A Physical Security Manager oversees the protection of tangible assets such as buildings, equipment, and personnel, ensuring secure access and safety protocols are enforced. In contrast, an Information Security Manager focuses on safeguarding digital information systems, managing cybersecurity measures, and preventing data breaches. Both roles are essential in a comprehensive security strategy, addressing distinct but complementary aspects of organizational protection.
Table of Comparison
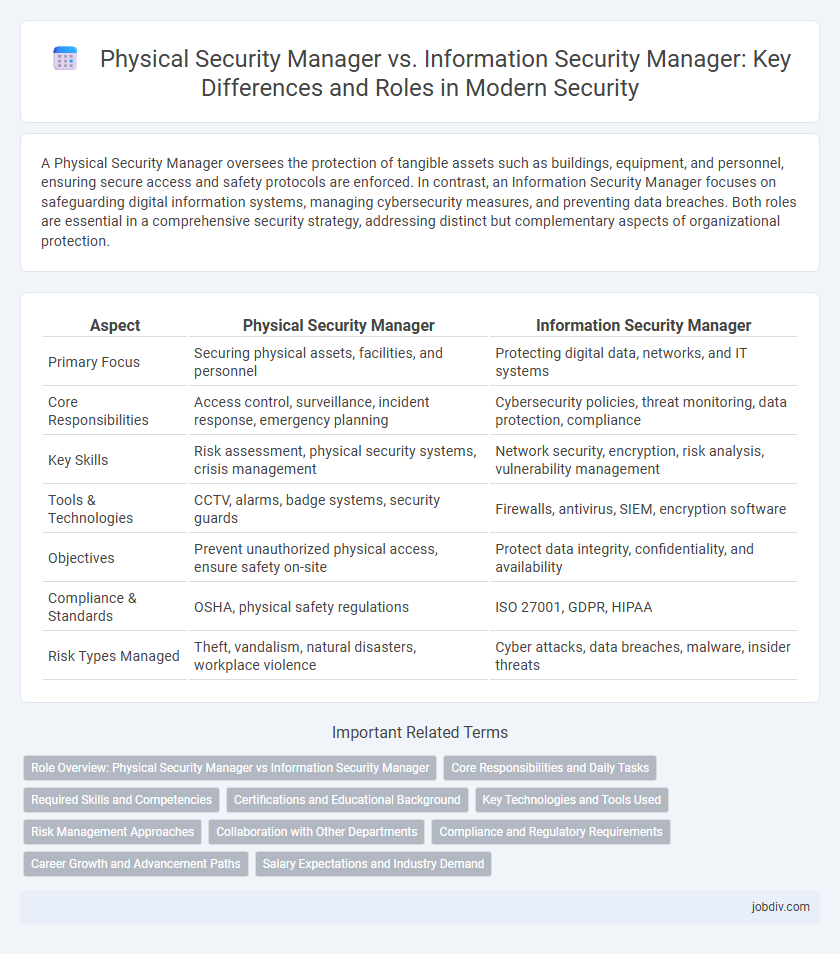
| Aspect | Physical Security Manager | Information Security Manager |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Securing physical assets, facilities, and personnel | Protecting digital data, networks, and IT systems |
| Core Responsibilities | Access control, surveillance, incident response, emergency planning | Cybersecurity policies, threat monitoring, data protection, compliance |
| Key Skills | Risk assessment, physical security systems, crisis management | Network security, encryption, risk analysis, vulnerability management |
| Tools & Technologies | CCTV, alarms, badge systems, security guards | Firewalls, antivirus, SIEM, encryption software |
| Objectives | Prevent unauthorized physical access, ensure safety on-site | Protect data integrity, confidentiality, and availability |
| Compliance & Standards | OSHA, physical safety regulations | ISO 27001, GDPR, HIPAA |
| Risk Types Managed | Theft, vandalism, natural disasters, workplace violence | Cyber attacks, data breaches, malware, insider threats |
Role Overview: Physical Security Manager vs Information Security Manager
A Physical Security Manager oversees the protection of tangible assets, including facilities, personnel, and equipment, using access control systems, surveillance, and emergency response planning. An Information Security Manager focuses on safeguarding digital information through cybersecurity strategies, risk assessment, data encryption, and compliance with information security standards such as ISO 27001 and NIST. Both roles require coordination with cross-functional teams to mitigate risks but specialize in distinct domains of organizational security.
