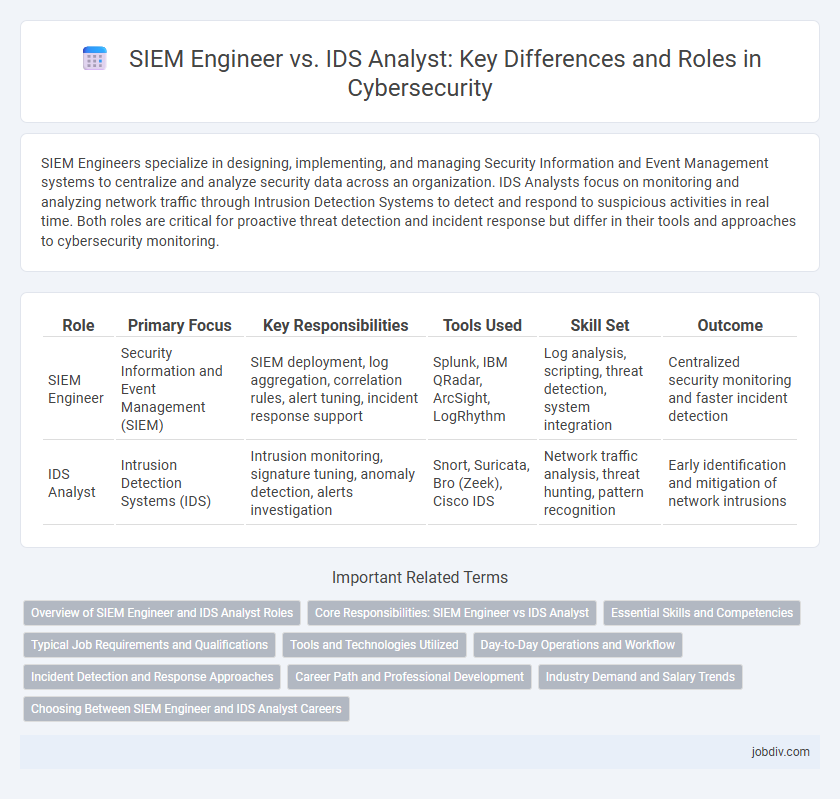
SIEM Engineers specialize in designing, implementing, and managing Security Information and Event Management systems to centralize and analyze security data across an organization. IDS Analysts focus on monitoring and analyzing network traffic through Intrusion Detection Systems to detect and respond to suspicious activities in real time. Both roles are critical for proactive threat detection and incident response but differ in their tools and approaches to cybersecurity monitoring.
Table of Comparison
| Role | Primary Focus | Key Responsibilities | Tools Used | Skill Set | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SIEM Engineer | Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) | SIEM deployment, log aggregation, correlation rules, alert tuning, incident response support | Splunk, IBM QRadar, ArcSight, LogRhythm | Log analysis, scripting, threat detection, system integration | Centralized security monitoring and faster incident detection |
| IDS Analyst | Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) | Intrusion monitoring, signature tuning, anomaly detection, alerts investigation | Snort, Suricata, Bro (Zeek), Cisco IDS | Network traffic analysis, threat hunting, pattern recognition | Early identification and mitigation of network intrusions |
Overview of SIEM Engineer and IDS Analyst Roles
SIEM Engineers design, implement, and manage Security Information and Event Management systems to collect and analyze security data from various sources for threat detection and compliance reporting. IDS Analysts focus on monitoring and analyzing Intrusion Detection System alerts to identify and respond to potential security breaches in real-time. Both roles collaborate to strengthen organizational cybersecurity by leveraging data analytics and incident response capabilities.
Core Responsibilities: SIEM Engineer vs IDS Analyst
SIEM Engineers primarily focus on designing, implementing, and managing Security Information and Event Management systems to collect, analyze, and correlate security data for threat detection. IDS Analysts specialize in monitoring Intrusion Detection Systems to identify and respond to network-based threats and suspicious activities, ensuring real-time detection and incident response. Both roles require deep knowledge of cybersecurity tools but differ in scope, with SIEM Engineers handling broader data aggregation and correlation, while IDS Analysts concentrate on specific intrusion alerts and network security events.
