Commercial agents specialize in property transactions involving office spaces, retail stores, and industrial buildings, requiring expertise in market trends and investment potential. Residential agents focus on buying and selling homes, working closely with individuals to navigate personal needs and preferences. Understanding the distinctions helps clients choose the right agent for their specific real estate goals.
Table of Comparison
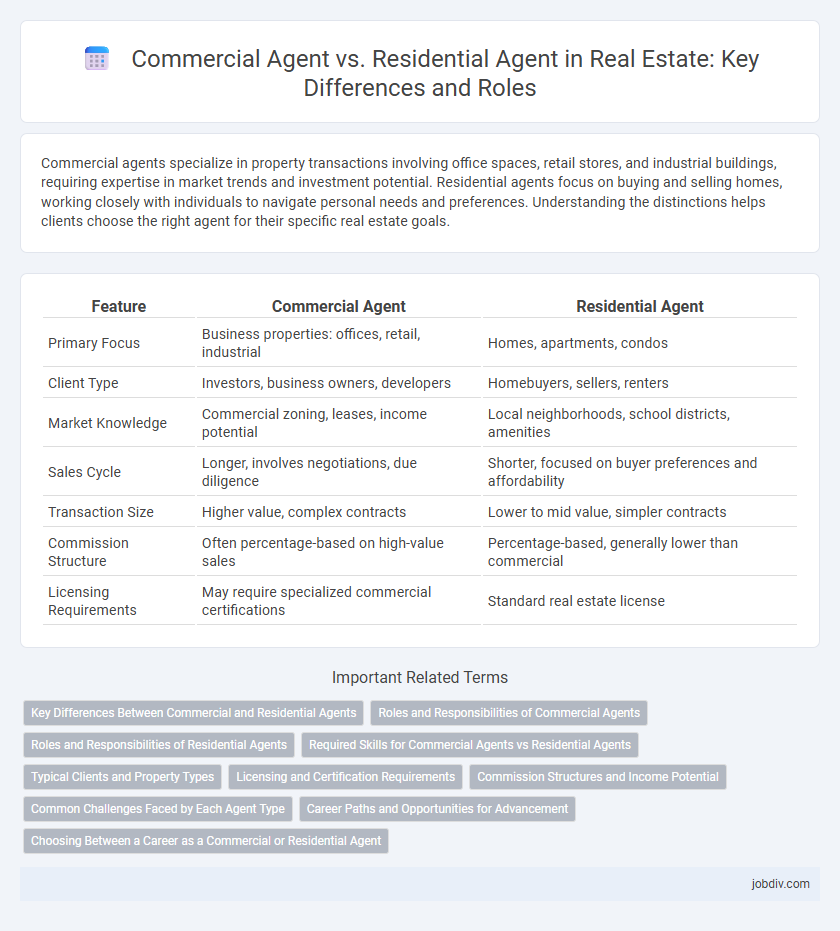
| Feature | Commercial Agent | Residential Agent |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Business properties: offices, retail, industrial | Homes, apartments, condos |
| Client Type | Investors, business owners, developers | Homebuyers, sellers, renters |
| Market Knowledge | Commercial zoning, leases, income potential | Local neighborhoods, school districts, amenities |
| Sales Cycle | Longer, involves negotiations, due diligence | Shorter, focused on buyer preferences and affordability |
| Transaction Size | Higher value, complex contracts | Lower to mid value, simpler contracts |
| Commission Structure | Often percentage-based on high-value sales | Percentage-based, generally lower than commercial |
| Licensing Requirements | May require specialized commercial certifications | Standard real estate license |
Key Differences Between Commercial and Residential Agents
Commercial agents specialize in properties used for business purposes, such as office buildings, retail spaces, and industrial facilities, requiring expertise in market trends, zoning laws, and investment analysis. Residential agents focus on helping clients buy, sell, or rent homes, apartments, and condominiums, emphasizing neighborhood knowledge, property valuation, and client lifestyle needs. The main differences lie in transaction complexity, target clientele, and regulatory requirements specific to commercial versus residential real estate sectors.
