Preventive repair involves regular maintenance and inspections to identify and address potential issues before they cause significant damage. Corrective repair occurs after a fault or failure has been detected, requiring immediate action to restore functionality. Prioritizing preventive repair can reduce downtime and increase the longevity of equipment, making it more cost-effective than relying solely on corrective repairs.
Table of Comparison
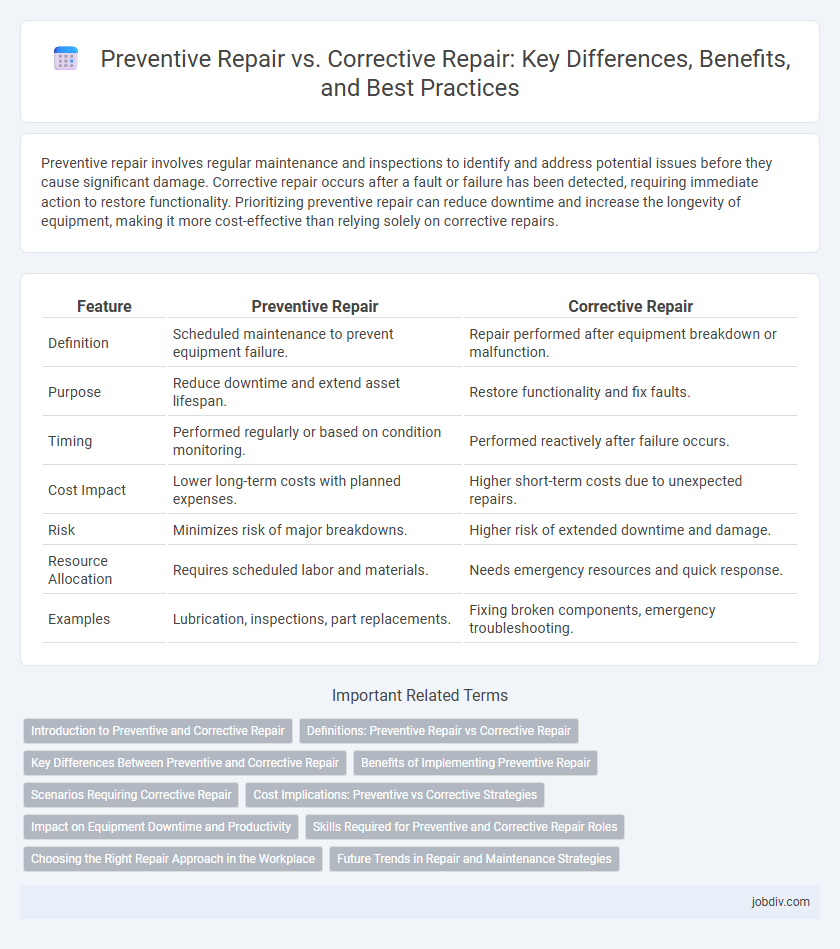
| Feature | Preventive Repair | Corrective Repair |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Scheduled maintenance to prevent equipment failure. | Repair performed after equipment breakdown or malfunction. |
| Purpose | Reduce downtime and extend asset lifespan. | Restore functionality and fix faults. |
| Timing | Performed regularly or based on condition monitoring. | Performed reactively after failure occurs. |
| Cost Impact | Lower long-term costs with planned expenses. | Higher short-term costs due to unexpected repairs. |
| Risk | Minimizes risk of major breakdowns. | Higher risk of extended downtime and damage. |
| Resource Allocation | Requires scheduled labor and materials. | Needs emergency resources and quick response. |
| Examples | Lubrication, inspections, part replacements. | Fixing broken components, emergency troubleshooting. |
Introduction to Preventive and Corrective Repair
Preventive repair involves routine maintenance tasks designed to identify and resolve potential issues before they result in equipment failure, enhancing reliability and reducing downtime. Corrective repair occurs after a fault or breakdown, focusing on diagnosing and fixing the problem to restore equipment functionality. Implementing a strategic balance between preventive and corrective repair optimizes asset performance and extends machinery lifespan.
