Technical writers focus on creating clear, concise manuals and guides that explain complex technologies for end-users. Documentation specialists manage and organize technical documents, ensuring accuracy, consistency, and easy accessibility across platforms. Both roles require strong writing skills but differ in scope, where technical writers produce content and documentation specialists oversee content lifecycle management.
Table of Comparison
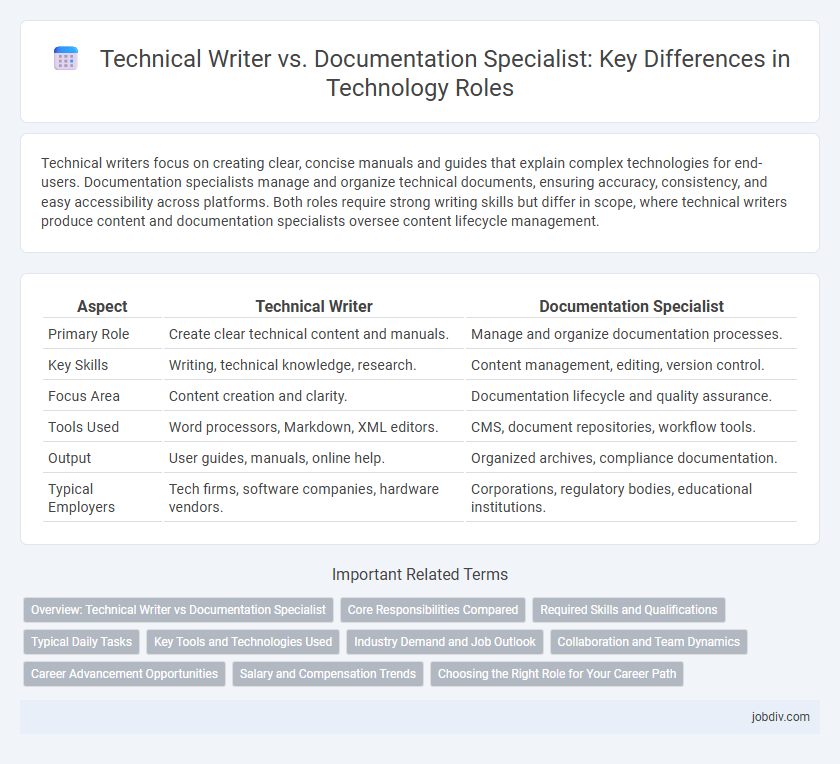
| Aspect | Technical Writer | Documentation Specialist |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Create clear technical content and manuals. | Manage and organize documentation processes. |
| Key Skills | Writing, technical knowledge, research. | Content management, editing, version control. |
| Focus Area | Content creation and clarity. | Documentation lifecycle and quality assurance. |
| Tools Used | Word processors, Markdown, XML editors. | CMS, document repositories, workflow tools. |
| Output | User guides, manuals, online help. | Organized archives, compliance documentation. |
| Typical Employers | Tech firms, software companies, hardware vendors. | Corporations, regulatory bodies, educational institutions. |
Overview: Technical Writer vs Documentation Specialist
Technical Writers focus on creating clear, user-friendly manuals, guides, and instructional content tailored for end-users to understand complex technology products. Documentation Specialists manage, organize, and maintain technical documents, ensuring accuracy, version control, and accessibility within a company's knowledge base. Both roles are crucial in technology environments but differ in content creation versus document management priorities.
Core Responsibilities Compared
Technical Writers primarily create clear, concise instructional content such as manuals, user guides, and online help for software and hardware products, focusing on translating complex technical information into accessible language. Documentation Specialists manage and organize technical content repositories, ensuring the accuracy, consistency, and proper version control of documents across various platforms. While Technical Writers emphasize content creation, Documentation Specialists prioritize content management and workflow optimization in technical communication processes.
Required Skills and Qualifications
Technical Writers require strong proficiency in writing, editing, and understanding complex technical concepts, often needing expertise in software tools like Adobe FrameMaker, MadCap Flare, or Microsoft Office Suite. Documentation Specialists emphasize meticulous attention to detail, organizational skills, and knowledge of content management systems (CMS) and version control software such as Git. Both roles demand excellent communication skills, familiarity with audience analysis, and the ability to collaborate effectively with engineers, product managers, and subject matter experts.
Typical Daily Tasks
Technical Writers create clear, concise manuals, guides, and FAQs by translating complex technical information into user-friendly content. Documentation Specialists manage and organize documentation workflows, ensuring accuracy, version control, and compliance with industry standards. Both roles frequently collaborate with developers and subject matter experts to update and maintain technical documents.
Key Tools and Technologies Used
Technical Writers primarily use tools like MadCap Flare, Adobe FrameMaker, and Microsoft Word for creating detailed manuals and guides, while Documentation Specialists often work with content management systems (CMS) such as Confluence and SharePoint to organize and maintain documentation libraries. Both roles utilize version control platforms like Git and collaboration tools such as Slack and Jira to ensure accuracy and streamline workflow. Proficiency in XML, HTML, and Markdown enhances content formatting and integration across multiple publishing platforms.
Industry Demand and Job Outlook
Technical Writers and Documentation Specialists both play vital roles in creating clear, user-friendly content, but the demand for Technical Writers is experiencing faster growth due to the expanding technology sector. Industry trends indicate a 10% increase in Technical Writer job openings over the next decade, driven by advancements in software, hardware, and complex technical products. Documentation Specialists are essential in maintaining and organizing content, with steady demand in industries like healthcare and manufacturing, but the broader tech industry's rapid evolution positions Technical Writers for more dynamic career opportunities.
Collaboration and Team Dynamics
Technical Writers and Documentation Specialists play distinct but complementary roles in collaborative technology environments, with Technical Writers focusing on creating clear, user-centric content and Documentation Specialists ensuring the accuracy and consistency of technical materials. Both professionals engage closely with engineers, product managers, and UX designers to align documentation with evolving project requirements and user feedback. Effective teamwork hinges on seamless communication and shared responsibility for maintaining high standards in technical communication deliverables.
Career Advancement Opportunities
Technical Writers often advance into senior writing roles, content strategy, or project management within technology firms due to their expertise in creating user manuals, software documentation, and technical guides. Documentation Specialists may transition into roles like information architects or knowledge managers, leveraging their skills in organizing and maintaining comprehensive document repositories for complex tech systems. Both career paths offer opportunities for specialization and leadership in documentation processes, but Technical Writers typically have broader options in creative and strategic content development.
Salary and Compensation Trends
Technical Writers typically earn median salaries ranging from $60,000 to $80,000 annually, while Documentation Specialists often see compensation between $55,000 and $75,000, reflecting slight market variances. Salary trends indicate growing demand for Technical Writers with expertise in complex software and regulatory compliance, driving higher pay scales. Organizations increasingly reward Documentation Specialists with performance bonuses as documentation quality directly impacts product usability and customer satisfaction.
Choosing the Right Role for Your Career Path
Technical Writers craft clear, concise manuals and guides, emphasizing content creation and user comprehension. Documentation Specialists manage the organization, maintenance, and accessibility of technical documents, often integrating content management systems and quality assurance processes. Selecting the right role depends on your strengths in writing clarity versus your skills in systematic organization and document lifecycle management.
Technical Writer vs Documentation Specialist Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com