Import brokers specialize in facilitating the movement of goods into a country by managing customs documentation, tariffs, and compliance with local regulations. Export brokers focus on arranging the shipment of products out of the country, ensuring adherence to export laws, licensing requirements, and international trade standards. Both brokers play critical roles in optimizing supply chains and reducing trade barriers, but their expertise centers on different sides of global commerce.
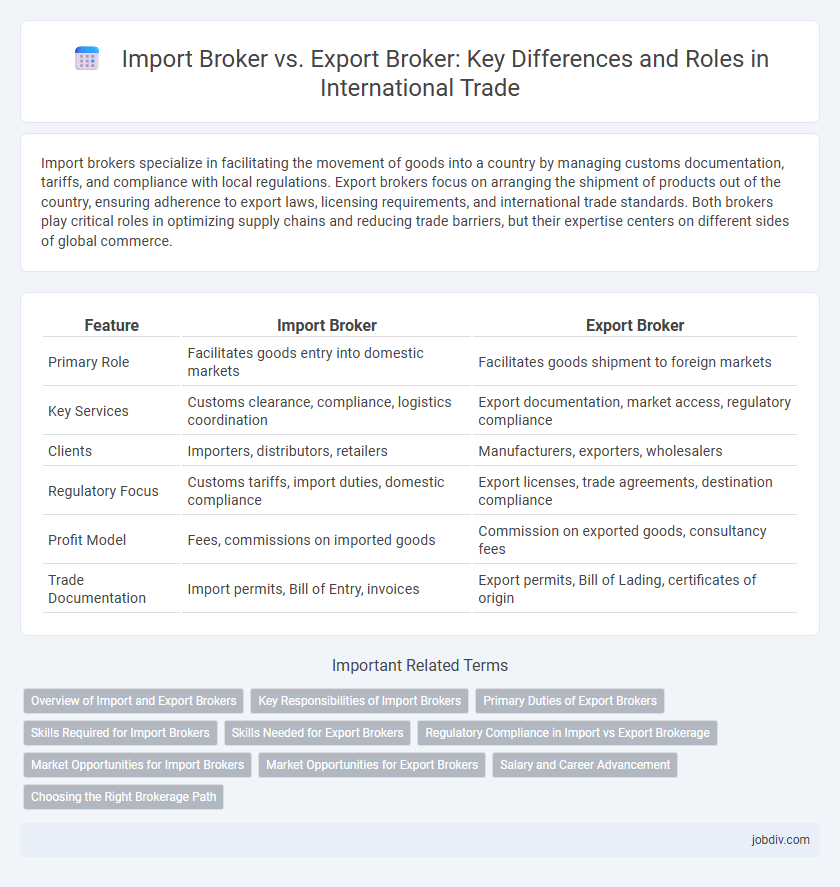
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Import Broker | Export Broker |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Facilitates goods entry into domestic markets | Facilitates goods shipment to foreign markets |
| Key Services | Customs clearance, compliance, logistics coordination | Export documentation, market access, regulatory compliance |
| Clients | Importers, distributors, retailers | Manufacturers, exporters, wholesalers |
| Regulatory Focus | Customs tariffs, import duties, domestic compliance | Export licenses, trade agreements, destination compliance |
| Profit Model | Fees, commissions on imported goods | Commission on exported goods, consultancy fees |
| Trade Documentation | Import permits, Bill of Entry, invoices | Export permits, Bill of Lading, certificates of origin |
Overview of Import and Export Brokers
Import brokers specialize in facilitating the purchase and delivery of foreign goods into a domestic market, handling customs clearance, tariffs, and regulatory compliance to ensure smooth transactions. Export brokers focus on connecting domestic sellers with international buyers, managing export documentation, shipping logistics, and adherence to foreign trade regulations. Both roles are crucial in global trade, streamlining cross-border transactions and reducing risks associated with international commerce.
Key Responsibilities of Import Brokers
Import brokers specialize in managing customs clearance, ensuring compliance with import regulations, and facilitating the smooth entry of goods into a country. They handle documentation such as the Bill of Lading, customs declarations, and tariff classifications to prevent delays and penalties. Their expertise in navigating import tariffs, duties, and regulations is essential for reducing costs and expediting deliveries in global trade.
Primary Duties of Export Brokers
Export brokers primarily facilitate international sales by connecting domestic exporters with foreign buyers, ensuring smooth transaction processes. They specialize in negotiating contracts, handling documentation like export licenses, and coordinating logistics to meet compliance with international trade regulations. Their expertise helps optimize export operations, reduce risks, and expand market access for exporting businesses.
Skills Required for Import Brokers
Import brokers require strong knowledge of customs regulations, international trade laws, and tariff classifications to ensure smooth clearance of goods. Proficiency in communication and negotiation skills is essential for coordinating with suppliers, customs officials, and clients to resolve issues efficiently. Analytical abilities and attention to detail enable import brokers to manage documentation, monitor shipments, and optimize supply chain processes effectively.
Skills Needed for Export Brokers
Export brokers require strong knowledge of international trade regulations, proficient communication skills for negotiating with foreign buyers, and expertise in logistics coordination to ensure smooth shipment processes. They must be adept at market analysis to identify export opportunities and compliance with customs documentation and export licensing. Additionally, cultural awareness and language skills enhance their ability to build trust and manage relationships in diverse global markets.
Regulatory Compliance in Import vs Export Brokerage
Import brokers must navigate complex customs regulations, requiring thorough knowledge of import tariffs, duties, and compliance with country-specific import restrictions to avoid delays and fines. Export brokers focus on export controls, including adherence to international trade agreements and export licensing requirements, ensuring goods meet destination country standards and embargo regulations. Both roles demand meticulous documentation and adherence to governmental policies to facilitate smooth cross-border transactions and mitigate legal risks.
Market Opportunities for Import Brokers
Import brokers leverage expanding global supply chains to connect domestic buyers with international sellers, capitalizing on rising demand for diverse products. They facilitate market entry for foreign manufacturers by navigating customs regulations and ensuring compliance, creating seamless trade flows. By specializing in import logistics and market intelligence, import brokers unlock new revenue streams and foster competitive advantages in import-driven sectors.
Market Opportunities for Export Brokers
Export brokers capitalize on expanding global demand by connecting domestic producers with international buyers, facilitating access to untapped markets. They specialize in navigating complex export regulations and customs procedures, ensuring smooth cross-border transactions that increase market reach and revenue potential. Their expertise in foreign market trends and trade agreements provides critical insights that help exporters identify profitable opportunities and mitigate risks.
Salary and Career Advancement
Import brokers typically earn an average annual salary ranging from $45,000 to $70,000, depending on experience and location, while export brokers often command slightly higher salaries due to increased complexity in international regulations. Career advancement for import brokers tends to involve moving into logistics management or customs compliance roles, whereas export brokers can progress into international sales management or global trade consultancy positions. Both roles offer opportunities for certification and specialization that significantly enhance earning potential and professional growth in the trade industry.
Choosing the Right Brokerage Path
Selecting the right brokerage path depends on your business goals and market focus; import brokers specialize in facilitating the entry of foreign goods, ensuring compliance with customs regulations and local standards. Export brokers streamline the sale and shipment of domestic products to international buyers, handling documentation and trade agreements to maximize global reach. Evaluating your supply chain needs, target markets, and regulatory environments helps determine whether an import broker or export broker aligns best with your trade strategy.
Import Broker vs Export Broker Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com