Definitions: Preventive Repair vs Corrective Repair
Preventive repair involves routine maintenance tasks designed to prevent equipment failures and extend asset lifespan by addressing potential issues before they occur. Corrective repair refers to fixing malfunctions or breakdowns after they have happened, restoring equipment to its proper working condition. These two approaches balance proactive maintenance with reactive solutions to optimize operational efficiency.
Key Differences Between Preventive and Corrective Repair
Preventive repair involves scheduled maintenance activities aimed at avoiding equipment failures by regularly inspecting and servicing machinery, which enhances reliability and extends asset lifespan. Corrective repair occurs after a failure or malfunction, focusing on restoring equipment to operational condition, often leading to unexpected downtime and higher repair costs. Key differences include timing and approach: preventive repair is proactive and planned, while corrective repair is reactive and unplanned.
Benefits of Implementing Preventive Repair
Implementing preventive repair significantly reduces equipment downtime by addressing potential issues before they escalate into major failures. This proactive approach extends the lifespan of machinery, leading to lower maintenance costs and improved operational efficiency. Regular maintenance schedules also enhance safety standards and ensure compliance with industry regulations, minimizing the risk of unexpected breakdowns.
Scenarios Requiring Corrective Repair
Scenarios requiring corrective repair typically involve unforeseen equipment failures or breakdowns that disrupt normal operations and demand immediate attention to restore functionality. These situations often arise from sudden mechanical faults, electrical issues, or software malfunctions that were not previously detected or prevented through maintenance. Corrective repair is essential in minimizing downtime and preventing further damage when preventive measures have failed or were not implemented.
Cost Implications: Preventive vs Corrective Strategies
Preventive repair strategies often involve lower long-term costs by minimizing unexpected equipment failures and reducing downtime, which helps avoid expensive emergency fixes. Corrective repair, while sometimes less costly upfront, can lead to significant financial burdens due to sudden breakdowns, lost productivity, and potential damage to other system components. Investing in preventive maintenance enhances asset reliability and operational efficiency, ultimately lowering overall maintenance expenses compared to corrective approaches.
Impact on Equipment Downtime and Productivity
Preventive repair reduces equipment downtime by scheduling maintenance before failures occur, ensuring consistent productivity and minimizing unexpected interruptions. Corrective repair, performed only after breakdowns, often leads to extended downtime and disrupts production schedules, causing significant productivity losses. Implementing preventive repair strategies enhances equipment reliability and operational efficiency compared to corrective repair approaches.
Skills Required for Preventive and Corrective Repair Roles
Preventive repair roles demand skills in routine maintenance, diagnostic analysis, and the ability to anticipate equipment failures to avoid downtime. Corrective repair roles require expertise in troubleshooting, rapid problem-solving, and hands-on technical abilities to restore functionality after breakdowns. Both roles benefit from knowledge of machinery, safety protocols, and effective communication within maintenance teams.
Choosing the Right Repair Approach in the Workplace
Choosing the right repair approach in the workplace significantly impacts equipment longevity and operational efficiency, with preventive repair focusing on scheduled maintenance to avoid breakdowns and corrective repair addressing issues after failure occurs. Implementing preventive repair reduces downtime, minimizes unexpected costs, and enhances safety by proactively identifying potential problems, whereas corrective repair can lead to extended outages and higher emergency repair expenses. Balancing these strategies requires assessing equipment criticality, maintenance budgets, and production schedules to determine the most cost-effective and reliable repair approach.
Future Trends in Repair and Maintenance Strategies
Future trends in repair and maintenance strategies emphasize the shift from corrective repair, which addresses failures after they occur, to preventive repair that anticipates and mitigates potential issues through scheduled maintenance. Integration of IoT sensors and predictive analytics enables real-time monitoring, allowing technicians to perform maintenance based on data-driven forecasts rather than reactive responses. Advances in artificial intelligence and machine learning further optimize repair schedules, reducing downtime and extending equipment lifespan while lowering overall operational costs.
Preventive Repair vs Corrective Repair Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com