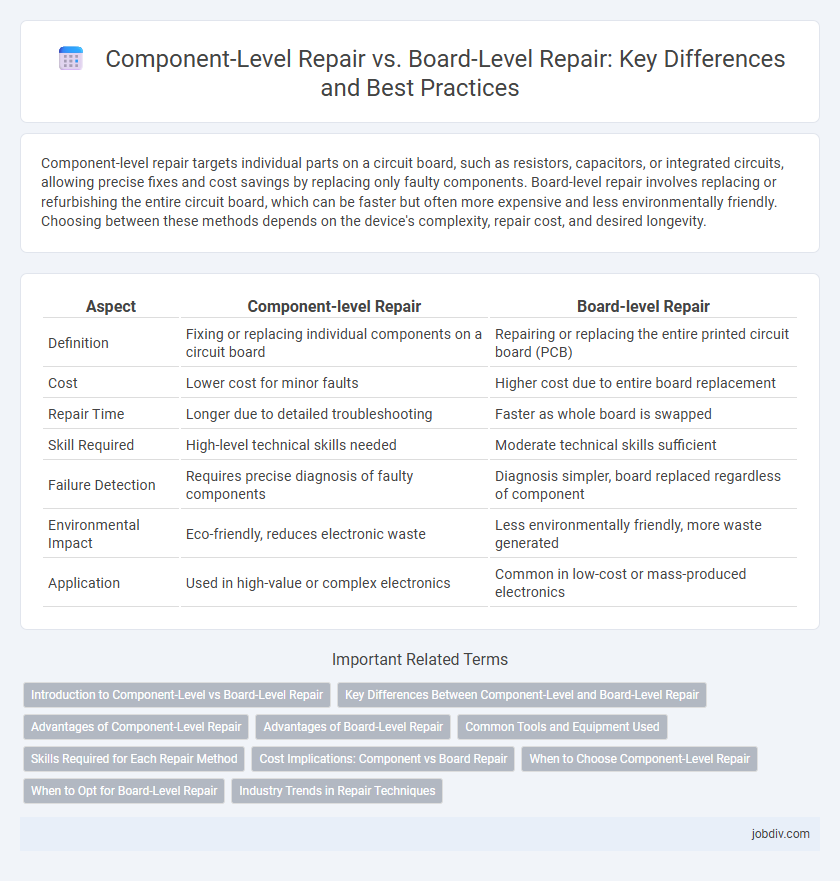
Component-level repair targets individual parts on a circuit board, such as resistors, capacitors, or integrated circuits, allowing precise fixes and cost savings by replacing only faulty components. Board-level repair involves replacing or refurbishing the entire circuit board, which can be faster but often more expensive and less environmentally friendly. Choosing between these methods depends on the device's complexity, repair cost, and desired longevity.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Component-level Repair | Board-level Repair |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fixing or replacing individual components on a circuit board | Repairing or replacing the entire printed circuit board (PCB) |
| Cost | Lower cost for minor faults | Higher cost due to entire board replacement |
| Repair Time | Longer due to detailed troubleshooting | Faster as whole board is swapped |
| Skill Required | High-level technical skills needed | Moderate technical skills sufficient |
| Failure Detection | Requires precise diagnosis of faulty components | Diagnosis simpler, board replaced regardless of component |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, reduces electronic waste | Less environmentally friendly, more waste generated |
| Application | Used in high-value or complex electronics | Common in low-cost or mass-produced electronics |
Introduction to Component-Level vs Board-Level Repair
Component-level repair focuses on identifying and fixing or replacing individual electronic components such as resistors, capacitors, and integrated circuits on a circuit board, enabling precise troubleshooting and cost-efficient restoration. Board-level repair involves addressing faults by repairing or replacing entire printed circuit boards (PCBs) rather than individual components, typically used when component-level diagnostics are impractical or when damage affects multiple areas of the board. Understanding the distinctions between component-level and board-level repair is crucial for selecting the most effective maintenance strategy in electronics refurbishment and repair services.
