Commodity traders specialize in the buying and selling of physical goods such as oil, gold, and agricultural products, analyzing supply chain factors and market demand to determine pricing. Currency traders focus on the forex market, trading currency pairs by evaluating economic indicators, interest rates, and geopolitical events to anticipate exchange rate movements. Both roles require a deep understanding of market trends, risk management, and technical analysis to maximize profitability.
Table of Comparison
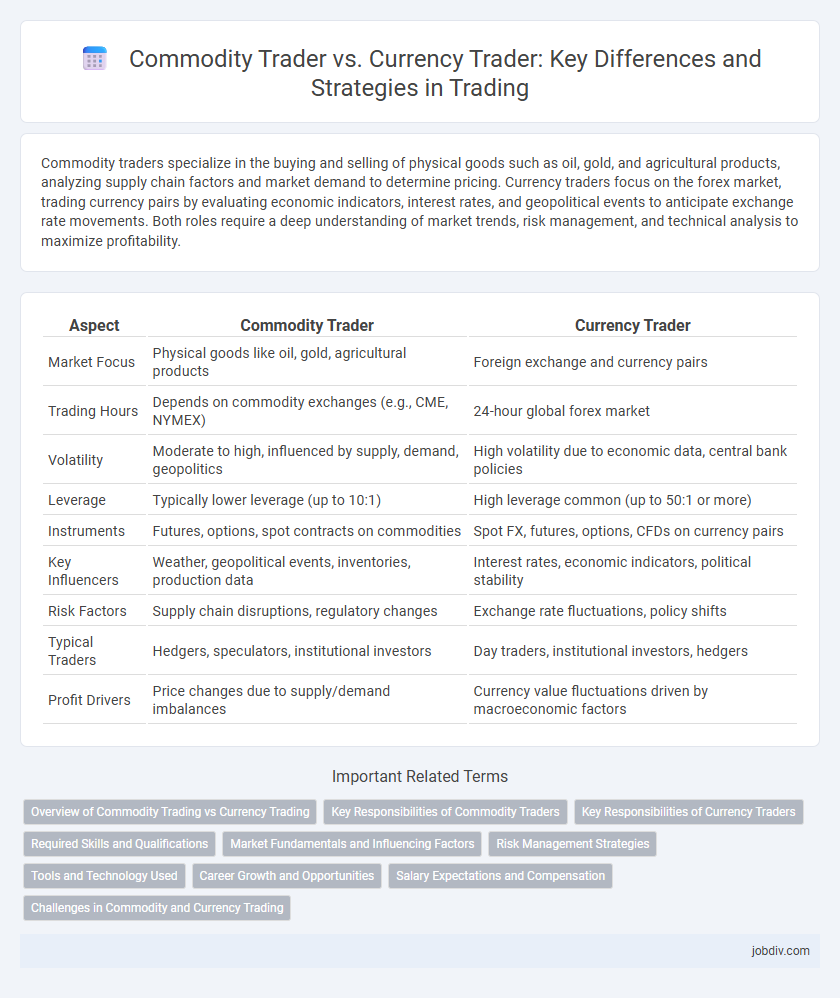
| Aspect | Commodity Trader | Currency Trader |
|---|---|---|
| Market Focus | Physical goods like oil, gold, agricultural products | Foreign exchange and currency pairs |
| Trading Hours | Depends on commodity exchanges (e.g., CME, NYMEX) | 24-hour global forex market |
| Volatility | Moderate to high, influenced by supply, demand, geopolitics | High volatility due to economic data, central bank policies |
| Leverage | Typically lower leverage (up to 10:1) | High leverage common (up to 50:1 or more) |
| Instruments | Futures, options, spot contracts on commodities | Spot FX, futures, options, CFDs on currency pairs |
| Key Influencers | Weather, geopolitical events, inventories, production data | Interest rates, economic indicators, political stability |
| Risk Factors | Supply chain disruptions, regulatory changes | Exchange rate fluctuations, policy shifts |
| Typical Traders | Hedgers, speculators, institutional investors | Day traders, institutional investors, hedgers |
| Profit Drivers | Price changes due to supply/demand imbalances | Currency value fluctuations driven by macroeconomic factors |
Overview of Commodity Trading vs Currency Trading
Commodity trading involves buying and selling physical goods like oil, gold, or agricultural products, with prices influenced by supply, demand, and geopolitical factors. Currency trading, or forex trading, focuses on exchanging national currencies, driven by interest rates, economic indicators, and global market sentiment. Both markets offer high liquidity but differ in volatility patterns and underlying assets.
