Mine surveyors specialize in measuring and mapping underground and surface mining areas to ensure accurate planning and safety compliance. Exploration geologists focus on identifying mineral deposits by analyzing rock samples and geological formations to guide resource extraction strategies. Both roles are crucial in mining, combining precise spatial data with mineral discovery to optimize operational efficiency.
Table of Comparison
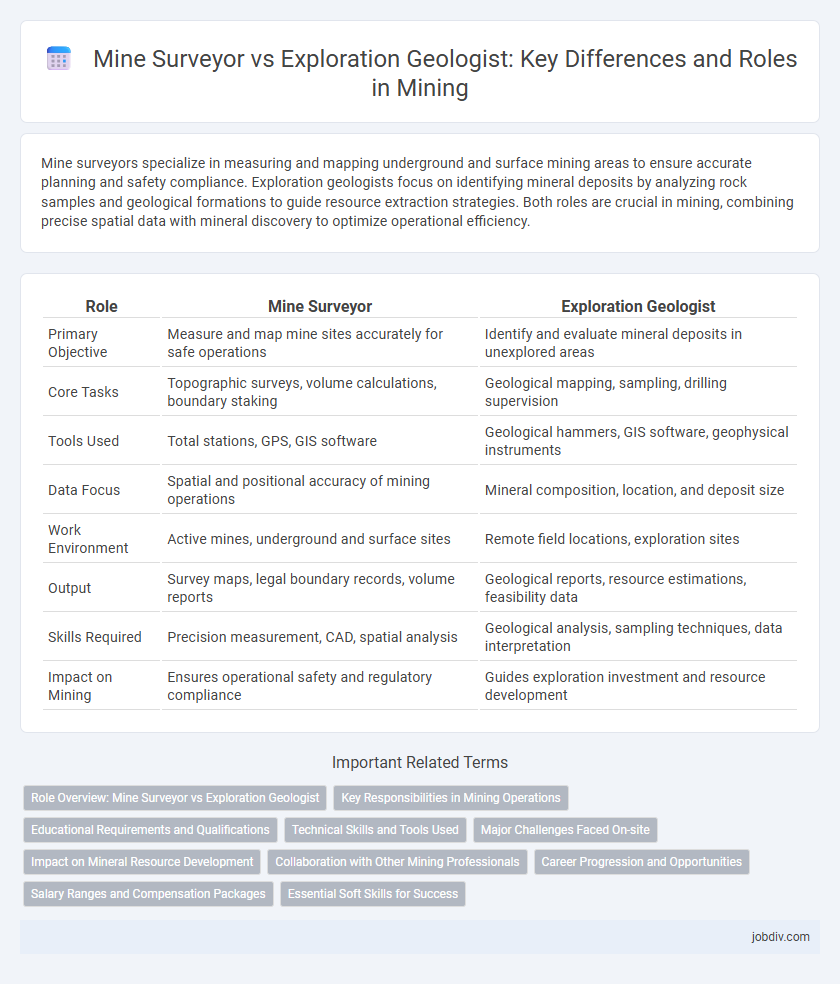
| Role | Mine Surveyor | Exploration Geologist |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Objective | Measure and map mine sites accurately for safe operations | Identify and evaluate mineral deposits in unexplored areas |
| Core Tasks | Topographic surveys, volume calculations, boundary staking | Geological mapping, sampling, drilling supervision |
| Tools Used | Total stations, GPS, GIS software | Geological hammers, GIS software, geophysical instruments |
| Data Focus | Spatial and positional accuracy of mining operations | Mineral composition, location, and deposit size |
| Work Environment | Active mines, underground and surface sites | Remote field locations, exploration sites |
| Output | Survey maps, legal boundary records, volume reports | Geological reports, resource estimations, feasibility data |
| Skills Required | Precision measurement, CAD, spatial analysis | Geological analysis, sampling techniques, data interpretation |
| Impact on Mining | Ensures operational safety and regulatory compliance | Guides exploration investment and resource development |
Role Overview: Mine Surveyor vs Exploration Geologist
A Mine Surveyor specializes in measuring and mapping underground and surface mining sites to ensure accurate layouts and safe operations. Exploration Geologists focus on discovering new mineral deposits by analyzing geological data, conducting field surveys, and assessing mineral potential. Both roles are critical, with surveyors maintaining spatial accuracy and geologists driving resource identification.
