A Pit Supervisor oversees daily operations within a mining pit, ensuring safety protocols and production targets are met efficiently. A Quarry Manager holds a broader role, managing the entire quarry site, including equipment maintenance, regulatory compliance, and workforce coordination. Both positions require strong leadership, but the Quarry Manager typically handles strategic planning and resource allocation beyond the immediate excavation activities.
Table of Comparison
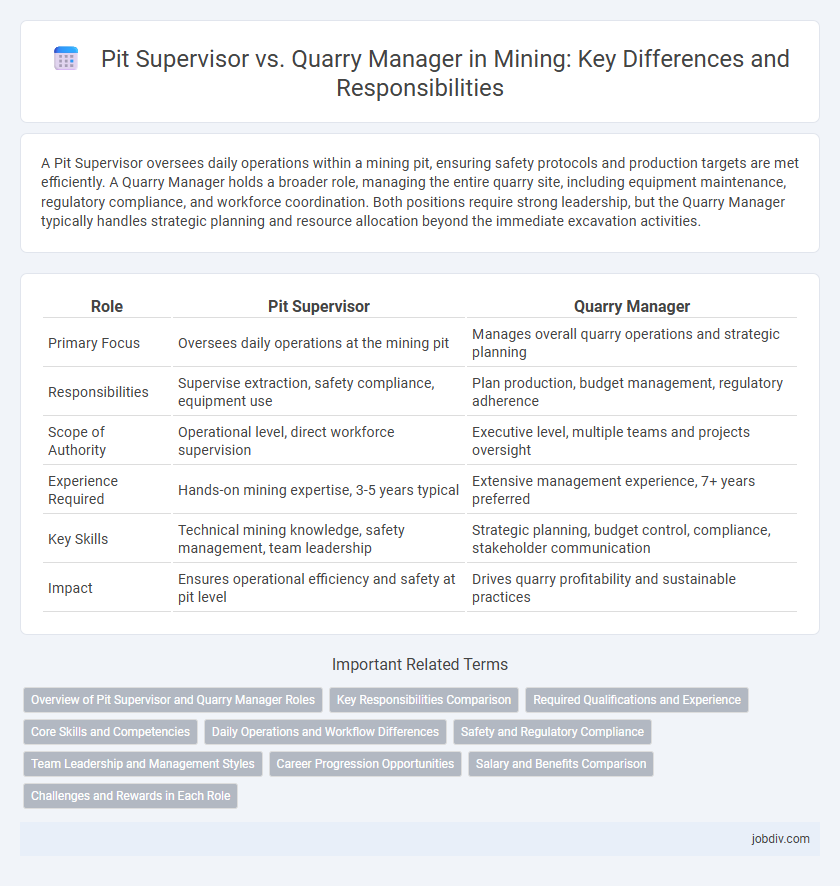
| Role | Pit Supervisor | Quarry Manager |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Oversees daily operations at the mining pit | Manages overall quarry operations and strategic planning |
| Responsibilities | Supervise extraction, safety compliance, equipment use | Plan production, budget management, regulatory adherence |
| Scope of Authority | Operational level, direct workforce supervision | Executive level, multiple teams and projects oversight |
| Experience Required | Hands-on mining expertise, 3-5 years typical | Extensive management experience, 7+ years preferred |
| Key Skills | Technical mining knowledge, safety management, team leadership | Strategic planning, budget control, compliance, stakeholder communication |
| Impact | Ensures operational efficiency and safety at pit level | Drives quarry profitability and sustainable practices |
Overview of Pit Supervisor and Quarry Manager Roles
Pit Supervisors oversee daily operations within mining pits, ensuring compliance with safety regulations and coordinating equipment use to maximize extraction efficiency. Quarry Managers handle broader responsibilities, including planning, budgeting, and supervising all quarry activities from extraction to material processing. Both roles require strong leadership and technical knowledge but differ mainly in scope and strategic involvement in mining operations.
