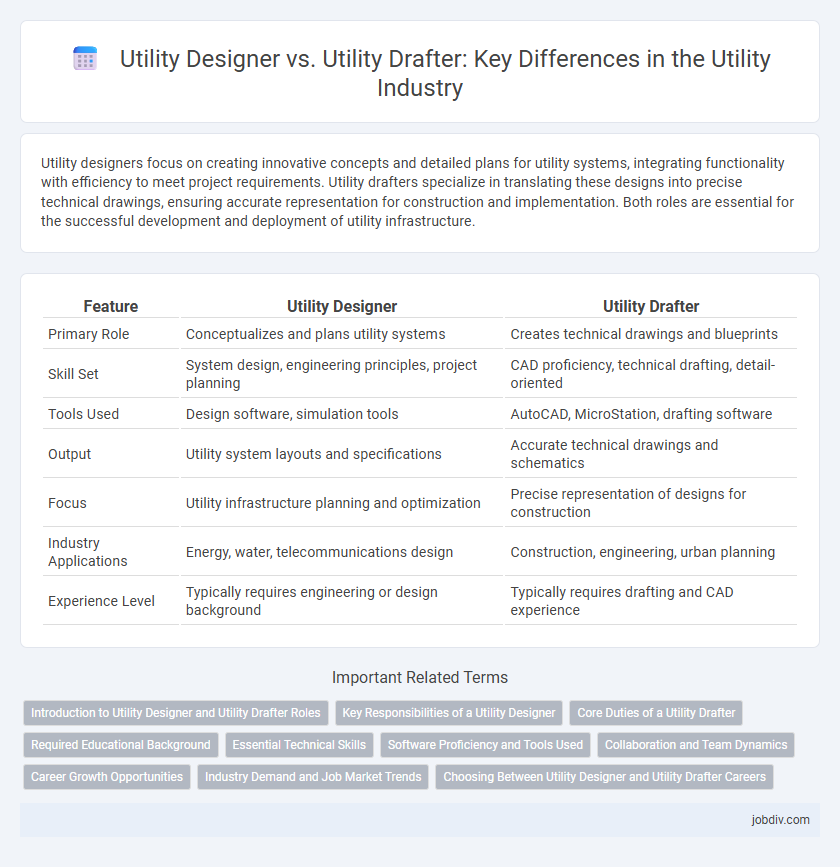
Utility designers focus on creating innovative concepts and detailed plans for utility systems, integrating functionality with efficiency to meet project requirements. Utility drafters specialize in translating these designs into precise technical drawings, ensuring accurate representation for construction and implementation. Both roles are essential for the successful development and deployment of utility infrastructure.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Utility Designer | Utility Drafter |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Conceptualizes and plans utility systems | Creates technical drawings and blueprints |
| Skill Set | System design, engineering principles, project planning | CAD proficiency, technical drafting, detail-oriented |
| Tools Used | Design software, simulation tools | AutoCAD, MicroStation, drafting software |
| Output | Utility system layouts and specifications | Accurate technical drawings and schematics |
| Focus | Utility infrastructure planning and optimization | Precise representation of designs for construction |
| Industry Applications | Energy, water, telecommunications design | Construction, engineering, urban planning |
| Experience Level | Typically requires engineering or design background | Typically requires drafting and CAD experience |
Introduction to Utility Designer and Utility Drafter Roles
Utility Designers develop detailed plans and specifications for utility systems, such as water, gas, or electrical networks, ensuring efficient design and compliance with regulatory standards. Utility Drafters create precise technical drawings based on these plans, converting engineers' and designers' concepts into clear, standardized blueprints for construction and maintenance. Both roles are essential in the utility industry, facilitating the seamless design-to-execution workflow critical for infrastructure development.
Key Responsibilities of a Utility Designer
Utility Designers are responsible for planning and developing detailed layouts of utility systems such as water, gas, electrical, and telecommunications networks. They collaborate with engineers and project managers to ensure designs meet regulatory standards, optimize functionality, and minimize environmental impact. Their key responsibilities include creating technical drawings, performing feasibility studies, and integrating advanced software tools to enhance design accuracy and project efficiency.
Core Duties of a Utility Drafter
Utility drafters specialize in creating detailed technical drawings and plans that map out utility systems such as water, gas, electrical, and telecommunications networks. Their core duties include drafting precise schematics, updating blueprints based on field data, and ensuring compliance with engineering specifications and local regulations. Unlike utility designers who focus on conceptual and system design, utility drafters concentrate on translating those designs into accurate, scalable construction documents.
Required Educational Background
Utility Designers typically require a bachelor's degree in civil engineering, electrical engineering, or a related technical field, emphasizing design principles and project management. Utility Drafters often hold an associate degree or diploma in drafting, CAD technology, or architectural engineering, focusing on technical drawing and blueprint creation. Professional certifications in CAD software and industry-specific standards significantly enhance qualifications for both roles.
Essential Technical Skills
Utility Designers require expertise in advanced 3D modeling software like AutoCAD Civil 3D and MicroStation, along with strong knowledge of utility system design principles and regulatory standards. Utility Drafters must excel in creating detailed technical drawings, annotations, and revisions using CAD software, emphasizing precision and adherence to design specifications. Both roles demand proficiency in interpreting engineering plans, but Designers focus more on conceptual design and system layout, while Drafters specialize in producing accurate construction documents.
Software Proficiency and Tools Used
Utility Designers typically utilize advanced design software such as AutoCAD Civil 3D, Bentley MicroStation, and GIS platforms to create detailed infrastructure plans, emphasizing precision and integration with geographic data. Utility Drafters often rely on drafting-specific tools like AutoCAD, Revit, and Autodesk Utility Design software to convert engineering designs into technical drawings and blueprints for construction use. Proficiency in software versions and interoperability across CAD and GIS systems distinguishes Utility Designers who manage complex projects from Utility Drafters focused on accurate documentation and implementation.
Collaboration and Team Dynamics
Utility designers and utility drafters collaborate closely to ensure accurate planning and execution of infrastructure projects. Designers conceptualize system layouts while drafters translate these concepts into precise technical drawings, requiring seamless communication to align project goals. Effective team dynamics depend on shared digital platforms and regular feedback loops to resolve discrepancies and optimize workflow.
Career Growth Opportunities
Utility Designers typically experience more robust career growth opportunities due to their involvement in complex planning, system design, and project management within utility infrastructure projects. Utility Drafters focus primarily on creating technical drawings and blueprints, which offers a more specialized and limited advancement path within drafting or CAD roles. Professionals aiming for leadership or engineering positions benefit from developing design expertise and cross-disciplinary skills beyond basic drafting.
Industry Demand and Job Market Trends
Utility Designers, skilled in advanced CAD software and systems integration, are increasingly sought after in the energy and infrastructure sectors due to their ability to create comprehensive utility layouts and optimize resource distribution. Utility Drafters, while essential for producing detailed technical drawings, face slower job growth as automation and digital modeling reduce the demand for manual drafting tasks. Industry demand trends emphasize a preference for Utility Designers who combine technical expertise with strategic planning, reflecting a shift towards more complex and digitally-driven utility projects.
Choosing Between Utility Designer and Utility Drafter Careers
Utility designers focus on creating comprehensive plans for utility systems such as water, gas, and electrical networks, using advanced software to optimize efficiency and compliance with regulations. Utility drafters specialize in preparing detailed technical drawings and blueprints based on designers' concepts, ensuring precise implementation of utility projects. Choosing between careers depends on whether one prefers conceptual design and planning (utility designer) or detailed technical drafting and documentation (utility drafter).
Utility Designer vs Utility Drafter Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com