Ventilation engineers specialize in designing and maintaining air flow systems within mines to ensure safe breathing conditions and control hazardous gases. Environmental engineers focus on minimizing the ecological impact of mining activities by managing waste, water quality, and land reclamation. Both roles are crucial for sustainable mining operations, balancing worker safety with environmental protection.
Table of Comparison
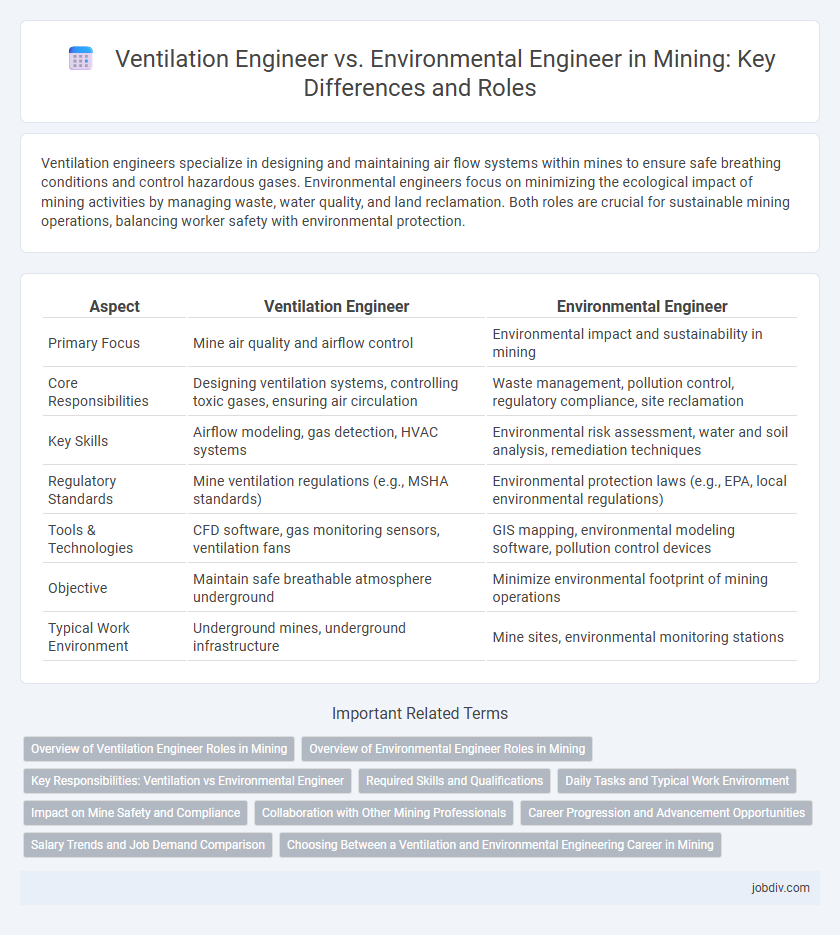
| Aspect | Ventilation Engineer | Environmental Engineer |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Mine air quality and airflow control | Environmental impact and sustainability in mining |
| Core Responsibilities | Designing ventilation systems, controlling toxic gases, ensuring air circulation | Waste management, pollution control, regulatory compliance, site reclamation |
| Key Skills | Airflow modeling, gas detection, HVAC systems | Environmental risk assessment, water and soil analysis, remediation techniques |
| Regulatory Standards | Mine ventilation regulations (e.g., MSHA standards) | Environmental protection laws (e.g., EPA, local environmental regulations) |
| Tools & Technologies | CFD software, gas monitoring sensors, ventilation fans | GIS mapping, environmental modeling software, pollution control devices |
| Objective | Maintain safe breathable atmosphere underground | Minimize environmental footprint of mining operations |
| Typical Work Environment | Underground mines, underground infrastructure | Mine sites, environmental monitoring stations |
Overview of Ventilation Engineer Roles in Mining
Ventilation engineers in mining play a critical role in designing and managing air flow systems to ensure safe and healthy underground environments, preventing the buildup of hazardous gases and controlling temperature and dust levels. Their responsibilities include monitoring air quality, maintaining ventilation equipment, and implementing strategies to optimize oxygen supply and reduce exposure to toxic substances. By contrast, environmental engineers focus more broadly on minimizing the ecological impact of mining operations, including waste management and land reclamation.
