Automotive repair typically involves maintenance and troubleshooting of gasoline-powered vehicles, covering systems like the engine, brakes, and electrical components. Diesel repair specializes in diesel engine vehicles, focusing on fuel injection systems, turbochargers, and heavy-duty engine diagnostics. Understanding the distinctions ensures proper servicing tailored to the vehicle's specific engine type and performance needs.
Table of Comparison
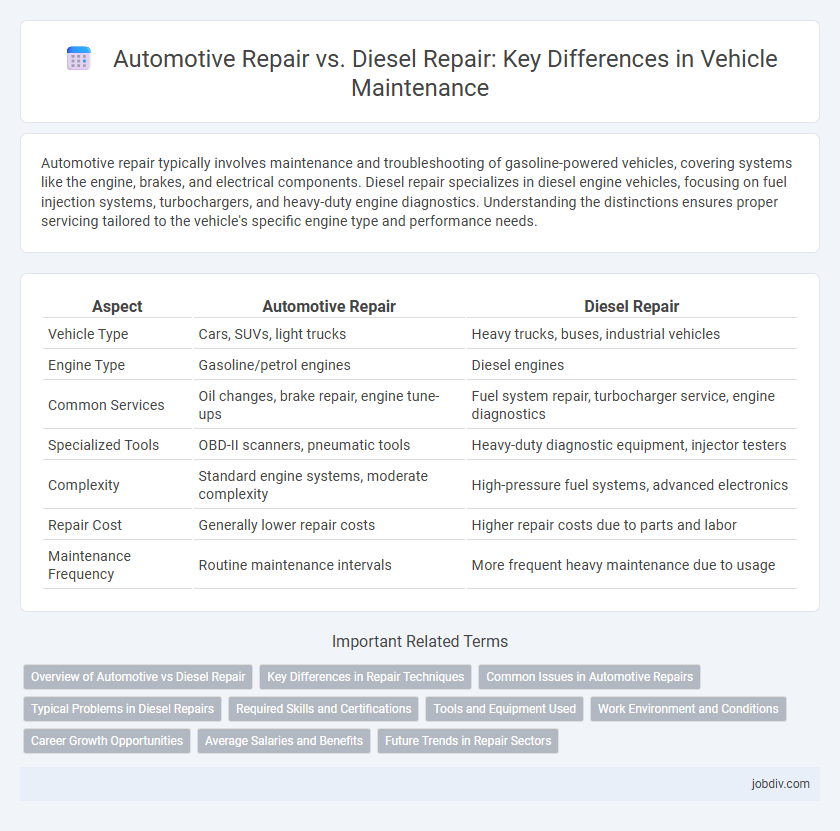
| Aspect | Automotive Repair | Diesel Repair |
|---|---|---|
| Vehicle Type | Cars, SUVs, light trucks | Heavy trucks, buses, industrial vehicles |
| Engine Type | Gasoline/petrol engines | Diesel engines |
| Common Services | Oil changes, brake repair, engine tune-ups | Fuel system repair, turbocharger service, engine diagnostics |
| Specialized Tools | OBD-II scanners, pneumatic tools | Heavy-duty diagnostic equipment, injector testers |
| Complexity | Standard engine systems, moderate complexity | High-pressure fuel systems, advanced electronics |
| Repair Cost | Generally lower repair costs | Higher repair costs due to parts and labor |
| Maintenance Frequency | Routine maintenance intervals | More frequent heavy maintenance due to usage |
Overview of Automotive vs Diesel Repair
Automotive repair primarily involves maintenance and fixing of gasoline-powered vehicles, focusing on components like spark plugs, fuel injectors, and emission systems. Diesel repair specializes in servicing diesel engines found in trucks and heavy machinery, dealing with fuel injection systems, glow plugs, and turbochargers. Expertise in diesel repair requires knowledge of high-compression engines and diesel-specific diagnostic tools, distinguishing it from general automotive repair.
