Automotive repairers specialize in maintaining and fixing light vehicles like cars and small trucks, working on systems such as brakes, engines, and electrical components. Diesel mechanics focus on heavy-duty diesel engines found in trucks, buses, and construction equipment, requiring expertise in fuel injection and emission control systems. Both professions require diagnostic skills, but diesel mechanics often handle larger, more complex machinery with different repair techniques.
Table of Comparison
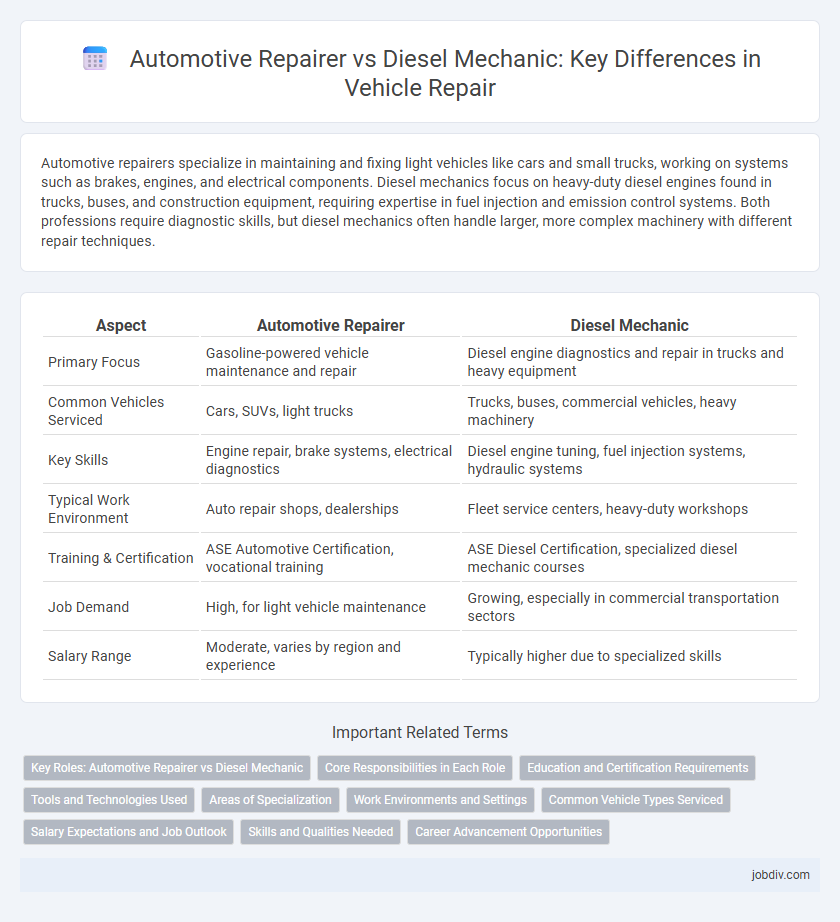
| Aspect | Automotive Repairer | Diesel Mechanic |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Gasoline-powered vehicle maintenance and repair | Diesel engine diagnostics and repair in trucks and heavy equipment |
| Common Vehicles Serviced | Cars, SUVs, light trucks | Trucks, buses, commercial vehicles, heavy machinery |
| Key Skills | Engine repair, brake systems, electrical diagnostics | Diesel engine tuning, fuel injection systems, hydraulic systems |
| Typical Work Environment | Auto repair shops, dealerships | Fleet service centers, heavy-duty workshops |
| Training & Certification | ASE Automotive Certification, vocational training | ASE Diesel Certification, specialized diesel mechanic courses |
| Job Demand | High, for light vehicle maintenance | Growing, especially in commercial transportation sectors |
| Salary Range | Moderate, varies by region and experience | Typically higher due to specialized skills |
Key Roles: Automotive Repairer vs Diesel Mechanic
Automotive repairers specialize in diagnosing and fixing cars, trucks, and light vehicles, focusing on engines, brakes, transmissions, and electrical systems to ensure optimal performance. Diesel mechanics primarily work on heavy-duty vehicles such as trucks, buses, and construction equipment, emphasizing diesel engines, fuel injection systems, and emission controls. Both roles require in-depth mechanical knowledge, but diesel mechanics handle larger, more complex engines with distinct fuel and maintenance needs compared to automotive repairers.
