An IT Security Auditor focuses on evaluating and testing an organization's information systems to identify vulnerabilities and ensure security controls are effective. A Compliance Officer ensures that the organization adheres to external regulations and internal policies, overseeing risk management and regulatory compliance processes. Both roles are critical for comprehensive IT security, with auditors targeting technical assessments and compliance officers managing governance and policy enforcement.
Table of Comparison
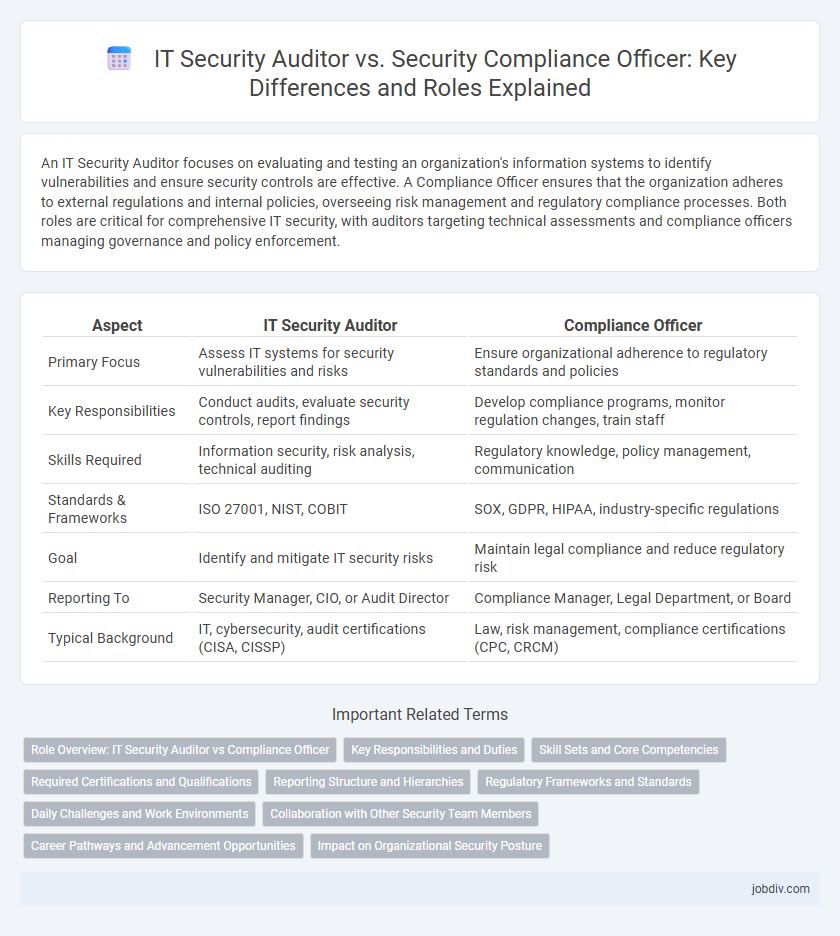
| Aspect | IT Security Auditor | Compliance Officer |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Assess IT systems for security vulnerabilities and risks | Ensure organizational adherence to regulatory standards and policies |
| Key Responsibilities | Conduct audits, evaluate security controls, report findings | Develop compliance programs, monitor regulation changes, train staff |
| Skills Required | Information security, risk analysis, technical auditing | Regulatory knowledge, policy management, communication |
| Standards & Frameworks | ISO 27001, NIST, COBIT | SOX, GDPR, HIPAA, industry-specific regulations |
| Goal | Identify and mitigate IT security risks | Maintain legal compliance and reduce regulatory risk |
| Reporting To | Security Manager, CIO, or Audit Director | Compliance Manager, Legal Department, or Board |
| Typical Background | IT, cybersecurity, audit certifications (CISA, CISSP) | Law, risk management, compliance certifications (CPC, CRCM) |
Role Overview: IT Security Auditor vs Compliance Officer
An IT Security Auditor evaluates an organization's information systems to identify vulnerabilities and ensure adherence to security policies and regulatory requirements, using comprehensive risk assessments and penetration tests. A Compliance Officer oversees the implementation and monitoring of internal controls, ensuring that business operations comply with industry standards, laws, and corporate governance frameworks. Both roles collaborate to mitigate risks and maintain robust cybersecurity postures, with auditors focusing on technical assessments and compliance officers managing procedural and regulatory obligations.
