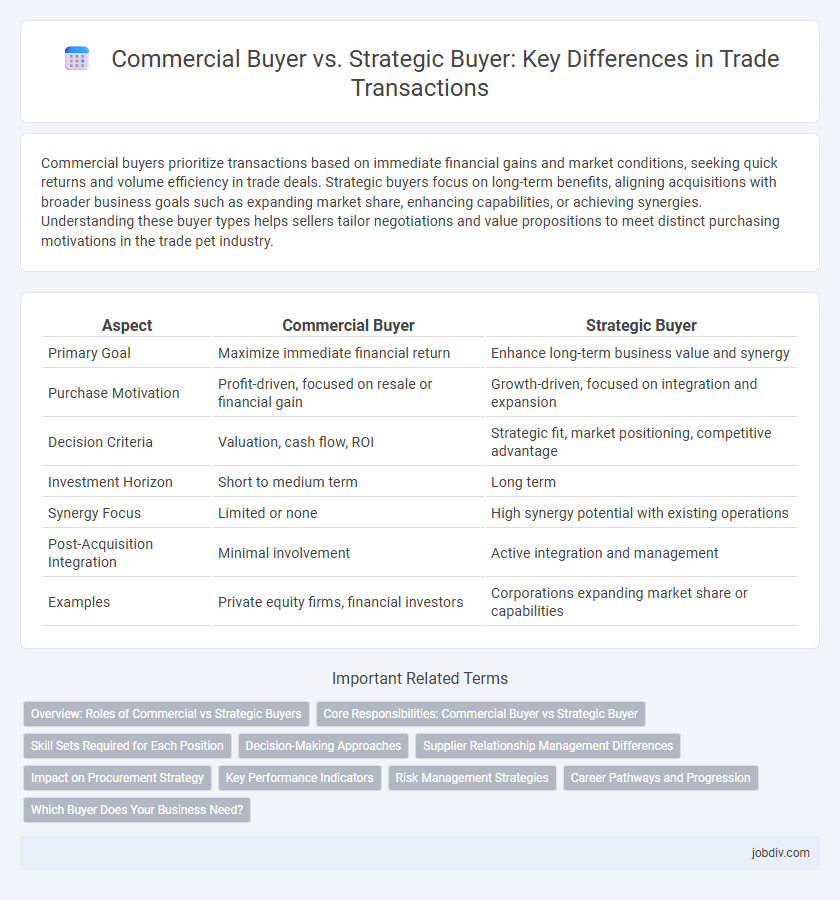
Commercial buyers prioritize transactions based on immediate financial gains and market conditions, seeking quick returns and volume efficiency in trade deals. Strategic buyers focus on long-term benefits, aligning acquisitions with broader business goals such as expanding market share, enhancing capabilities, or achieving synergies. Understanding these buyer types helps sellers tailor negotiations and value propositions to meet distinct purchasing motivations in the trade pet industry.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Commercial Buyer | Strategic Buyer |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Maximize immediate financial return | Enhance long-term business value and synergy |
| Purchase Motivation | Profit-driven, focused on resale or financial gain | Growth-driven, focused on integration and expansion |
| Decision Criteria | Valuation, cash flow, ROI | Strategic fit, market positioning, competitive advantage |
| Investment Horizon | Short to medium term | Long term |
| Synergy Focus | Limited or none | High synergy potential with existing operations |
| Post-Acquisition Integration | Minimal involvement | Active integration and management |
| Examples | Private equity firms, financial investors | Corporations expanding market share or capabilities |
Overview: Roles of Commercial vs Strategic Buyers
Commercial buyers focus on purchasing products or services to meet immediate operational needs, emphasizing cost-efficiency and transactional value. Strategic buyers prioritize long-term impact, seeking acquisitions that align with broader corporate goals, such as market expansion or technological advancement. The distinct roles influence negotiation tactics, decision-making processes, and value assessment criteria in trade deals.