Core Responsibilities and Daily Tasks
A Physical Security Manager oversees the protection of tangible assets, managing access control systems, surveillance, and emergency response plans to ensure the safety of personnel and property. In contrast, an Information Security Manager focuses on safeguarding digital information by implementing cybersecurity policies, monitoring for data breaches, and managing incident response protocols. Both roles require risk assessment and coordination with other departments but diverge in their focus on physical versus digital security measures.
Required Skills and Competencies
A Physical Security Manager requires expertise in risk assessment, access control systems, surveillance technologies, and emergency response coordination to protect facilities and personnel effectively. In contrast, an Information Security Manager must possess strong knowledge of cybersecurity frameworks, threat detection, data encryption, and incident response to safeguard digital assets and sensitive information. Both roles demand leadership skills, regulatory compliance awareness, and the ability to develop and enforce security policies, but their technical proficiencies and operational focus differ significantly.
Certifications and Educational Background
Physical Security Managers often hold certifications like CPP (Certified Protection Professional) and PSAP (Physical Security Awareness Program) with backgrounds in criminal justice or facility management, emphasizing risk assessment and infrastructure protection. Information Security Managers typically possess certifications such as CISSP (Certified Information Systems Security Professional) and CISM (Certified Information Security Manager), paired with degrees in computer science, cybersecurity, or information technology, focusing on data protection and cyber threat mitigation. Both roles benefit from continuous education, but Information Security Managers require stronger technical expertise due to the evolving nature of digital threats.
Key Technologies and Tools Used
Physical Security Managers rely on access control systems, surveillance cameras, and intrusion detection technologies to safeguard facilities and personnel. Information Security Managers utilize firewalls, encryption software, intrusion prevention systems (IPS), and security information and event management (SIEM) tools to protect digital assets and network integrity. Both roles require proficiency in risk assessment technologies and incident response platforms tailored to their respective security domains.
Risk Management Approaches
Physical Security Managers prioritize tangible threats by implementing risk management strategies that include access control, surveillance, and environmental safeguards to protect assets and personnel from physical harm. Information Security Managers focus on digital threats through risk assessment methodologies such as vulnerability scanning, threat modeling, and incident response planning to secure data integrity and prevent cyber attacks. Both roles require continuous monitoring and adaptation of risk mitigation techniques to address evolving security challenges effectively.
Collaboration with Other Departments
Physical Security Managers coordinate closely with facilities, human resources, and emergency response teams to implement comprehensive safety protocols that protect tangible assets and personnel. Information Security Managers work in tandem with IT, legal, and compliance departments to safeguard digital information, ensuring cybersecurity measures align with regulatory requirements. Both roles require cross-functional collaboration to create an integrated risk management strategy that addresses both physical and cyber threats effectively.
Compliance and Regulatory Requirements
A Physical Security Manager ensures compliance with safety regulations such as OSHA and building codes, managing access control systems and emergency response protocols to protect physical assets. An Information Security Manager enforces cybersecurity standards like GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS, overseeing data protection measures and risk assessments to maintain information confidentiality and integrity. Both roles are critical for comprehensive organizational compliance, with distinct regulatory focuses tailored to physical versus digital security environments.
Career Growth and Advancement Paths
Physical Security Managers often progress to roles such as Director of Facilities Security or Corporate Security Manager, leveraging expertise in risk assessment, access control systems, and emergency response planning. Information Security Managers typically advance toward positions like Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) or IT Security Director by deepening skills in cybersecurity frameworks, threat intelligence, and regulatory compliance. Career growth for both demands continuous skill enhancement, with Information Security roles increasingly prioritizing certifications like CISSP or CISM to navigate evolving digital threats.
Salary Expectations and Industry Demand
Physical Security Managers typically earn between $70,000 and $110,000 annually, reflecting steady demand in sectors like manufacturing and logistics. Information Security Managers command higher salaries, often ranging from $100,000 to $150,000, driven by increasing threats in the tech and financial industries. The demand for Information Security Managers is growing rapidly due to cybersecurity concerns, whereas Physical Security Managers maintain consistent need for safeguarding physical assets.
Physical Security Manager vs Information Security Manager Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com