Information Assurance Analysts focus on ensuring the integrity, availability, and confidentiality of data through risk management, compliance, and policy implementation. Information Security Analysts concentrate on protecting systems and networks from cyber threats by monitoring, detecting, and responding to security incidents. Both roles are essential for comprehensive cybersecurity, with Information Assurance emphasizing governance and Information Security targeting technical defenses.
Table of Comparison
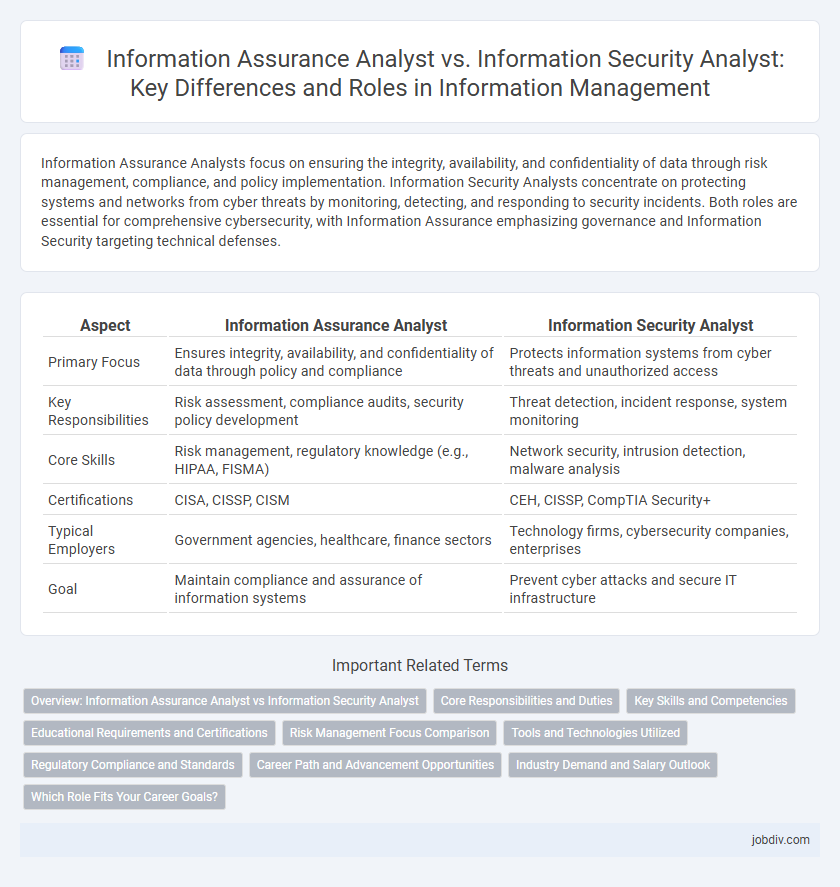
| Aspect | Information Assurance Analyst | Information Security Analyst |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Ensures integrity, availability, and confidentiality of data through policy and compliance | Protects information systems from cyber threats and unauthorized access |
| Key Responsibilities | Risk assessment, compliance audits, security policy development | Threat detection, incident response, system monitoring |
| Core Skills | Risk management, regulatory knowledge (e.g., HIPAA, FISMA) | Network security, intrusion detection, malware analysis |
| Certifications | CISA, CISSP, CISM | CEH, CISSP, CompTIA Security+ |
| Typical Employers | Government agencies, healthcare, finance sectors | Technology firms, cybersecurity companies, enterprises |
| Goal | Maintain compliance and assurance of information systems | Prevent cyber attacks and secure IT infrastructure |
Overview: Information Assurance Analyst vs Information Security Analyst
Information Assurance Analysts focus on managing risks related to data integrity, availability, and confidentiality by developing policies and auditing compliance within organizational systems. Information Security Analysts specialize in protecting digital assets by implementing security measures such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and responding to cyber threats. Both roles play critical parts in safeguarding information but differ in their emphasis on risk management versus technical security operations.
Core Responsibilities and Duties
Information Assurance Analysts focus on ensuring data integrity, availability, and confidentiality through risk assessments, policy development, and compliance monitoring to protect organizational information systems. Information Security Analysts primarily concentrate on implementing security measures, monitoring for threats, and responding to security incidents to safeguard IT infrastructure. Both roles require expertise in cybersecurity frameworks, but Information Assurance Analysts emphasize strategic risk management while Information Security Analysts engage in tactical defense operations.
