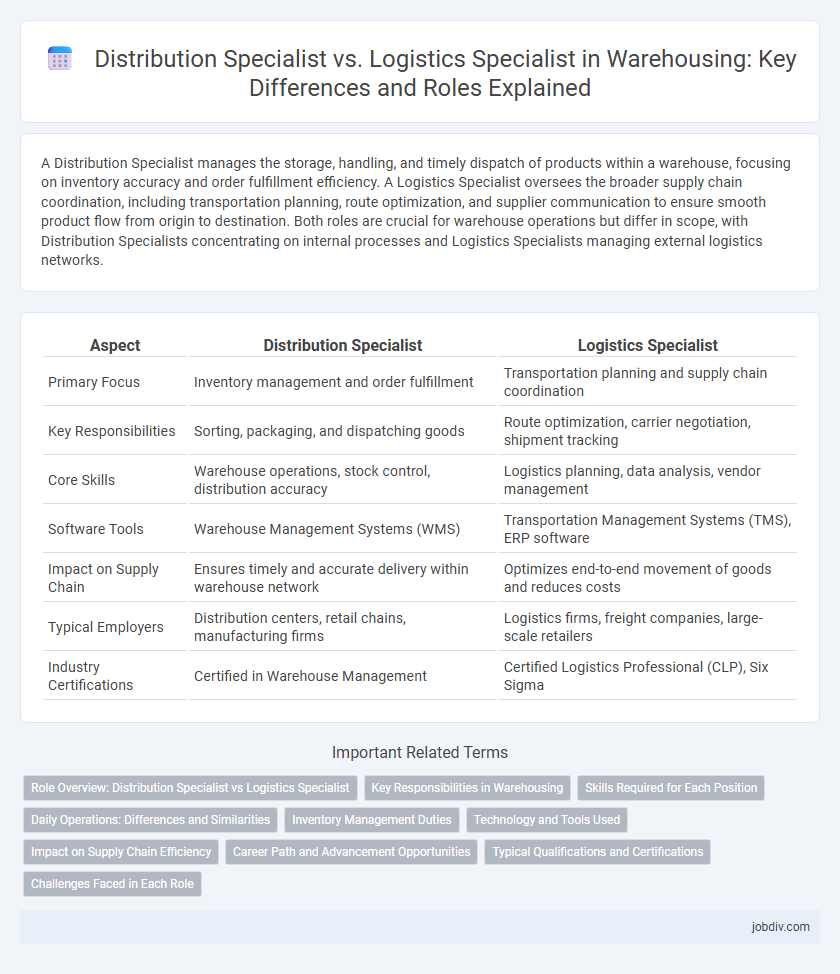
A Distribution Specialist manages the storage, handling, and timely dispatch of products within a warehouse, focusing on inventory accuracy and order fulfillment efficiency. A Logistics Specialist oversees the broader supply chain coordination, including transportation planning, route optimization, and supplier communication to ensure smooth product flow from origin to destination. Both roles are crucial for warehouse operations but differ in scope, with Distribution Specialists concentrating on internal processes and Logistics Specialists managing external logistics networks.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Distribution Specialist | Logistics Specialist |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Inventory management and order fulfillment | Transportation planning and supply chain coordination |
| Key Responsibilities | Sorting, packaging, and dispatching goods | Route optimization, carrier negotiation, shipment tracking |
| Core Skills | Warehouse operations, stock control, distribution accuracy | Logistics planning, data analysis, vendor management |
| Software Tools | Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) | Transportation Management Systems (TMS), ERP software |
| Impact on Supply Chain | Ensures timely and accurate delivery within warehouse network | Optimizes end-to-end movement of goods and reduces costs |
| Typical Employers | Distribution centers, retail chains, manufacturing firms | Logistics firms, freight companies, large-scale retailers |
| Industry Certifications | Certified in Warehouse Management | Certified Logistics Professional (CLP), Six Sigma |
Role Overview: Distribution Specialist vs Logistics Specialist
A Distribution Specialist manages the efficient allocation and delivery of goods from warehouses to customers, ensuring inventory accuracy and timely order fulfillment. A Logistics Specialist coordinates the entire supply chain process, including transportation planning, inventory control, and warehouse operations to optimize movement and storage of products. Both roles require expertise in inventory management systems and supply chain optimization, but distribution specialists focus more on outbound distribution while logistics specialists oversee end-to-end logistics operations.
