A millwright in mining specializes in installing, aligning, and repairing heavy machinery used in mills and processing plants, requiring precision in mechanical systems and equipment setup. A maintenance fitter focuses on routine upkeep, troubleshooting, and repairing various mining equipment to ensure continuous operation and minimize downtime. Both roles are essential for efficient mining operations, with millwrights handling complex installations and maintenance fitters addressing everyday mechanical issues.
Table of Comparison
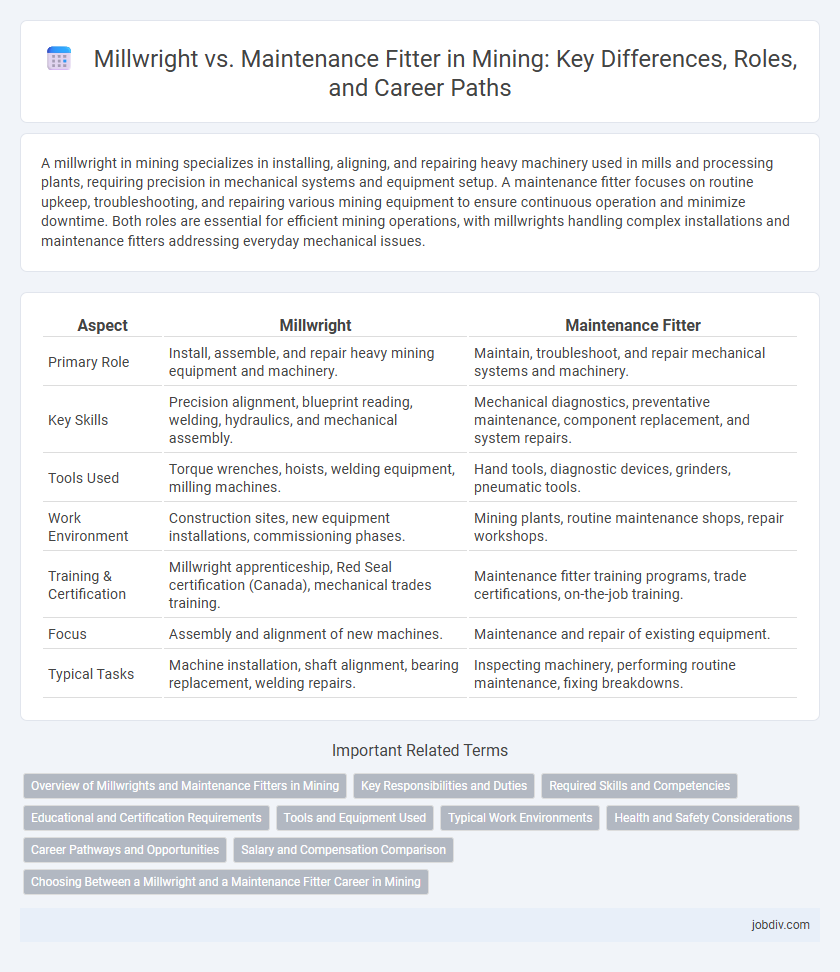
| Aspect | Millwright | Maintenance Fitter |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Install, assemble, and repair heavy mining equipment and machinery. | Maintain, troubleshoot, and repair mechanical systems and machinery. |
| Key Skills | Precision alignment, blueprint reading, welding, hydraulics, and mechanical assembly. | Mechanical diagnostics, preventative maintenance, component replacement, and system repairs. |
| Tools Used | Torque wrenches, hoists, welding equipment, milling machines. | Hand tools, diagnostic devices, grinders, pneumatic tools. |
| Work Environment | Construction sites, new equipment installations, commissioning phases. | Mining plants, routine maintenance shops, repair workshops. |
| Training & Certification | Millwright apprenticeship, Red Seal certification (Canada), mechanical trades training. | Maintenance fitter training programs, trade certifications, on-the-job training. |
| Focus | Assembly and alignment of new machines. | Maintenance and repair of existing equipment. |
| Typical Tasks | Machine installation, shaft alignment, bearing replacement, welding repairs. | Inspecting machinery, performing routine maintenance, fixing breakdowns. |
Overview of Millwrights and Maintenance Fitters in Mining
Millwrights in mining specialize in installing, aligning, and repairing heavy machinery such as conveyors, crushers, and grinding mills critical to mineral processing operations. Maintenance fitters focus on routine upkeep, troubleshooting, and repairing mechanical components to ensure continuous and efficient plant performance. Both roles require expertise in mechanical systems, but millwrights handle more complex installations and precision alignments, while maintenance fitters execute preventative maintenance and quick repairs.