Key Responsibilities in Mining Operations
Mine Surveyors are responsible for measuring and mapping mine sites, ensuring accurate spatial data for excavation, safety, and resource estimation. Exploration Geologists analyze geological data, identify mineral deposits, and guide drilling programs to locate economically viable ore bodies. Both roles are integral to efficient mining operations, with surveyors focusing on precise spatial assessments and geologists on resource evaluation and exploration strategy.
Educational Requirements and Qualifications
Mine surveyors typically require a bachelor's degree in geomatics, surveying, or mining engineering, along with certification from recognized bodies such as the National Society of Professional Surveyors (NSPS). Exploration geologists usually hold a degree in geology, earth sciences, or mining engineering, often supplemented by field experience and professional accreditation like the Geological Society of America (GSA) membership. Both roles demand strong technical skills, but exploration geologists focus more on geological mapping and data interpretation, while mine surveyors prioritize precision measurement and spatial data management.
Technical Skills and Tools Used
Mine Surveyors utilize advanced GPS, total stations, and laser scanning technology to create precise mine maps and ensure accurate site measurements. Exploration Geologists rely heavily on geophysical instruments, core drilling equipment, and geological software for mineral identification and resource estimation. Both professionals require strong technical skills; surveyors excel in spatial data analysis, while geologists specialize in geological modeling and interpretation.
Major Challenges Faced On-site
Mine surveyors confront major challenges such as ensuring precise spatial measurements in complex underground environments and maintaining accurate mapping despite unstable ground conditions and limited visibility. Exploration geologists face difficulties in accurately interpreting geological data on-site, dealing with unpredictable rock formations, and obtaining reliable samples under harsh environmental conditions. Both roles require adapting to dynamic terrain and coordinating closely to mitigate risks and enhance site safety.
Impact on Mineral Resource Development
Mine surveyors accurately map underground and surface mine features, providing critical spatial data essential for planning and optimizing mineral extraction, which directly influences resource development efficiency. Exploration geologists identify and evaluate mineral deposits through geological mapping, sampling, and analysis, determining the quality and quantity of resources that guide investment and development decisions. Their combined expertise ensures precise resource delineation and extraction strategies, maximizing mineral recovery and economic viability.
Collaboration with Other Mining Professionals
Mine surveyors and exploration geologists collaborate closely to ensure accurate mapping and resource estimation, enhancing the efficiency of mining operations. Mine surveyors provide precise spatial data and topographic information critical for geologists to identify mineral deposits and plan drilling programs. This synergy improves decision-making in resource evaluation, mine design, and safety management across multidisciplinary mining teams.
Career Progression and Opportunities
Mine surveyors often advance by gaining expertise in advanced surveying technologies such as LiDAR and GIS, leading to roles as senior surveyors or mine planning specialists. Exploration geologists typically progress through stages of increasing technical responsibility, moving from field data collection to exploration management and resource evaluation roles. Career opportunities for mine surveyors center on precise spatial data management and mine layout optimization, while exploration geologists focus on identifying mineral deposits and advising on exploration strategies.
Salary Ranges and Compensation Packages
Mine Surveyors typically earn between $60,000 and $100,000 annually, with compensation packages often including bonuses, overtime pay, and field allowances. Exploration Geologists generally have higher salary ranges from $70,000 to $120,000, reflecting specialized skills in resource evaluation and risk assessment. Both roles may receive benefits such as health insurance, retirement plans, and relocation assistance, but Exploration Geologists tend to secure more lucrative stock options and performance-based incentives in mining companies.
Essential Soft Skills for Success
Mine Surveyors excel in spatial awareness and precision communication, crucial for accurate mapping and resource estimation in mining operations. Exploration Geologists prioritize critical thinking and adaptability to analyze geological data and navigate unpredictable field conditions effectively. Both roles rely heavily on teamwork and problem-solving skills to ensure successful project outcomes and safety compliance.
Mine Surveyor vs Exploration Geologist Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com