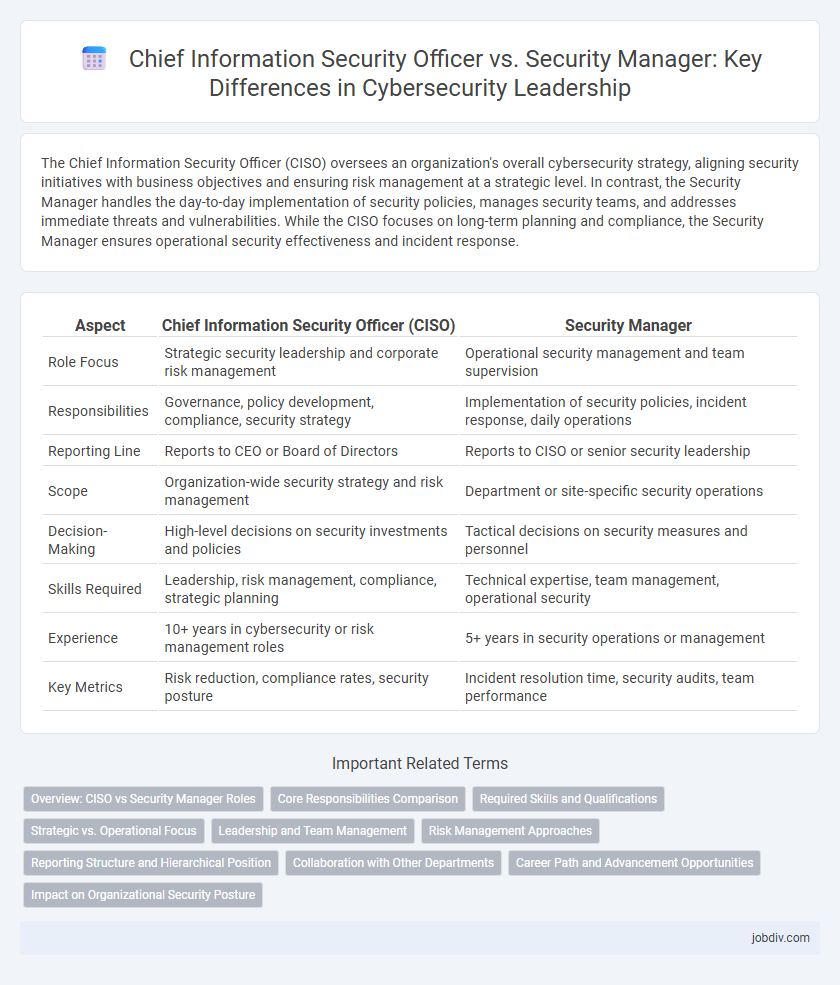
The Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) oversees an organization's overall cybersecurity strategy, aligning security initiatives with business objectives and ensuring risk management at a strategic level. In contrast, the Security Manager handles the day-to-day implementation of security policies, manages security teams, and addresses immediate threats and vulnerabilities. While the CISO focuses on long-term planning and compliance, the Security Manager ensures operational security effectiveness and incident response.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) | Security Manager |
|---|---|---|
| Role Focus | Strategic security leadership and corporate risk management | Operational security management and team supervision |
| Responsibilities | Governance, policy development, compliance, security strategy | Implementation of security policies, incident response, daily operations |
| Reporting Line | Reports to CEO or Board of Directors | Reports to CISO or senior security leadership |
| Scope | Organization-wide security strategy and risk management | Department or site-specific security operations |
| Decision-Making | High-level decisions on security investments and policies | Tactical decisions on security measures and personnel |
| Skills Required | Leadership, risk management, compliance, strategic planning | Technical expertise, team management, operational security |
| Experience | 10+ years in cybersecurity or risk management roles | 5+ years in security operations or management |
| Key Metrics | Risk reduction, compliance rates, security posture | Incident resolution time, security audits, team performance |
Overview: CISO vs Security Manager Roles
The Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) oversees the organization's entire cybersecurity strategy, aligning security initiatives with business objectives and managing risk at the executive level. A Security Manager focuses on implementing and maintaining security operations, supervising security teams, and handling day-to-day incident response and compliance tasks. While the CISO drives policy and strategic direction, the Security Manager ensures practical execution and operational security effectiveness.