Key Responsibilities Comparison
A Pit Supervisor oversees daily mining operations, ensuring safety compliance, equipment efficiency, and material extraction quality. Quarry Managers handle broader responsibilities including operational planning, resource allocation, regulatory adherence, and coordinating with contractors and stakeholders. While both roles prioritize safety and productivity, the Pit Supervisor focuses on tactical site management, whereas the Quarry Manager directs strategic operational goals and regulatory frameworks.
Required Qualifications and Experience
Pit Supervisors typically require a diploma or degree in mining engineering or a related field, along with 3-5 years of hands-on experience in pit operations. Quarry Managers usually hold a higher qualification, such as a bachelor's degree in mining or civil engineering, paired with 5-10 years of managerial experience overseeing quarry activities. Both roles demand strong knowledge of safety regulations, equipment management, and operational efficiency within mining environments.
Core Skills and Competencies
Pit Supervisors excel in hands-on operational skills such as drilling, blasting, and pit safety management, ensuring efficient extraction processes and adherence to safety protocols. Quarry Managers demonstrate strong leadership, strategic planning, and resource management competencies, overseeing overall site productivity and regulatory compliance. Both roles require expertise in equipment maintenance, workforce coordination, and environmental impact assessment to optimize mining operations.
Daily Operations and Workflow Differences
Pit Supervisors oversee daily extraction activities, ensuring compliance with safety protocols and operational efficiency at the mining face. Quarry Managers coordinate broader workflow planning, including equipment allocation, workforce scheduling, and regulatory reporting across the entire site. The Pit Supervisor's role is more focused on hands-on supervision of site crews, while the Quarry Manager integrates strategic planning to optimize production and resource management.
Safety and Regulatory Compliance
Pit Supervisors and Quarry Managers both play crucial roles in ensuring safety and regulatory compliance within mining operations, but their responsibilities differ in scope and focus. Pit Supervisors oversee daily operational safety protocols on-site, directly managing workers to adhere to safety standards and immediately address hazards, while Quarry Managers develop and implement comprehensive safety programs, ensuring long-term compliance with mining regulations and environmental laws. Effective coordination between these roles is essential to maintain a secure work environment and meet legal mining industry requirements.
Team Leadership and Management Styles
Pit Supervisors typically emphasize hands-on team leadership, directly overseeing daily operations and ensuring safety compliance in mining pits. Quarry Managers adopt a strategic management style, coordinating multiple teams and aligning quarry production goals with company objectives. Effective mining operations benefit from integrating the Pit Supervisor's operational focus with the Quarry Manager's broader organizational leadership.
Career Progression Opportunities
Pit Supervisors gain hands-on experience in daily mining operations, focusing on safety and team coordination, which builds a strong foundation for leadership roles. Quarry Managers oversee broader operational management, including planning, budgeting, and regulatory compliance, offering expanded career growth into senior management positions. Transitioning from Pit Supervisor to Quarry Manager typically involves acquiring advanced skills in project management and operational strategy, enhancing prospects for executive-level roles in the mining industry.
Salary and Benefits Comparison
Pit Supervisors typically earn an average salary between $55,000 and $70,000 annually, whereas Quarry Managers command higher compensation ranging from $70,000 to $95,000 due to greater managerial responsibilities. Benefits for Quarry Managers often include enhanced health insurance, performance bonuses, and profit-sharing options not commonly available to Pit Supervisors. Salary disparities reflect differences in operational oversight, with Quarry Managers frequently receiving additional allowances for leadership and safety compliance.
Challenges and Rewards in Each Role
Pit Supervisors face challenges managing day-to-day operations, ensuring safety compliance, and optimizing extraction processes within often confined and hazardous environments, with rewards including direct impact on productivity and hands-on leadership experience. Quarry Managers tackle broader challenges involving strategic planning, regulatory adherence, equipment maintenance, and workforce coordination across expansive sites, gaining rewards such as higher decision-making authority, operational control, and increased career advancement opportunities. Both roles require strong problem-solving skills, but the Pit Supervisor operates at an operational level while the Quarry Manager handles managerial and strategic responsibilities.
Pit Supervisor vs Quarry Manager Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com