Core Responsibilities: Commercial Buyer vs Strategic Buyer
Commercial buyers focus on procuring goods and services at the best price and quality to meet immediate operational needs, managing supplier relationships, and ensuring timely delivery. Strategic buyers prioritize long-term value creation through supplier development, risk management, and alignment with the company's broader business objectives. Core responsibilities of strategic buyers include market analysis, strategic sourcing initiatives, and fostering innovation within the supply chain.
Skill Sets Required for Each Position
Commercial buyers require strong negotiation skills, market analysis expertise, and the ability to manage supplier relationships efficiently to optimize procurement costs. Strategic buyers need advanced analytical capabilities, long-term planning skills, and cross-functional collaboration to align purchases with overall business strategy and sustain competitive advantage. Both roles demand proficiency in risk management and contract administration, but strategic buyers emphasize innovation sourcing and trend forecasting more heavily.
Decision-Making Approaches
Commercial buyers prioritize cost-efficiency and operational compatibility, focusing on short-term ROI and transactional benefits during decision-making. Strategic buyers emphasize long-term value creation, considering factors like market expansion, competitive advantage, and synergy integration. Their approach incorporates comprehensive due diligence and alignment with broader corporate objectives beyond immediate financial metrics.
Supplier Relationship Management Differences
Commercial buyers typically emphasize transactional efficiency and cost savings, prioritizing short-term supplier contracts and competitive pricing to meet immediate procurement needs. Strategic buyers focus on long-term partnerships, fostering collaborative innovation and integrated supply chains that enhance value creation and risk mitigation over time. Supplier relationship management for strategic buyers involves continuous performance improvement, joint development initiatives, and alignment with overall business strategy, whereas commercial buyers maintain arm's-length interactions centered on price and delivery terms.
Impact on Procurement Strategy
Commercial buyers prioritize cost efficiency and short-term savings, influencing procurement strategies to focus on competitive pricing and transactional negotiations. Strategic buyers emphasize long-term partnerships and value creation, steering procurement toward supplier collaboration, innovation, and risk management. This distinction affects supplier selection, contract terms, and overall supply chain resilience in procurement planning.
Key Performance Indicators
Commercial buyers prioritize short-term financial metrics such as revenue growth, profit margins, and cost efficiency to evaluate potential acquisitions. Strategic buyers emphasize long-term KPIs, including market share expansion, synergies creation, and integration success rates to align acquisitions with overarching business goals. Both buyer types monitor customer retention and operational scalability as crucial indicators of acquisition value.
Risk Management Strategies
Commercial buyers typically focus on transactional risk management by leveraging volume discounts and securing standard contractual terms to minimize immediate financial exposure. Strategic buyers emphasize long-term risk mitigation through relationship-building, aligning acquisitions with corporate growth objectives, and integrating supply chain resilience measures. Both approaches deploy tailored due diligence to identify operational vulnerabilities and market fluctuations, optimizing procurement risk management.
Career Pathways and Progression
Commercial buyers typically follow a career path focused on procurement efficiency, cost management, and supplier relations, progressing from junior purchasing roles to senior procurement managers or supply chain directors. Strategic buyers advance by emphasizing long-term partnerships, market analysis, and value creation, often moving into roles like strategic sourcing director, category manager, or chief procurement officer. Both pathways require strong negotiation skills and industry knowledge, but strategic buying careers demand a deeper focus on aligning purchasing strategies with overall business goals for sustained competitive advantage.
Which Buyer Does Your Business Need?
Choosing between a commercial buyer and a strategic buyer depends on your business goals and long-term vision. Commercial buyers prioritize financial returns and operational efficiency, offering a straightforward transaction focused on profitability. Strategic buyers seek synergy and integration opportunities, aiming to enhance their existing business through the acquisition, which can drive growth but may involve complex negotiations and alignment of corporate cultures.
Commercial Buyer vs Strategic Buyer Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com