Key Responsibilities of Commodity Traders
Commodity traders manage the buying and selling of physical goods such as oil, metals, and agricultural products, ensuring timely delivery and quality compliance. They analyze market trends, supply chain logistics, and geopolitical factors to make informed decisions on price fluctuations and inventory management. Risk assessment and contract negotiation are also critical responsibilities to secure profitable trades in volatile commodity markets.
Key Responsibilities of Currency Traders
Currency traders analyze global economic indicators, monitor geopolitical events, and execute foreign exchange transactions to capitalize on currency fluctuations. They manage risk by employing hedging strategies and use technical and fundamental analysis to predict market trends. Their key responsibility is ensuring optimal timing and pricing in buying or selling currencies to maximize profit in the volatile forex market.
Required Skills and Qualifications
Commodity traders require strong analytical skills in market trends, a deep understanding of supply chain logistics, and expertise in commodities like oil, metals, or agricultural products. Currency traders need proficiency in macroeconomic analysis, foreign exchange markets, and risk management, alongside the ability to operate under high-pressure environments. Both roles demand sharp decision-making abilities, proficiency in trading platforms, and often a background in finance, economics, or related fields.
Market Fundamentals and Influencing Factors
Commodity traders analyze supply-demand dynamics driven by factors such as weather conditions, geopolitical events, and global production levels that affect physical goods like oil, metals, and agricultural products. Currency traders focus on macroeconomic indicators, interest rate differentials, inflation rates, and central bank policies that influence forex market movements. Understanding these distinct fundamentals helps traders develop strategies tailored to the volatility and liquidity characteristic of each market type.
Risk Management Strategies
Commodity traders mitigate risks using hedging techniques such as futures contracts and options to protect against price volatility in raw materials like oil and grains. Currency traders focus on managing exchange rate risks through stop-loss orders, position sizing, and diversification across multiple currency pairs to limit exposure to currency fluctuations. Both rely on real-time market data and technical analysis tools to make informed, risk-adjusted trading decisions.
Tools and Technology Used
Commodity traders utilize specialized platforms such as Bloomberg Terminal and Thomson Reuters Eikon, integrating real-time market data and analytics for commodities like oil, metals, and agricultural products. Currency traders rely heavily on forex trading platforms like MetaTrader 4 and 5, leveraging advanced algorithmic trading tools, automated bots, and high-frequency trading systems to capitalize on currency pair fluctuations. Both use risk management software and API integrations but differ in market data sources and technical analysis tools tailored to their specific asset classes.
Career Growth and Opportunities
Commodity traders specialize in physical goods like oil, metals, and agricultural products, offering career growth through roles in risk management, trading floors, and supply chain analytics. Currency traders focus on the foreign exchange market, with opportunities in global finance institutions, hedge funds, and central banks, emphasizing rapid decision-making and market analysis. Both paths demand strong analytical skills but differ in market volatility, asset types, and regulatory environments, influencing long-term career trajectories and compensation structures.
Salary Expectations and Compensation
Commodity traders typically earn higher base salaries ranging from $80,000 to $150,000 annually, with total compensation often exceeding $300,000 including bonuses tied to performance and market volatility. Currency traders' salaries usually start lower, around $60,000 to $120,000, but high-performing traders can also surpass $250,000 through commissions and profit-sharing schemes. Both roles demand strong analytical skills and risk tolerance, influencing compensation variability based on market conditions and trading success.
Challenges in Commodity and Currency Trading
Commodity traders face challenges such as price volatility driven by supply disruptions, geopolitical tensions, and weather conditions affecting physical goods. Currency traders encounter complexities due to global macroeconomic factors, interest rate differentials, and central bank policies that influence exchange rates. Both markets require managing liquidity risks and executing timely trades amid rapidly changing market sentiments.
Commodity Trader vs Currency Trader Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com