Key Differences in Repair Techniques
Automotive repair primarily involves gasoline engines, emphasizing spark plug maintenance, catalytic converter servicing, and electronic fuel injection systems, whereas diesel repair focuses on high-pressure fuel injection, turbocharging components, and glow plug diagnostics. Diesel engines require specialized tools and techniques to address compression ignition issues, fuel injector calibration, and particulate filter regeneration. Understanding these distinctions ensures accurate diagnostics, efficient repairs, and optimal engine performance tailored to each vehicle type.
Common Issues in Automotive Repairs
Common issues in automotive repairs typically include engine malfunctions, brake system failures, and transmission problems. Regular maintenance often uncovers worn-out spark plugs, faulty sensors, and fluid leaks, which can significantly affect vehicle performance. Diesel repair, while sharing some similarities, uniquely addresses challenges like fuel injector clogs, turbocharger failures, and emission control system faults.
Typical Problems in Diesel Repairs
Typical problems in diesel repairs often involve issues with fuel injection systems, turbochargers, and diesel particulate filters due to the engine's complexity and higher compression ratios. Diesel engines are prone to injector failure, clogged fuel filters, and glow plug malfunctions, which require specialized diagnostic equipment and expertise. Addressing these problems promptly enhances engine performance, reduces emissions, and prolongs the vehicle's lifespan, differentiating diesel repair from general automotive repair.
Required Skills and Certifications
Automotive repair technicians typically require certifications such as the ASE Automotive Service Excellence, with skills centered around gasoline engines, electrical systems, and computerized diagnostics. Diesel repair specialists must possess certifications like the ASE Medium/Heavy Truck or EPA 609, emphasizing expertise in diesel engines, emission systems, and heavy-duty vehicle maintenance. Both fields demand strong mechanical aptitude and problem-solving abilities but differ significantly in engine technology and regulatory compliance requirements.
Tools and Equipment Used
Automotive repair primarily involves tools such as diagnostic scanners, impact wrenches, and hydraulic lifts designed for gasoline-powered vehicles, while diesel repair requires heavy-duty equipment like high-pressure fuel injection tools, turbocharger analyzers, and diesel compression testers. Diesel engines often necessitate specialized calibration equipment and particulate filter cleaning machines to address their complex emission systems and robust components. Both fields demand precision instruments, but diesel repair emphasizes rugged, industrial-grade tools to handle higher torque and engine durability.
Work Environment and Conditions
Automotive repair shops typically feature well-lit, temperature-controlled environments optimized for a variety of gas and electric vehicles, while diesel repair facilities often have larger, more industrial spaces to accommodate heavy-duty trucks and machinery. Technicians in diesel repair work with heavier equipment and may face more exposure to dirt, grease, and outdoor elements due to the size and nature of diesel engines. Both environments demand strict adherence to safety protocols, but diesel repair often requires handling higher torque tools and more robust personal protective equipment due to the complexity and scale of repairs.
Career Growth Opportunities
Automotive repair offers a broad range of career growth opportunities due to the increasing complexity of modern vehicles and the demand for skilled technicians in electric and hybrid systems. Diesel repair careers tend to specialize in heavy machinery, commercial trucks, and industrial equipment, with growth driven by logistics, construction, and agriculture industries. Both fields provide paths to advanced certifications and leadership roles, but diesel repair often commands higher pay due to specialized skill requirements.
Average Salaries and Benefits
Automotive repair technicians earn an average salary ranging from $35,000 to $50,000 annually, with benefits often including health insurance, retirement plans, and paid time off. Diesel repair specialists typically command higher wages, averaging between $45,000 and $65,000 per year, due to the specialized skills required for heavy-duty engines, coupled with similar comprehensive benefits packages. The salary discrepancy reflects the complexity and demand for diesel repair expertise in commercial and industrial sectors.
Future Trends in Repair Sectors
The future of automotive repair is increasingly influenced by advancements in electric vehicle technology and autonomous systems, requiring technicians to acquire specialized skills in software diagnostics and battery management. Diesel repair is shifting towards more stringent emissions standards and the integration of hybrid diesel-electric powertrains, necessitating expertise in advanced filtration systems and electronic controls. Both sectors are embracing digital tools like augmented reality for training and remote diagnostics to improve efficiency and precision in repairs.
Automotive Repair vs Diesel Repair Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com