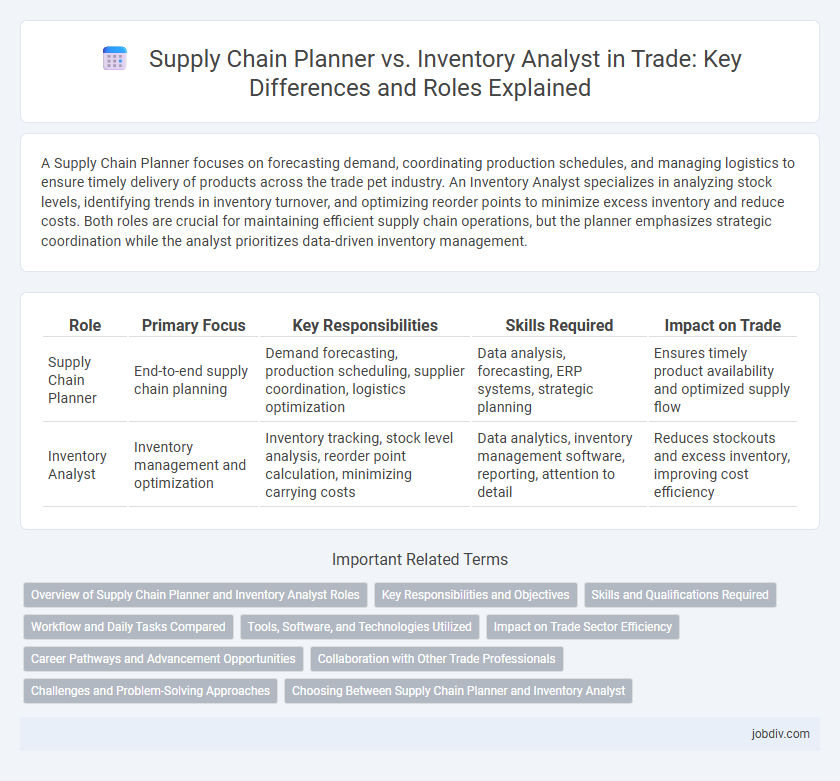
A Supply Chain Planner focuses on forecasting demand, coordinating production schedules, and managing logistics to ensure timely delivery of products across the trade pet industry. An Inventory Analyst specializes in analyzing stock levels, identifying trends in inventory turnover, and optimizing reorder points to minimize excess inventory and reduce costs. Both roles are crucial for maintaining efficient supply chain operations, but the planner emphasizes strategic coordination while the analyst prioritizes data-driven inventory management.
Table of Comparison
| Role | Primary Focus | Key Responsibilities | Skills Required | Impact on Trade |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supply Chain Planner | End-to-end supply chain planning | Demand forecasting, production scheduling, supplier coordination, logistics optimization | Data analysis, forecasting, ERP systems, strategic planning | Ensures timely product availability and optimized supply flow |
| Inventory Analyst | Inventory management and optimization | Inventory tracking, stock level analysis, reorder point calculation, minimizing carrying costs | Data analytics, inventory management software, reporting, attention to detail | Reduces stockouts and excess inventory, improving cost efficiency |
Overview of Supply Chain Planner and Inventory Analyst Roles
Supply Chain Planners coordinate demand forecasting, production scheduling, and logistics to optimize the end-to-end supply chain process, ensuring timely delivery and cost-efficiency. Inventory Analysts focus on monitoring stock levels, analyzing inventory data, and identifying trends to minimize carrying costs and prevent stockouts. Both roles play critical parts in inventory management but differ in scope, with planners handling broader supply chain coordination and analysts concentrating on inventory accuracy and optimization.
Key Responsibilities and Objectives
A Supply Chain Planner focuses on forecasting demand, optimizing production schedules, and coordinating logistics to ensure timely delivery of goods across the supply chain. An Inventory Analyst monitors stock levels, analyzes inventory turnover, and recommends reorder points to minimize holding costs while preventing stockouts. Both roles aim to enhance operational efficiency and maintain balance between supply and demand within trade enterprises.