Key Skills and Competencies
Information Assurance Analysts specialize in risk management, compliance, and policy development, emphasizing vulnerability assessments, risk mitigation strategies, and regulatory frameworks such as HIPAA or GDPR. Information Security Analysts focus on threat detection, incident response, and security infrastructure management, demonstrating expertise in intrusion detection systems, firewall configuration, and security protocols like SSL/TLS. Both roles require strong analytical skills, knowledge of cybersecurity principles, and proficiency in tools like SIEM platforms, but Information Assurance leans more towards governance and auditing, whereas Information Security centers on technical defense mechanisms.
Educational Requirements and Certifications
Information Assurance Analysts typically require a bachelor's degree in computer science, information technology, or a related field, alongside certifications like Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA) to validate their expertise in risk management and compliance. Information Security Analysts often hold degrees in cybersecurity, information technology, or computer science, with certifications such as Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP) or CompTIA Security+ emphasizing skills in threat detection and incident response. Both roles benefit from specialized training, but Information Assurance leans more towards governance and policy, while Information Security prioritizes technical defense mechanisms.
Risk Management Focus Comparison
Information Assurance Analysts prioritize risk management by developing policies to ensure data integrity, availability, and confidentiality across organizational systems. Information Security Analysts focus on identifying, assessing, and mitigating cyber threats and vulnerabilities to protect digital assets and maintain compliance with security standards. Both roles emphasize proactive risk assessment, but Information Assurance Analysts align risk strategies with overall business objectives while Information Security Analysts implement technical controls for threat prevention and incident response.
Tools and Technologies Utilized
Information Assurance Analysts primarily utilize risk management frameworks, compliance auditing tools, and vulnerability assessment software such as RSA Archer and Nessus to ensure data integrity and regulatory adherence. Information Security Analysts focus on cybersecurity technologies including firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), and endpoint protection platforms like Palo Alto Networks and Symantec to protect organizational assets from cyber threats. Both roles require proficiency in Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) tools such as Splunk or IBM QRadar for real-time monitoring and incident response.
Regulatory Compliance and Standards
Information Assurance Analysts primarily focus on ensuring organizational adherence to regulatory compliance and standards such as HIPAA, GDPR, and ISO/IEC 27001 by developing and implementing policies that safeguard information integrity and availability. Information Security Analysts emphasize the technical enforcement of these standards through risk assessments, vulnerability management, and continuous monitoring of security controls to protect against cyber threats. Both roles collaborate to align security measures with legal requirements, but Information Assurance Analysts concentrate on compliance frameworks, while Information Security Analysts handle operational security practices.
Career Path and Advancement Opportunities
Information Assurance Analysts prioritize managing risk and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards, creating a foundation for roles such as Risk Manager or Compliance Officer. Information Security Analysts focus on protecting systems against cyber threats, advancing toward roles like Security Architect or Cybersecurity Manager. Both career paths offer growth through specialization in areas such as threat intelligence, incident response, or governance frameworks.
Industry Demand and Salary Outlook
Information Assurance Analysts focus on risk management and compliance, ensuring data integrity and availability, which sees steady demand in highly regulated industries like finance and healthcare, with average salaries around $90,000 to $110,000 annually. Information Security Analysts specialize in protecting systems against cyber threats, experiencing faster job growth with increasing cybersecurity incidents, typically earning between $95,000 and $120,000 per year. Both roles command competitive salaries, but Information Security Analysts often benefit from higher demand and salary premiums in sectors emphasizing proactive threat mitigation.
Which Role Fits Your Career Goals?
Information Assurance Analysts focus on risk management, ensuring compliance with regulations and policies to protect organizational data, making this role ideal for professionals aiming to specialize in governance and risk mitigation. Information Security Analysts concentrate on defending networks, systems, and data from cyber threats through monitoring, incident response, and security tool implementation, fitting career goals centered on hands-on cybersecurity defense and threat analysis. Choosing between these roles depends on whether your career aspirations lie in strategic policy enforcement or active cybersecurity operations.
Information Assurance Analyst vs Information Security Analyst Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com