An Explosives Technician is responsible for the design, handling, and maintenance of explosive materials, ensuring compliance with safety regulations and technical standards in mining operations. A Shotfirer strictly focuses on the controlled initiation and execution of blasting rounds, following predetermined blast patterns to optimize rock fragmentation. Both roles require specialized training, but the Explosives Technician typically holds broader expertise in explosives management and regulatory oversight.
Table of Comparison
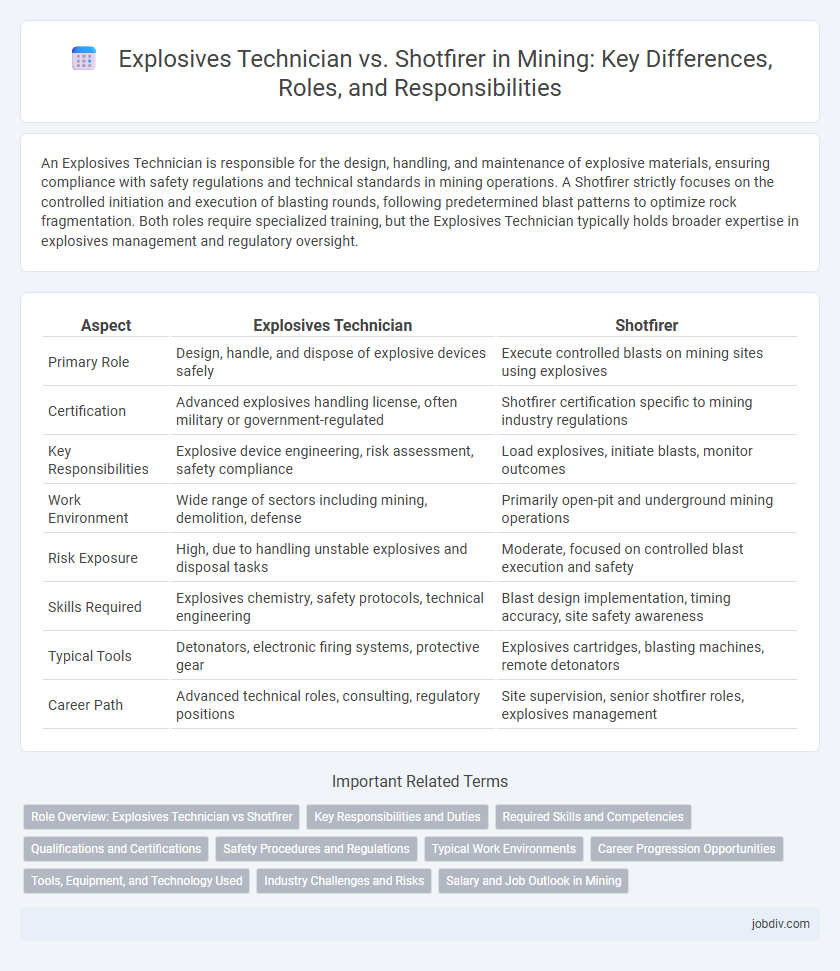
| Aspect | Explosives Technician | Shotfirer |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Design, handle, and dispose of explosive devices safely | Execute controlled blasts on mining sites using explosives |
| Certification | Advanced explosives handling license, often military or government-regulated | Shotfirer certification specific to mining industry regulations |
| Key Responsibilities | Explosive device engineering, risk assessment, safety compliance | Load explosives, initiate blasts, monitor outcomes |
| Work Environment | Wide range of sectors including mining, demolition, defense | Primarily open-pit and underground mining operations |
| Risk Exposure | High, due to handling unstable explosives and disposal tasks | Moderate, focused on controlled blast execution and safety |
| Skills Required | Explosives chemistry, safety protocols, technical engineering | Blast design implementation, timing accuracy, site safety awareness |
| Typical Tools | Detonators, electronic firing systems, protective gear | Explosives cartridges, blasting machines, remote detonators |
| Career Path | Advanced technical roles, consulting, regulatory positions | Site supervision, senior shotfirer roles, explosives management |
Role Overview: Explosives Technician vs Shotfirer
Explosives Technicians specialize in handling, storing, and transporting explosives, ensuring compliance with safety regulations and conducting technical inspections to prevent accidents. Shotfirers are responsible for planning and executing explosive blasts on mining sites, including the precise placement and detonation of charges to optimize rock fragmentation. Both roles require knowledge of explosive materials and safety protocols, but Explosives Technicians focus more on regulatory compliance and technical management, while Shotfirers concentrate on blast design and onsite implementation.
