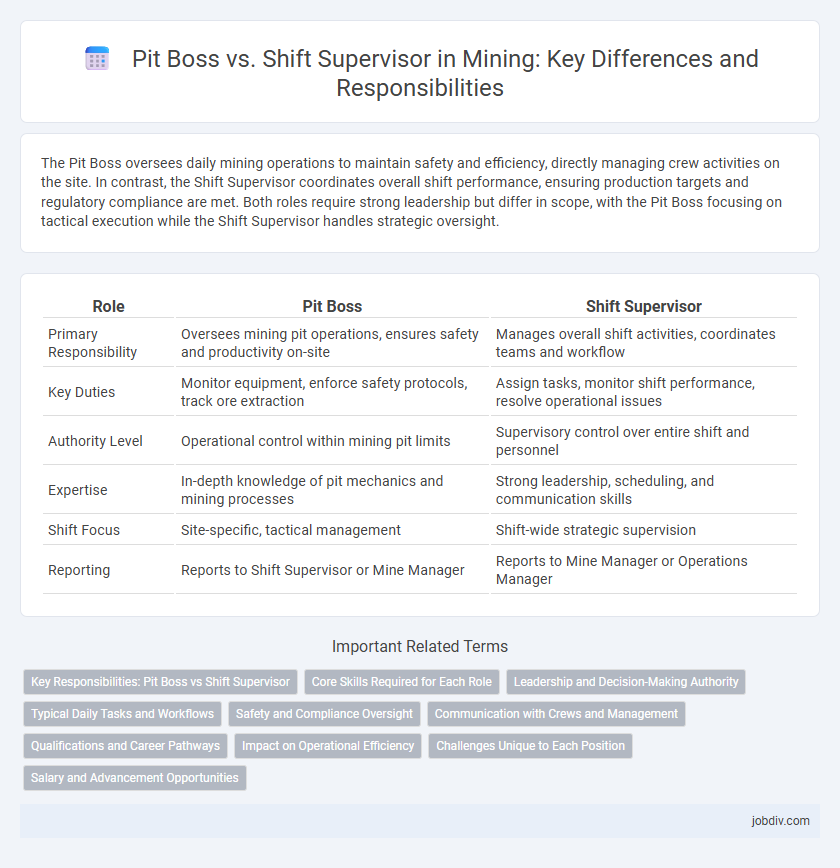
The Pit Boss oversees daily mining operations to maintain safety and efficiency, directly managing crew activities on the site. In contrast, the Shift Supervisor coordinates overall shift performance, ensuring production targets and regulatory compliance are met. Both roles require strong leadership but differ in scope, with the Pit Boss focusing on tactical execution while the Shift Supervisor handles strategic oversight.
Table of Comparison
| Role | Pit Boss | Shift Supervisor |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Responsibility | Oversees mining pit operations, ensures safety and productivity on-site | Manages overall shift activities, coordinates teams and workflow |
| Key Duties | Monitor equipment, enforce safety protocols, track ore extraction | Assign tasks, monitor shift performance, resolve operational issues |
| Authority Level | Operational control within mining pit limits | Supervisory control over entire shift and personnel |
| Expertise | In-depth knowledge of pit mechanics and mining processes | Strong leadership, scheduling, and communication skills |
| Shift Focus | Site-specific, tactical management | Shift-wide strategic supervision |
| Reporting | Reports to Shift Supervisor or Mine Manager | Reports to Mine Manager or Operations Manager |
Key Responsibilities: Pit Boss vs Shift Supervisor
The Pit Boss in mining oversees the overall operations of the pit, ensuring equipment efficiency, safety compliance, and effective resource allocation across shifts. The Shift Supervisor manages day-to-day activities on-site, directing personnel, monitoring production targets, and addressing immediate operational challenges during their shift. Both roles require leadership and communication skills, but the Pit Boss focuses on strategic oversight while the Shift Supervisor handles tactical execution.