Core Responsibilities Comparison
The Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) oversees the organization's entire cybersecurity strategy, including risk management, compliance, and aligning security initiatives with business goals. In contrast, the Security Manager focuses on implementing and managing day-to-day security operations, incident response, and team supervision. The CISO drives high-level policy development and executive reporting, while the Security Manager handles tactical enforcement and operational security controls.
Required Skills and Qualifications
A Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) requires advanced expertise in cybersecurity strategy, risk management, regulatory compliance, and leadership, often holding certifications such as CISSP, CISM, or CISA alongside extensive experience in executive decision-making. Security Managers need strong technical knowledge in network security, incident response, and security policy implementation, typically supported by certifications like CompTIA Security+, CEH, or SSCP, and experience managing security teams. Both roles demand excellent communication skills, but the CISO focuses more on aligning security initiatives with business goals, while Security Managers emphasize operational execution and team coordination.
Strategic vs. Operational Focus
The Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) drives the organization's cybersecurity strategy, aligning security initiatives with business goals and overseeing risk management at the executive level. In contrast, the Security Manager focuses on operational execution, managing daily security activities, enforcing policies, and responding to incidents. This strategic versus operational focus delineates the CISO's role in long-term planning from the Security Manager's hands-on approach to security implementation.
Leadership and Team Management
The Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) leads enterprise-wide security strategy, aligning cybersecurity initiatives with business goals and managing cross-functional teams. The Security Manager focuses on operational leadership, overseeing daily security activities and directly managing security personnel to ensure policy compliance and incident response. Effective leadership in cybersecurity requires the CISO's strategic vision combined with the Security Manager's hands-on team management for robust protection.
Risk Management Approaches
The Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) establishes enterprise-wide risk management frameworks, aligning security strategies with organizational goals and regulatory compliance requirements. Security Managers implement these frameworks through operational risk assessments and incident response plans, ensuring day-to-day security controls effectively mitigate identified threats. CISOs focus on strategic risk prioritization and resource allocation, while Security Managers handle tactical risk mitigation and continuous monitoring.
Reporting Structure and Hierarchical Position
The Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) typically reports directly to the CEO or CIO, reflecting a high-ranking executive position responsible for enterprise-wide security strategy and policy development. Security Managers usually report to the CISO or IT Director, holding a mid-level role focused on managing security operations and enforcing policies within specific departments or regions. The hierarchical position of the CISO is senior, emphasizing strategic oversight, whereas Security Managers operate with tactical responsibility and day-to-day implementation of security measures.
Collaboration with Other Departments
The Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) leads strategic collaboration across departments to align security initiatives with business objectives, fostering a unified approach to risk management. Security Managers engage closely with IT, legal, and compliance teams to implement policies and ensure operational security measures are consistently applied. Both roles require effective communication and coordination to create a resilient security posture throughout the organization.
Career Path and Advancement Opportunities
Chief Information Security Officers (CISOs) typically have a broader strategic role overseeing enterprise-wide information security programs, often advancing from senior security management or executive leadership positions. Security Managers usually focus on operational aspects of security teams and systems, serving as a critical stepping stone toward higher executive roles such as CISO or Director of Security. Career advancement for CISOs involves enhanced responsibilities in risk management, governance, and cross-departmental collaboration, whereas Security Managers gain depth in technical and team leadership skills critical for progression.
Impact on Organizational Security Posture
The Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) shapes the strategic vision and governance frameworks that define an organization's overall security posture, ensuring alignment with business objectives and regulatory compliance. In contrast, the Security Manager implements and oversees operational security controls, incident response, and day-to-day risk mitigation activities. Together, CISOs and Security Managers drive a resilient defense ecosystem by bridging high-level security strategy with tactical execution.
Chief Information Security Officer vs Security Manager Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com