Essential Skills and Competencies
SIEM Engineers require expertise in security information and event management platforms, proficiency in log analysis, correlation rules, and incident response automation, alongside scripting skills for customization and integration. IDS Analysts must excel in network traffic analysis, intrusion detection system configuration, real-time threat identification, and forensic investigation to detect and mitigate security breaches effectively. Both roles demand strong knowledge of cybersecurity frameworks, threat intelligence, and continuous monitoring to protect organizational assets.
Typical Job Requirements and Qualifications
SIEM Engineers require expertise in security information and event management platforms such as Splunk, QRadar, or ArcSight, alongside strong skills in log analysis, threat detection, and incident response automation. IDS Analysts need proficiency in intrusion detection systems like Snort or Suricata, deep knowledge of network protocols, and the ability to analyze alerts to identify false positives and real threats. Both roles typically demand certifications such as CISSP, CEH, or GIAC and experience in cybersecurity frameworks and scripting languages for effective threat monitoring and mitigation.
Tools and Technologies Utilized
SIEM Engineers primarily utilize Security Information and Event Management platforms like Splunk, IBM QRadar, and ArcSight to centralize and analyze security data from diverse sources. IDS Analysts focus on Intrusion Detection Systems such as Snort, Suricata, and Cisco Secure IDS to monitor network traffic and identify potential threats in real time. Both roles leverage advanced alerting, correlation engines, and threat intelligence integration to enhance organizational security posture.
Day-to-Day Operations and Workflow
SIEM Engineers focus on configuring, managing, and fine-tuning Security Information and Event Management systems to correlate and analyze large volumes of security data for threat detection. IDS Analysts specialize in monitoring and interpreting alerts from Intrusion Detection Systems to identify and respond to potential intrusions in real time. Both roles involve continuous log analysis, incident investigation, and collaboration with security teams to ensure proactive defense and rapid incident response.
Incident Detection and Response Approaches
SIEM Engineers focus on integrating, correlating, and analyzing large volumes of security event data from multiple sources to provide comprehensive incident detection and response through centralized dashboards and automated alerting. IDS Analysts specialize in monitoring network traffic and system activities for signs of malicious behavior or policy violations, employing signature-based and anomaly-based detection techniques to identify and respond to threats in real-time. SIEM solutions offer a broader, holistic incident response framework, while IDS tools provide focused, granular intrusion detection capabilities critical for rapid threat identification.
Career Path and Professional Development
SIEM Engineers specialize in integrating and managing Security Information and Event Management systems, advancing their careers through expertise in platform customization and incident correlation methodologies. IDS Analysts focus on monitoring and analyzing Intrusion Detection Systems to identify threats, developing skills in threat intelligence and signature tuning. Both paths offer professional development opportunities in cybersecurity certifications like CISSP, CEH, and advanced training in network forensics and threat hunting.
Industry Demand and Salary Trends
SIEM Engineers are in high demand due to their expertise in managing complex security information and event management systems, with average salaries ranging from $90,000 to $130,000 annually depending on experience and location. IDS Analysts typically focus on intrusion detection systems and threat analysis, commanding salaries between $70,000 and $110,000, reflecting the growing need for specialized threat detection roles. The industry trend shows a rising preference for SIEM Engineers as organizations prioritize integrated security monitoring and analytics to combat sophisticated cyber threats.
Choosing Between SIEM Engineer and IDS Analyst Careers
SIEM Engineers specialize in designing and managing Security Information and Event Management systems to collect and analyze security data in real-time, providing comprehensive threat detection across an organization's entire network. IDS Analysts focus on monitoring and analyzing Intrusion Detection Systems to identify and respond to specific security incidents by examining network traffic and alert patterns. Choosing between these careers depends on interest in strategic data integration and correlation for SIEM Engineers versus hands-on threat hunting and incident response for IDS Analysts.
SIEM Engineer vs IDS Analyst Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com