Key Responsibilities and Duties
An IT Security Auditor primarily evaluates and tests the effectiveness of an organization's information security controls, identifying vulnerabilities and ensuring compliance with security policies and industry standards such as ISO 27001 and NIST. In contrast, a Compliance Officer focuses on developing, implementing, and maintaining internal policies to ensure the organization adheres to legal regulations and regulatory requirements, including GDPR, HIPAA, and SOX. Both roles collaborate to mitigate risks, but the auditor is more assessment-driven while the compliance officer emphasizes policy enforcement and regulatory alignment.
Skill Sets and Core Competencies
IT Security Auditors possess strong technical skills in vulnerability assessment, risk analysis, and knowledge of security frameworks such as ISO 27001, NIST, and COBIT, enabling them to identify and mitigate security weaknesses. Compliance Officers excel in regulatory knowledge, policy development, and audit management, ensuring organizational adherence to legal standards like GDPR, HIPAA, and SOX. Both roles require analytical thinking and attention to detail, but IT Security Auditors prioritize technical security controls while Compliance Officers focus on regulatory compliance and governance frameworks.
Required Certifications and Qualifications
IT Security Auditors typically require certifications such as Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA) or Certified Information Security Manager (CISM) to validate their expertise in auditing and managing information security controls. Compliance Officers often pursue certifications like Certified Compliance and Ethics Professional (CCEP) or Certified Information Privacy Professional (CIPP) to demonstrate proficiency in regulatory requirements and ethical standards. Both roles benefit from a strong understanding of frameworks like ISO 27001, GDPR, and HIPAA, but their certifications emphasize audit rigor versus regulatory adherence.
Reporting Structure and Hierarchies
IT Security Auditors typically report to the Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) or Security Manager, ensuring independent assessment of security controls and risk management practices. Compliance Officers often fall under the Legal or Risk Management departments, reporting to Chief Compliance Officers or General Counsel to oversee adherence to regulatory requirements. The hierarchical distinction emphasizes auditors' technical focus on IT security framework evaluations, while compliance officers concentrate on organizational policy enforcement and regulatory compliance.
Regulatory Frameworks and Standards
IT Security Auditors assess an organization's adherence to regulatory frameworks such as GDPR, HIPAA, and ISO 27001 by conducting thorough security audits and vulnerability assessments. Compliance Officers develop and enforce policies ensuring ongoing alignment with standards like NIST, PCI-DSS, and SOX to mitigate legal and financial risks. Both roles collaborate to maintain robust security postures that meet external regulatory requirements and internal control objectives.
Daily Challenges and Work Environments
IT Security Auditors face daily challenges in identifying vulnerabilities, assessing risk management frameworks, and ensuring systems adhere to cybersecurity standards like ISO 27001 and NIST. Compliance Officers focus on monitoring regulatory adherence, managing internal policies for standards such as GDPR or HIPAA, and addressing audit findings to avoid legal penalties. While IT Security Auditors operate primarily within technical environments evaluating IT infrastructure, Compliance Officers engage across departments to enforce corporate governance and regulatory compliance.
Collaboration with Other Security Team Members
An IT Security Auditor collaborates closely with cybersecurity analysts and risk managers to identify vulnerabilities and ensure effective security controls. Compliance Officers work alongside IT auditors and legal teams to interpret regulatory requirements and implement policies that align with industry standards. Both roles require seamless communication with incident response and governance teams to maintain a robust security posture across the organization.
Career Pathways and Advancement Opportunities
IT Security Auditors specialize in assessing and improving an organization's cybersecurity controls and risk management processes, often advancing towards roles such as Senior Security Auditor or IT Risk Manager. Compliance Officers focus on ensuring adherence to regulatory requirements, progressing into positions like Compliance Manager or Chief Compliance Officer with expertise in legal and industry standards. Both career paths offer advancement opportunities in governance, risk, and compliance (GRC) fields, though IT Security Auditors tend to emphasize technical skills, while Compliance Officers concentrate on policy and regulatory frameworks.
Impact on Organizational Security Posture
IT Security Auditors enhance organizational security posture by systematically evaluating security controls, identifying vulnerabilities, and ensuring adherence to cybersecurity standards. Compliance Officers focus on enforcing regulatory requirements and internal policies to maintain legal and ethical integrity, reducing the risk of penalties and reputational damage. Together, their combined efforts fortify the organization's defense mechanisms and ensure continuous alignment with evolving security frameworks.
IT Security Auditor vs Compliance Officer Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com