Core Responsibilities in Each Role
Automotive repairers specialize in diagnosing and fixing issues in passenger vehicles, focusing on engine performance, brake systems, and electrical diagnostics. Diesel mechanics concentrate on heavy-duty diesel engines found in trucks, buses, and construction equipment, emphasizing fuel systems, turbochargers, and emission controls. Both roles require expertise in mechanical systems, but diesel mechanics handle larger, more complex engines with specialized diagnostic tools.
Education and Certification Requirements
Automotive repairers typically require a high school diploma or GED, followed by technical training at a vocational school or community college, where they learn about gasoline engines, electrical systems, and diagnostics. Diesel mechanics often pursue more specialized education focused on heavy-duty diesel engines, including formal apprenticeships or certification programs accredited by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE). ASE certifications, such as Medium-Heavy Truck Specialist for diesel mechanics and Automobile & Light Truck certifications for automotive repairers, are crucial credentials that validate expertise and enhance job prospects in both fields.
Tools and Technologies Used
Automotive repairers commonly use diagnostic scanners, computerized engine analyzers, and handheld multimeters to address combustion engine and electronic system issues, while diesel mechanics rely on heavy-duty diagnostic tools such as diesel engine analyzers, fuel injection testers, and specialized software for electronic control modules (ECMs). Both technicians utilize impact wrenches, torque wrenches, and hydraulic lifts, but diesel mechanics often require larger-scale equipment like brake drum pullers and compression gauges designed specifically for diesel engines. Advanced technologies such as onboard diagnostics (OBD-II) systems and emissions analyzers are key tools for automotive repairers, whereas diesel mechanics integrate CAN bus analyzers and particulate matter sensors into their diagnostic processes.
Areas of Specialization
Automotive repairers specialize in a wide range of passenger vehicles, focusing on systems such as brakes, suspension, and electrical diagnostics for cars and light trucks. Diesel mechanics concentrate on heavy-duty diesel engines found in trucks, buses, and construction equipment, emphasizing engine performance, fuel systems, and emission controls. While automotive repairers handle routine maintenance and electronic system repairs, diesel mechanics are experts in large engine overhauls and complex diesel fuel injection systems.
Work Environments and Settings
Automotive repairers typically work in well-lit, climate-controlled garages or service centers focused on passenger vehicles such as cars and light trucks. Diesel mechanics usually operate in larger facilities or outdoor settings, servicing heavy-duty vehicles like trucks, buses, and construction equipment, often exposed to harsher environmental conditions. Both professionals rely on specialized diagnostic tools and must adapt to varied work environments based on vehicle type and mechanical complexity.
Common Vehicle Types Serviced
Automotive repairers primarily service passenger cars, light trucks, and SUVs, specializing in gasoline engines and electronic systems common to personal vehicles. Diesel mechanics focus on heavy-duty trucks, buses, and commercial vehicles powered by diesel engines, handling complex fuel injection systems and large engine components. Both professions require expertise in diagnostics and maintenance but differ significantly in vehicle types and engine technologies serviced.
Salary Expectations and Job Outlook
Automotive repairers typically earn a median annual salary of around $45,000, with job growth projected at 3% through 2030, reflecting steady demand in vehicle maintenance and repair. Diesel mechanics command higher salaries, averaging approximately $52,000 annually, due to specialized skills required for heavy-duty engines, while experiencing a similar job growth rate of 4%, driven by the transportation and freight industries. Both careers offer stable employment opportunities, but diesel mechanics generally have better salary prospects and increased demand in commercial sectors.
Skills and Qualities Needed
Automotive repairers require a broad understanding of vehicle systems, including electrical, hydraulic, and computerized components, alongside strong diagnostic and problem-solving skills to address a wide range of passenger vehicles. Diesel mechanics specialize in heavy-duty engines, demanding expertise in diesel technology, fuel injection systems, and emission controls, paired with physical stamina and precision in handling larger machinery. Both professions need attention to detail, mechanical aptitude, and the ability to interpret technical manuals and schematics for efficient and safe repairs.
Career Advancement Opportunities
Automotive repairers primarily focus on gasoline-powered vehicles and often start with entry-level positions but can advance to specialized roles such as diagnostic technicians or shop supervisors. Diesel mechanics, specializing in heavy-duty trucks and industrial engines, typically experience faster career growth due to high demand in logistics and transportation industries. Both careers offer certifications that enhance advancement opportunities, with diesel mechanics often accessing higher wage brackets through expertise in complex diesel systems.
Automotive Repairer vs Diesel Mechanic Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com