Core Skills Required for Each Role
Pit Boss positions in mining prioritize expertise in safety compliance, real-time operational decision-making, and equipment efficiency monitoring. Shift Supervisors require strong leadership, team coordination, and communication skills to effectively manage workforce productivity and incident response. Both roles demand proficiency in regulatory knowledge and problem-solving under pressure, but Pit Bosses lean more towards technical oversight while Shift Supervisors emphasize personnel management.
Leadership and Decision-Making Authority
The Pit Boss in mining holds greater decision-making authority, overseeing day-to-day operational leadership and ensuring compliance with safety protocols. Shift Supervisors manage specific teams, implementing the Pit Boss's directives and maintaining workflow efficiency during assigned shifts. Leadership roles of the Pit Boss involve strategic planning and conflict resolution, while Shift Supervisors focus on operational execution and immediate issue management.
Typical Daily Tasks and Workflows
Pit Boss oversees overall mine operations, coordinating crews, monitoring equipment performance, and ensuring safety compliance throughout the shift. Shift Supervisors focus on implementing operational plans, managing daily workflows, assigning tasks to miners, and promptly addressing production issues at the coal, metal, or aggregate mining site. Both roles demand real-time decision-making to optimize throughput, maintain regulatory standards, and minimize downtime in surface or underground mining environments.
Safety and Compliance Oversight
Pit Bosses ensure real-time safety and compliance by actively monitoring mining operations and enforcing site-specific regulations, reducing incident risks. Shift Supervisors oversee broader departmental safety protocols and coordinate compliance audits to maintain regulatory standards across shifts. Both roles collaborate to implement corrective actions swiftly, enhancing overall workplace safety and regulatory adherence in mining environments.
Communication with Crews and Management
Pit Boss excels in real-time communication with crews by providing clear, immediate guidance on pit operations, ensuring safety and efficiency underground. Shift Supervisors maintain a broader communication role, coordinating between management and crews to implement strategic plans and address operational challenges. Effective dialogue between Pit Bosses and Shift Supervisors is crucial for synchronized workflow and timely decision-making in mining operations.
Qualifications and Career Pathways
Pit Bosses in mining typically require extensive experience in underground operations, strong leadership skills, and certifications in safety and mine regulations, often progressing from roles such as Shift Supervisor or Miner. Shift Supervisors usually hold qualifications in mining technology or engineering and gain hands-on experience managing daily operations and crew shifts before advancing to Pit Boss positions. Career pathways in mining favor those with a blend of technical knowledge, operational expertise, and proven supervisory capabilities, with Pit Bosses overseeing broader operational responsibilities compared to Shift Supervisors.
Impact on Operational Efficiency
Pit Bosses directly oversee underground mining operations, ensuring equipment performance and worker safety align with production goals, which significantly enhances operational efficiency. Shift Supervisors coordinate surface activities and maintain workflow continuity, focusing on resource allocation and real-time problem solving to minimize downtime. The combined roles of Pit Boss and Shift Supervisor create a synergistic effect that optimizes productivity, reduces operational bottlenecks, and improves overall mine output.
Challenges Unique to Each Position
Pit Boss roles demand real-time decision-making under high pressure, managing operational disruptions and ensuring miner safety in dynamic environments. Shift Supervisors face scheduling complexities, workforce coordination, and compliance with regulatory standards across entire shifts. Each position requires tailored problem-solving skills adapted to their distinct responsibilities within mining operations.
Salary and Advancement Opportunities
Pit Boss positions in mining typically offer higher base salaries compared to Shift Supervisors due to the increased responsibility of overseeing large-scale operations and safety compliance. Advancement opportunities for Pit Bosses often lead to roles in general management or mine operations, while Shift Supervisors may progress to senior supervisory or specialized technical roles within the mine. Salary ranges vary by location and company, with Pit Boss earnings averaging between $70,000 and $110,000 annually, whereas Shift Supervisors generally earn $50,000 to $85,000 per year.
Pit Boss vs Shift Supervisor Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com