Key Responsibilities in Warehousing
Distribution Specialists manage inventory flow, oversee order fulfillment, and coordinate product storage to ensure timely dispatch from warehouses. Logistics Specialists plan and optimize transportation routes, manage supply chain processes, and handle inbound and outbound shipments for efficient warehouse operations. Both roles collaborate to maintain seamless inventory movement and meet delivery deadlines within warehousing environments.
Skills Required for Each Position
Distribution Specialists require strong inventory management, order fulfillment, and coordination skills to ensure products move efficiently from warehouses to end customers. Logistics Specialists need expertise in transportation planning, supply chain optimization, and data analysis to manage the flow of goods and minimize costs. Both roles demand proficiency in warehouse management systems (WMS) and effective communication to align cross-functional teams.
Daily Operations: Differences and Similarities
Distribution Specialists oversee the efficient allocation and movement of products from warehouses to end customers, managing inventory levels and coordinating shipment schedules. Logistics Specialists focus on the broader supply chain, optimizing transportation routes, managing carrier relationships, and ensuring timely delivery across multiple distribution points. Both roles require strong coordination skills, but Distribution Specialists prioritize order fulfillment accuracy, while Logistics Specialists emphasize supply chain efficiency.
Inventory Management Duties
Distribution Specialists primarily manage inventory allocation and order fulfillment, ensuring accurate stock levels and timely dispatch to meet customer demands. Logistics Specialists oversee the broader supply chain processes, including inventory tracking, transportation coordination, and warehouse storage optimization to maintain efficient stock flow. Both roles require expertise in inventory management systems and real-time data analysis to minimize stockouts and reduce carrying costs.
Technology and Tools Used
Distribution Specialists primarily utilize warehouse management systems (WMS) and inventory tracking software to optimize order fulfillment and ensure accurate stock levels. Logistics Specialists leverage transportation management systems (TMS), GPS tracking, and route optimization tools to coordinate the efficient movement of goods from warehouses to final destinations. Both roles increasingly rely on automation technologies such as RFID, barcode scanners, and data analytics platforms to enhance supply chain visibility and operational efficiency.
Impact on Supply Chain Efficiency
Distribution Specialists optimize warehouse storage and order fulfillment processes, directly improving inventory accuracy and reducing lead times. Logistics Specialists coordinate transportation, route planning, and carrier management, ensuring timely delivery and minimizing shipping costs. Together, their roles enhance overall supply chain efficiency by streamlining both internal warehouse operations and external distribution networks.
Career Path and Advancement Opportunities
Distribution Specialists concentrate on managing inventory flow and order fulfillment within warehouses, offering career advancement opportunities in supply chain coordination and warehouse management. Logistics Specialists oversee broader transportation and distribution networks, providing pathways to roles in transportation planning, procurement, and supply chain analytics. Both career paths offer advancement into senior management positions, with Logistics Specialists often progressing toward strategic roles due to their comprehensive supply chain oversight.
Typical Qualifications and Certifications
Distribution Specialists typically hold certifications such as Certified Supply Chain Professional (CSCP) or Certified in Logistics, Transportation and Distribution (CLTD), emphasizing knowledge in inventory management and order fulfillment processes. Logistics Specialists often possess qualifications like the Certified Logistics Professional (CLP) or Six Sigma Green Belt, highlighting expertise in transportation planning, route optimization, and supply chain coordination. Both roles generally require a background in supply chain, business administration, or logistics, with experience in warehouse management systems (WMS) and proficiency in data analysis tools.
Challenges Faced in Each Role
Distribution specialists face challenges managing inventory accuracy, coordinating timely shipments, and optimizing warehouse space to meet fluctuating demand effectively. Logistics specialists encounter difficulties in route planning, ensuring compliance with transportation regulations, and managing supply chain disruptions. Both roles require problem-solving skills to streamline operations and reduce costs within the warehousing and transportation process.
Distribution Specialist vs Logistics Specialist Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com