Key Responsibilities and Duties
Explosives Technicians specialize in the design, handling, and deployment of explosive materials, ensuring all safety protocols and regulatory standards are meticulously followed during mining blasts. Shotfirers are responsible for the precise placement and initiation of explosives in blast holes to maximize fragmentation and control blast effects, while monitoring environmental and operational safety conditions. Both roles require in-depth knowledge of explosive materials, strict adherence to safety procedures, and coordination with mining engineers to optimize efficiency and minimize risks.
Required Skills and Competencies
Explosives Technicians require advanced knowledge in explosive materials, safety protocols, and precision handling to design controlled blasts, emphasizing expertise in chemistry and engineering principles. Shotfirers must possess strong skills in detonator placement, timing coordination, and ground vibration management, ensuring effective and safe blast execution at mining sites. Both roles demand rigorous adherence to legal regulations, risk assessment capabilities, and physical fitness to operate in high-risk mining environments.
Qualifications and Certifications
Explosives Technicians typically require advanced certifications such as a Diploma in Explosives Engineering and licenses endorsed by regulatory bodies like MSHA or OSHA, emphasizing expertise in handling complex blasting operations. Shotfirers usually hold certifications at a foundational level, including Shotfirer Qualifications and Blaster Permits, allowing them to execute controlled blasts under supervision. Both roles mandate rigorous safety training, but Explosives Technicians possess higher qualifications to design blast patterns and oversee detonations, whereas Shotfirers primarily carry out the blasting tasks.
Safety Procedures and Regulations
Explosives Technicians and Shotfirers both operate under strict safety procedures and regulations to prevent accidents in mining environments, with Explosives Technicians typically handling the design and implementation of explosive charges while Shotfirers focus on the actual detonation process. Compliance with regulatory standards such as the Occupational Health and Safety Act and the Mine Safety and Health Administration (MSHA) guidelines is mandatory, ensuring risk assessments, secure handling, and precise timing during blasting operations. Both roles require rigorous training and certification, emphasizing personal protective equipment (PPE) use, communication protocols, and emergency response plans to maintain a controlled and safe blasting environment.
Typical Work Environments
Explosives Technicians primarily operate in open-pit mines, underground tunnels, and construction sites where precise handling and placement of explosives are critical for controlled detonations. Shotfirers work in similar environments but are more frequently found directly managing blast initiation on-site, ensuring safety protocols are strictly followed during blasting operations. Both roles require working under strict safety regulations within hazardous environments involving heavy machinery and volatile materials.
Career Progression Opportunities
Explosives Technicians often advance to supervisory roles overseeing shotfirers and complex blasting operations due to their extensive technical expertise in explosive materials and safety protocols. Shotfirers typically gain field experience managing blast setups, which can lead to promotions into explosives technician positions or specialized roles in blast design and compliance. Career progression in mining explosives roles depends on certifications, on-the-job training, and demonstrated proficiency in handling and deploying explosives safely.
Tools, Equipment, and Technology Used
Explosives Technicians use advanced electronic detonators, blast vibration monitors, and precision initiation systems to ensure controlled explosions in mining operations. Shotfirers primarily rely on commercial explosives, initiation devices such as non-electric or electric detonators, and blast hole drills to execute planned blasts safely. Both roles integrate digital blast design software and safety communication tools, but Explosives Technicians typically handle more specialized technology for blast monitoring and environmental impact assessment.
Industry Challenges and Risks
Explosives Technicians and Shotfirers face significant industry challenges including stringent safety regulations and the constant risk of accidental detonations in mining operations. Both roles require precise handling of explosives to mitigate dangers such as premature blasts, environmental damage, and equipment failure. Maintaining compliance with evolving legislation and managing the health hazards associated with explosive materials remain critical concerns in ensuring operational safety and efficiency.
Salary and Job Outlook in Mining
Explosives Technicians in mining typically earn higher salaries than Shotfirers, reflecting their advanced expertise in handling complex explosive materials and overseeing blasting operations. The job outlook for Explosives Technicians is strong due to increasing demand for skilled professionals able to ensure safety and efficiency in large-scale mining projects. Shotfirers also maintain steady employment opportunities but often face slower wage growth and fewer advancement prospects compared to Explosives Technicians.
Explosives Technician vs Shotfirer Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com