An Electronics Repair Technician specializes in diagnosing and fixing electronic devices such as computers, phones, and circuit boards, ensuring precise component-level repairs. An Electrical Maintenance Technician focuses on maintaining and repairing electrical systems and machinery, emphasizing system functionality and safety in industrial settings. Both roles require strong technical skills, but the Electronics Repair Technician is more device-oriented, while the Electrical Maintenance Technician handles broader electrical infrastructure.
Table of Comparison
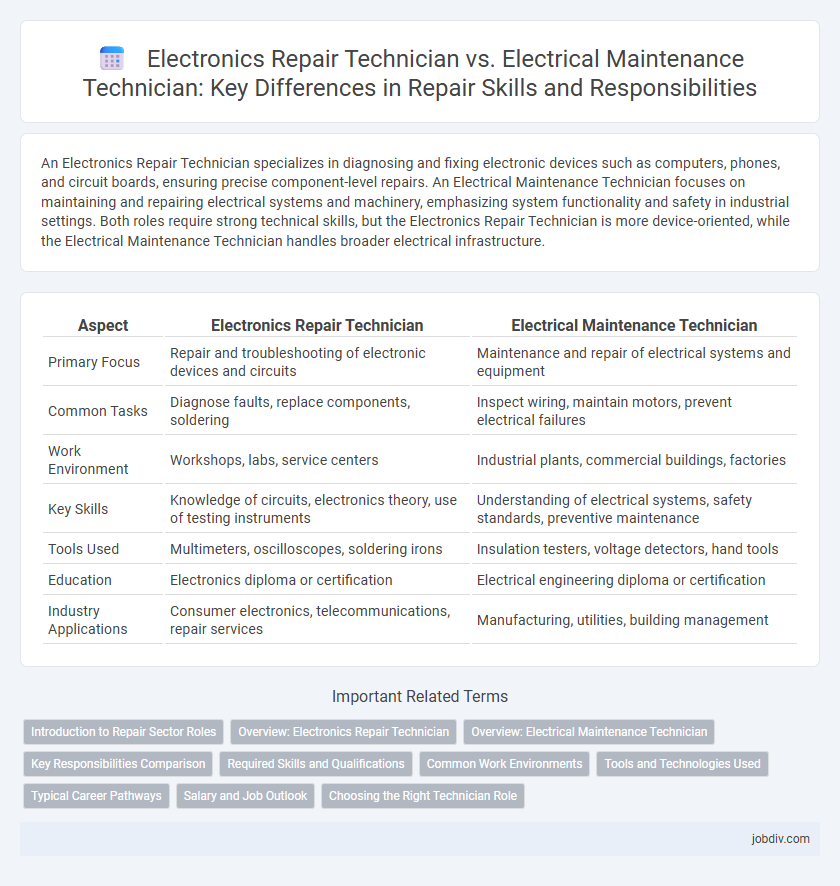
| Aspect | Electronics Repair Technician | Electrical Maintenance Technician |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Repair and troubleshooting of electronic devices and circuits | Maintenance and repair of electrical systems and equipment |
| Common Tasks | Diagnose faults, replace components, soldering | Inspect wiring, maintain motors, prevent electrical failures |
| Work Environment | Workshops, labs, service centers | Industrial plants, commercial buildings, factories |
| Key Skills | Knowledge of circuits, electronics theory, use of testing instruments | Understanding of electrical systems, safety standards, preventive maintenance |
| Tools Used | Multimeters, oscilloscopes, soldering irons | Insulation testers, voltage detectors, hand tools |
| Education | Electronics diploma or certification | Electrical engineering diploma or certification |
| Industry Applications | Consumer electronics, telecommunications, repair services | Manufacturing, utilities, building management |
Introduction to Repair Sector Roles
Electronics Repair Technicians specialize in diagnosing and fixing complex electronic systems, such as circuit boards, audio equipment, and digital devices, requiring in-depth knowledge of microelectronics and signal processing. Electrical Maintenance Technicians focus on maintaining and repairing electrical equipment and machinery in industrial settings, ensuring system reliability, safety compliance, and optimal performance. Both roles play crucial parts in the repair sector by addressing different technical challenges within electronics and electrical engineering domains.
