resolve conflicts and negotiate agreements between parties. Both professionals play critical roles in education and community development by fostering communication and understanding among diverse stakeholders.
Training and Certification Paths for Facilitators vs Mediators
Facilitator training programs emphasize skills in group dynamics, consensus-building, and workshop design, often culminating in certifications like the International Association of Facilitators (IAF) Certified Professional Facilitator. Mediator certification paths focus on conflict resolution techniques, negotiation strategies, and legal frameworks, with widely recognized credentials including the Mediation Certification from the Academy of Conflict Resolution. Both roles require ongoing professional development, but facilitators typically pursue training tailored to collaboration and process management, whereas mediators engage deeply with dispute resolution methodologies and ethical standards.
Choosing the Right Role: Facilitator or Mediator for Your Organization
Selecting the appropriate role between facilitator and mediator hinges on the organization's needs for either guiding group discussions or resolving conflicts. Facilitators optimize collaborative processes by encouraging open communication and consensus building, while mediators intervene to address disputes and restore relationships. Assessing the organizational context, conflict intensity, and desired outcomes ensures the right professional approach aligns with strategic goals.
Facilitator vs Mediator Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com