Skills and Qualifications Required
Supply Chain Planners require expertise in demand forecasting, production scheduling, and logistics optimization, with proficiency in ERP systems and strong analytical skills to balance supply and demand efficiently. Inventory Analysts must possess skills in data analysis, inventory management, and stock replenishment, often utilizing tools like Excel and inventory management software to minimize carrying costs and avoid stockouts. Both roles demand a strong understanding of supply chain principles, attention to detail, and effective communication abilities to collaborate with suppliers and internal teams.
Workflow and Daily Tasks Compared
Supply Chain Planners focus on demand forecasting, production scheduling, and coordinating with suppliers to ensure materials arrive on time, optimizing the overall supply chain workflow. Inventory Analysts primarily monitor stock levels, analyze inventory turnover rates, and generate reports to prevent stockouts or overstock situations. Both roles require data-driven decision-making, but Supply Chain Planners emphasize forward-looking supply coordination while Inventory Analysts concentrate on current inventory status and efficiency.
Tools, Software, and Technologies Utilized
Supply Chain Planners primarily utilize advanced demand forecasting software such as SAP Integrated Business Planning (IBP) and Oracle Supply Chain Planning Cloud to optimize production schedules and inventory levels. Inventory Analysts focus on inventory management systems like NetSuite and Fishbowl Inventory, leveraging data analytics tools including Tableau and Power BI to monitor stock accuracy and turnover rates. Both roles increasingly incorporate AI-driven platforms and automation technologies to enhance decision-making efficiency and reduce operational costs.
Impact on Trade Sector Efficiency
Supply Chain Planners optimize the end-to-end flow of goods, reducing lead times and minimizing stockouts, which directly enhances trade sector efficiency by ensuring timely delivery and cost-effective logistics. Inventory Analysts focus on maintaining optimal stock levels through data-driven forecasts, preventing excess inventory and obsolescence that can tie up capital and disrupt trade operations. Together, these roles streamline trade supply chains, boost operational agility, and improve overall market responsiveness.
Career Pathways and Advancement Opportunities
Supply Chain Planners typically advance into roles such as Supply Chain Manager or Operations Director, leveraging expertise in demand forecasting and production scheduling to optimize logistics and reduce costs. Inventory Analysts often transition to Inventory Control Manager or Procurement Specialist positions, focusing on inventory optimization, stock accuracy, and supplier coordination to improve turnover rates and minimize holding costs. Both career paths offer strong growth potential in logistics, procurement, and supply chain strategy, with opportunities to specialize in data analysis, process improvement, or strategic sourcing.
Collaboration with Other Trade Professionals
Supply Chain Planners collaborate closely with procurement managers, logistics coordinators, and demand forecasters to optimize product flow and meet delivery deadlines. Inventory Analysts work alongside sales teams, warehouse supervisors, and financial analysts to maintain accurate stock levels and support cost control strategies. Effective coordination between these roles ensures seamless inventory management and enhances overall supply chain efficiency.
Challenges and Problem-Solving Approaches
Supply Chain Planners face challenges in demand forecasting accuracy and coordinating multi-tier supplier networks, employing advanced analytics and scenario planning to optimize inventory flow and production schedules. Inventory Analysts address issues related to stock imbalances and turnover rates by leveraging real-time inventory tracking systems and data-driven optimization models to reduce carrying costs and prevent stockouts. Both roles utilize integrated ERP platforms to enhance visibility and facilitate proactive decision-making in dynamic trade environments.
Choosing Between Supply Chain Planner and Inventory Analyst
Choosing between a Supply Chain Planner and an Inventory Analyst depends on your business priorities; a Supply Chain Planner focuses on optimizing end-to-end supply chain operations, including demand forecasting, production scheduling, and logistics coordination, to ensure timely product availability. An Inventory Analyst specializes in managing stock levels, analyzing inventory turnover, and minimizing carrying costs to maintain optimal inventory balance. Businesses aiming for strategic supply chain efficiency may prefer a Supply Chain Planner, while those emphasizing precise inventory control and cost reduction often opt for an Inventory Analyst.
Supply Chain Planner vs Inventory Analyst Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com