Key Differences Between Component-Level and Board-Level Repair
Component-level repair involves diagnosing and fixing individual electronic parts such as resistors, capacitors, or ICs, offering targeted and cost-effective solutions. Board-level repair addresses faults at the printed circuit board (PCB) level, often requiring specialized equipment to replace or rework surface-mounted components and traces. Key differences include the scope of repair, with component-level focusing on singular elements and board-level encompassing more complex rework of entire sections or layers of the PCB.
Advantages of Component-Level Repair
Component-level repair offers significant cost savings by targeting and replacing defective individual parts rather than entire circuit boards. This approach reduces electronic waste and extends the lifespan of devices through precise diagnostics and minimal part replacement. Enhanced repair turnaround times and improved maintenance efficiency are achieved by addressing faults at the component scale, benefiting industries reliant on complex electronics.
Advantages of Board-Level Repair
Board-level repair offers significant cost savings by replacing or fixing entire circuit boards instead of individual components, reducing labor time and complexity. This approach enhances reliability by ensuring tested and validated boards are used, minimizing the risk of component mismatches or improper repairs. Board-level repair also speeds up turnaround time, improving service efficiency and minimizing equipment downtime in critical applications.
Common Tools and Equipment Used
Common tools and equipment used in component-level repair include precision soldering irons, multimeters, oscilloscopes, and IC testers, enabling technicians to accurately diagnose and replace individual components. Board-level repair typically requires rework stations with hot air guns, BGA reflow machines, and specialized magnification devices to handle complex surface-mount technology (SMT) and multilayer printed circuit boards (PCBs). Both repair levels rely on ESD-safe workstations and diagnostic software to prevent damage and enhance troubleshooting accuracy.
Skills Required for Each Repair Method
Component-level repair demands specialized skills in micro-soldering, circuit analysis, and precise diagnostics to identify and replace individual electronic parts. Board-level repair requires expertise in handling multilayer PCBs, understanding circuit schematics, and utilizing advanced testing equipment to address faults on entire circuit boards. Technicians skilled in component-level repair enable targeted fixes, while those proficient in board-level repair manage complex assemblies, ensuring optimal functionality.
Cost Implications: Component vs Board Repair
Component-level repair offers significant cost savings by targeting only the faulty parts, reducing the need for expensive full board replacements. Board-level repair often incurs higher expenses due to the complexity and labor involved in diagnosing and fixing issues affecting multiple components. Choosing component repair maximizes resource efficiency by minimizing material costs and downtime, especially in high-value or densely packed electronic assemblies.
When to Choose Component-Level Repair
Choose component-level repair when identifying and replacing individual faulty parts can significantly reduce costs and minimize downtime, especially in complex or high-value electronic devices. This approach is ideal for addressing issues like malfunctioning resistors, capacitors, or integrated circuits without discarding the entire board. It extends the lifespan of the equipment by preserving functional subassemblies and improving diagnostic accuracy.
When to Opt for Board-Level Repair
Board-level repair is appropriate when multiple components on a printed circuit board (PCB) malfunction, causing complex circuit failures difficult to isolate at the component level. It is cost-effective for addressing issues like broken traces, solder joint failures, or damage to surface-mount technology (SMT) components that compromise the entire PCB functionality. Choosing board-level repair minimizes downtime and expands repair options for modern electronics with densely packed or multi-layer PCBs.
Industry Trends in Repair Techniques
Component-level repair improves cost efficiency and sustainability in electronics maintenance by targeting faulty components individually, extending device lifespans. Industry trends show increasing adoption of automated diagnostic tools and precision soldering technologies to enhance accuracy and reduce turnaround times in both component- and board-level repairs. Growing demand for eco-friendly practices drives manufacturers to prioritize component-level repairs over board replacements, minimizing electronic waste and resource consumption.
Component-level Repair vs Board-level Repair Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com