Overview: Electronics Repair Technician
Electronics Repair Technicians specialize in diagnosing, troubleshooting, and repairing complex electronic devices such as computers, communication equipment, and medical instruments. Their expertise includes working with circuit boards, microprocessors, and digital components, ensuring precise functionality and system reliability. Proficiency in soldering, schematic reading, and using diagnostic tools distinguishes their role in maintaining and restoring advanced electronic systems.
Overview: Electrical Maintenance Technician
Electrical Maintenance Technicians specialize in diagnosing, repairing, and maintaining electrical systems and equipment in industrial and commercial settings. Their expertise includes troubleshooting wiring, motors, control panels, and automated machinery to ensure operational efficiency and safety compliance. Proficiency in interpreting electrical schematics, performing preventive maintenance, and adhering to industry standards is essential for minimizing downtime and extending equipment lifespan.
Key Responsibilities Comparison
Electronics Repair Technicians specialize in diagnosing and fixing electronic devices, circuit boards, and digital systems, ensuring optimal performance of consumer electronics, medical equipment, and communication devices. Electrical Maintenance Technicians focus on maintaining and troubleshooting electrical systems such as wiring, motors, transformers, and industrial machinery to prevent downtime and ensure safety compliance. The key difference lies in Electronics Repair Technicians handling intricate electronic components, while Electrical Maintenance Technicians manage broader electrical infrastructure and equipment upkeep.
Required Skills and Qualifications
Electronics Repair Technicians require proficiency in diagnosing and fixing circuit boards, soldering, and understanding microprocessors, usually needing an associate degree in electronics or equivalent certification. Electrical Maintenance Technicians must possess strong skills in troubleshooting electrical systems, preventive maintenance, and operating high-voltage equipment, often requiring a technical diploma or apprenticeship experience. Both roles demand knowledge of safety regulations and the ability to read technical manuals, but Electronics Repair Technicians emphasize component-level repair while Electrical Maintenance Technicians focus on system-wide electrical functionality.
Common Work Environments
Electronics Repair Technicians commonly work in manufacturing plants, electronics repair shops, and laboratories, handling delicate circuit boards and consumer electronic devices. Electrical Maintenance Technicians are frequently found in industrial facilities, power plants, and commercial buildings, focusing on maintaining and troubleshooting electrical systems and machinery. Both roles require adherence to safety protocols, but the environments vary in equipment complexity and exposure to heavy machinery.
Tools and Technologies Used
Electronics Repair Technicians primarily use oscilloscopes, multimeters, soldering irons, and diagnostic software to troubleshoot and repair circuit boards, microcontrollers, and semiconductor devices. Electrical Maintenance Technicians rely on tools like insulation testers, clamp meters, thermal imaging cameras, and programmable logic controllers (PLCs) for maintaining and repairing electrical systems and industrial machinery. Both technicians require proficiency in interpreting technical schematics, but Electronics Repair Technicians focus more on microelectronic components, while Electrical Maintenance Technicians specialize in high-voltage systems and electrical infrastructure.
Typical Career Pathways
Electronics Repair Technicians often begin their careers with associate degrees or technical certifications in electronics, progressing from entry-level diagnostic roles to specialized positions in device troubleshooting and system upgrades. Electrical Maintenance Technicians typically start through apprenticeships or vocational training, advancing from junior maintenance roles to senior positions responsible for the upkeep and repair of industrial electrical systems. Both career pathways emphasize continuous skill development in emerging technologies like automation, programmable logic controllers (PLCs), and digital control systems.
Salary and Job Outlook
Electronics Repair Technicians typically earn an average salary ranging from $40,000 to $60,000 annually, with strong job growth driven by increasing consumer electronics demand. Electrical Maintenance Technicians command slightly higher salaries, averaging $50,000 to $70,000 per year, benefiting from steady employment opportunities in industrial and manufacturing sectors. Both careers offer positive job outlooks, but Electrical Maintenance Technicians often enjoy more consistent demand due to the critical nature of industrial equipment upkeep.
Choosing the Right Technician Role
Choosing the right technician role depends on the specific repair needs: Electronics Repair Technicians specialize in diagnosing and fixing complex circuit boards, semiconductors, and electronic devices, ensuring functionality in consumer and industrial electronics. Electrical Maintenance Technicians focus on maintaining, troubleshooting, and repairing electrical systems, wiring, and machinery in facilities to prevent downtime and ensure safety compliance. Understanding whether your issue involves intricate electronic components or broader electrical infrastructure helps target the expertise required for efficient and reliable repair service.
Electronics Repair Technician vs Electrical Maintenance Technician Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com