Key Responsibilities and Duties
Millwrights in mining are responsible for installing, maintaining, and repairing heavy machinery and equipment, ensuring operational efficiency and safety. Maintenance fitters focus on troubleshooting, servicing, and repairing mechanical components to minimize downtime and maximize equipment reliability. Both roles require strong technical skills, precision, and adherence to safety protocols to support continuous mining operations.
Required Skills and Competencies
Millwrights in mining require advanced mechanical skills, including precision alignment, machinery installation, and troubleshooting rotating equipment, with expertise in interpreting technical drawings and using precision measurement tools. Maintenance Fitters focus on repairing and maintaining mining machinery, requiring strong welding, fabrication, and hydraulic system knowledge, along with proficiency in diagnostic tools and routine maintenance procedures. Both roles demand mechanical aptitude, problem-solving skills, and adherence to safety standards, but Millwrights typically hold more specialized training in machine installation and heavy equipment assembly.
Educational and Certification Requirements
Millwrights in mining typically require completion of a trade apprenticeship program and certification as a Red Seal journeyperson, emphasizing skills in mechanical assembly, alignment, and installation of heavy equipment. Maintenance Fitters often need a combination of technical diploma in mechanical engineering technology or industrial mechanics and certifications in rigging, welding, or safety standards specific to mining environments. Both roles demand ongoing safety training and compliance with industry regulations, but Millwrights focus more on equipment installation while Maintenance Fitters specialize in troubleshooting and repairing machinery.
Tools and Equipment Used
Millwrights in mining primarily use precision measuring tools, torque wrenches, and hydraulic systems for installing and aligning heavy machinery, while maintenance fitters rely on hand tools, grinders, and diagnostic equipment to repair and maintain existing machinery. Both roles utilize welding equipment and mechanical hoists, but millwrights often operate cranes and laser alignment tools to assemble new installations. The emphasis for millwrights is on setup and alignment accuracy, whereas maintenance fitters focus on troubleshooting and equipment upkeep.
Typical Work Environments
Millwrights in mining typically work on-site in processing plants and heavy machinery installations, often dealing with large-scale equipment like crushers, conveyors, and grinding mills. Maintenance Fitters usually operate within confined spaces of underground mines or maintenance workshops, specializing in the repair and upkeep of mining vehicles, mechanical systems, and hydraulic components. Both roles require adaptability to harsh environmental conditions including dust, noise, and varying temperatures commonly found in mining operations.
Health and Safety Considerations
Millwrights and Maintenance Fitters in mining face distinct health and safety considerations due to their specific roles; Millwrights often engage in heavy machinery installation and precise alignment tasks, requiring stringent adherence to lockout/tagout procedures and fall protection standards. Maintenance Fitters focus on repairing and maintaining equipment, necessitating awareness of confined space hazards and proper use of personal protective equipment (PPE) to prevent injuries from moving parts or electrical components. Both roles demand comprehensive safety training aligned with mining industry regulations such as MSHA and use of hazard identification protocols to mitigate risks on site.
Career Pathways and Opportunities
Millwrights in mining specialize in installing, repairing, and maintaining heavy machinery, providing a strong foundation for advancing into supervisory or engineering roles. Maintenance fitters focus on routine equipment upkeep and troubleshooting, often transitioning into specialized technician or maintenance manager positions. Both career pathways offer opportunities for skill development, with millwrights typically engaging in more complex mechanical work, enabling broader prospects within mining operations.
Salary and Compensation Comparison
Millwrights in mining typically earn an average annual salary ranging from $60,000 to $85,000, reflecting their specialized skills in equipment installation and alignment. Maintenance fitters usually have a slightly lower salary bracket, averaging $55,000 to $75,000, due to their focus on routine machinery repairs and upkeep. Compensation packages for both roles often include benefits such as overtime pay, hazard allowances, and performance bonuses, with millwrights frequently receiving higher premiums due to their technical expertise.
Choosing Between a Millwright and a Maintenance Fitter Career in Mining
Choosing between a Millwright and a Maintenance Fitter career in mining depends on specific skill sets and job responsibilities; Millwrights specialize in installing, repairing, and maintaining heavy mining equipment and machinery, requiring strong mechanical and hydraulic knowledge. Maintenance Fitters focus on routine equipment maintenance, troubleshooting, and preventive tasks to ensure operational efficiency, emphasizing welding, machining, and mechanical repairs. Career advancement and salary potential in mining vary with experience, certifications, and the complexity of machinery handled by each role.
Millwright vs Maintenance Fitter Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com