Overview of Environmental Engineer Roles in Mining
Environmental engineers in mining focus on designing and implementing systems to control pollution, manage waste, and ensure regulatory compliance for sustainable mining operations. Their roles include monitoring air and water quality, developing remediation plans for contaminated sites, and minimizing environmental impact through innovative technologies. Collaboration with ventilation engineers ensures the optimization of air quality and worker safety within underground mining environments.
Key Responsibilities: Ventilation vs Environmental Engineer
Ventilation engineers in mining specialize in designing and maintaining airflow systems to ensure safe oxygen levels and remove hazardous gases such as methane and dust, directly enhancing mine safety and worker health. Environmental engineers focus on minimizing the mining operation's ecological impact by managing waste disposal, monitoring water and air quality, and ensuring compliance with environmental regulations. Both roles are critical for sustainable mining operations, with ventilation engineers prioritizing underground air quality and environmental engineers addressing broader environmental protection and regulatory adherence.
Required Skills and Qualifications
Ventilation engineers in mining require expertise in airflow dynamics, HVAC systems, and regulatory compliance to ensure safe underground air quality, with strong skills in computer modeling and risk assessment. Environmental engineers focus on environmental impact mitigation, waste management, and sustainability practices, needing proficiency in environmental regulations, soil and water analysis, and pollution control technologies. Both roles demand degrees in engineering fields, with ventilation engineers often specializing in mining or mechanical engineering, while environmental engineers typically hold degrees in environmental or civil engineering.
Daily Tasks and Typical Work Environment
Ventilation engineers in mining focus on designing and maintaining airflow systems to ensure safe breathing conditions, regularly monitoring gas levels, airflow rates, and air quality within underground tunnels. Environmental engineers concentrate on assessing and mitigating mining's ecological impact, managing waste disposal, water quality, and land reclamation projects at surface and subsurface sites. Both roles operate in harsh, noisy, and dusty mine environments, but ventilation engineers typically work underground, while environmental engineers spend more time on surface facilities and monitoring stations.
Impact on Mine Safety and Compliance
Ventilation Engineers design and maintain airflow systems to control hazardous gases and dust, directly reducing risks of explosions and respiratory issues, ensuring compliance with mine safety standards like MSHA regulations. Environmental Engineers assess and mitigate environmental impacts of mining operations, managing waste, controlling pollution, and ensuring adherence to environmental laws such as the Clean Water Act and EPA guidelines. Both roles collaborate to balance worker safety with environmental compliance, minimizing operational shutdowns and legal liabilities in mining environments.
Collaboration with Other Mining Professionals
Ventilation engineers and environmental engineers collaborate closely with geologists, health and safety officers, and mine planners to optimize underground air quality and ensure regulatory compliance. Their joint efforts involve designing ventilation systems that reduce harmful emissions and control dust, while implementing environmental monitoring programs to safeguard worker health and minimize ecological impact. Leveraging data from sensors and modeling software, both engineers coordinate to enhance mine safety and sustainability through integrated planning and risk management.
Career Progression and Advancement Opportunities
Ventilation engineers in mining specialize in designing and managing airflow systems to ensure safe underground working conditions, often advancing to senior technical roles or site management positions due to their critical expertise in operational safety. Environmental engineers focus on minimizing mining's ecological impact by developing sustainable practices and regulatory compliance strategies, progressing toward leadership roles in environmental planning or corporate sustainability departments. Career progression for ventilation engineers typically emphasizes technical leadership and safety management, while environmental engineers see advancement in policy development, environmental risk assessment, and corporate social responsibility initiatives.
Salary Trends and Job Demand Comparison
Ventilation engineers in mining typically earn salaries ranging from $70,000 to $110,000 annually, driven by the critical need to ensure underground air quality and worker safety. Environmental engineers often command similar or slightly higher wages, between $75,000 and $120,000, due to increasing regulatory demands and sustainability initiatives in mining operations. Job demand for ventilation engineers remains steady with a focus on operational safety, while environmental engineers experience faster growth fueled by expanding environmental compliance and remediation requirements.
Choosing Between a Ventilation and Environmental Engineering Career in Mining
Ventilation engineers in mining specialize in designing and managing airflow systems to ensure underground worker safety by controlling toxic gases and maintaining breathable air quality. Environmental engineers focus on minimizing mining's ecological impact by developing strategies for waste management, land reclamation, and water pollution control. Choosing between these careers depends on whether you are more interested in occupational health and safety or ecological sustainability within the mining industry.
Ventilation Engineer vs Environmental Engineer Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com