Roles and Responsibilities of Commercial Agents
Commercial real estate agents specialize in properties used for business purposes, such as office buildings, retail spaces, and industrial warehouses. Their roles include conducting market analysis, negotiating leases or sales, and advising clients on investment opportunities and zoning regulations. These agents must possess a deep understanding of commercial property valuation, financing methods, and legal aspects to effectively serve businesses and investors.
Roles and Responsibilities of Residential Agents
Residential agents specialize in assisting clients with buying, selling, or renting homes, focusing on single-family houses, condos, and apartments. Their responsibilities include conducting market analysis, arranging property showings, negotiating offers, and guiding clients through the financing and closing processes. They prioritize understanding neighborhood trends, school districts, and local amenities to help clients make informed residential decisions.
Required Skills for Commercial Agents vs Residential Agents
Commercial agents require strong financial analysis skills, expertise in market trends, and negotiation abilities tailored to complex lease and investment contracts. Residential agents excel in interpersonal communication, local market knowledge, and client-focused service to help individuals buy or sell homes. Both roles demand negotiation skills, but commercial agents often handle higher-stakes transactions involving commercial properties and business clients.
Typical Clients and Property Types
Commercial agents typically serve business clients such as corporations, investors, and developers, specializing in properties like office buildings, retail spaces, warehouses, and industrial facilities. Residential agents focus on individual homebuyers, sellers, and renters, dealing primarily with single-family homes, condominiums, townhouses, and apartments. Understanding client needs in commercial real estate involves analyzing investment potential and business functionality, while residential agents prioritize lifestyle preferences and neighborhood amenities.
Licensing and Certification Requirements
Commercial real estate agents typically require a real estate license that includes specialized training or certification in commercial property transactions, reflecting the complex nature of leasing, sales, and investment. Residential agents must obtain a state-specific real estate license and often pursue certifications such as the Accredited Buyer's Representative (ABR) or Residential Specialist (RS) to enhance their expertise in the residential market. Licensing requirements are governed by state real estate commissions and can include pre-licensing courses, exams, background checks, and continuing education tailored to commercial or residential property focus.
Commission Structures and Income Potential
Commercial agents typically earn higher commissions, often ranging from 3% to 6% of the transaction value, because commercial property deals involve larger sums and longer contract terms. Residential agents usually work with commissions between 5% and 6%, split with brokers, on relatively lower-priced properties, resulting in more frequent but smaller transactions. Income potential for commercial agents is often greater due to higher property values and lease commissions, while residential agents benefit from a steadier volume of sales.
Common Challenges Faced by Each Agent Type
Commercial agents often face challenges like negotiating complex lease agreements, managing long sales cycles, and navigating zoning laws. Residential agents commonly deal with emotional client decisions, fluctuating market demand, and tight transaction timelines. Both agent types must continuously adapt to regulatory changes and market trends to maintain client satisfaction and close deals effectively.
Career Paths and Opportunities for Advancement
Commercial agents often work with larger-scale transactions involving businesses, retail spaces, and industrial properties, leading to higher earning potential and opportunities to specialize in investment analysis or property management. Residential agents typically focus on helping individuals buy or sell homes, with career advancement available through gaining certifications, expanding networks, or moving into brokerage roles. Both career paths offer unique opportunities for growth, but commercial real estate tends to provide a more complex market environment with diverse professional development options.
Choosing Between a Career as a Commercial or Residential Agent
Choosing between a career as a commercial or residential real estate agent depends on expertise and market focus; commercial agents specialize in properties like office buildings, retail spaces, and industrial sites, requiring knowledge of market trends and investment analysis. Residential agents concentrate on buying and selling homes, offering deep understanding of neighborhood dynamics, client preferences, and financing options. Career success in either field depends on client relationships, negotiation skills, and familiarity with relevant local and legal regulations.
Commercial Agent vs Residential Agent Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com