A Real Estate Valuer specializes in determining the market value of properties through inspections, market research, and comparative analysis to support sales, mortgages, and taxation. In contrast, a Real Estate Analyst evaluates broader market trends, financial data, and investment opportunities to guide strategic decisions and portfolio management. Both roles are essential for informed real estate transactions, yet they focus on different aspects of property assessment and investment analysis.
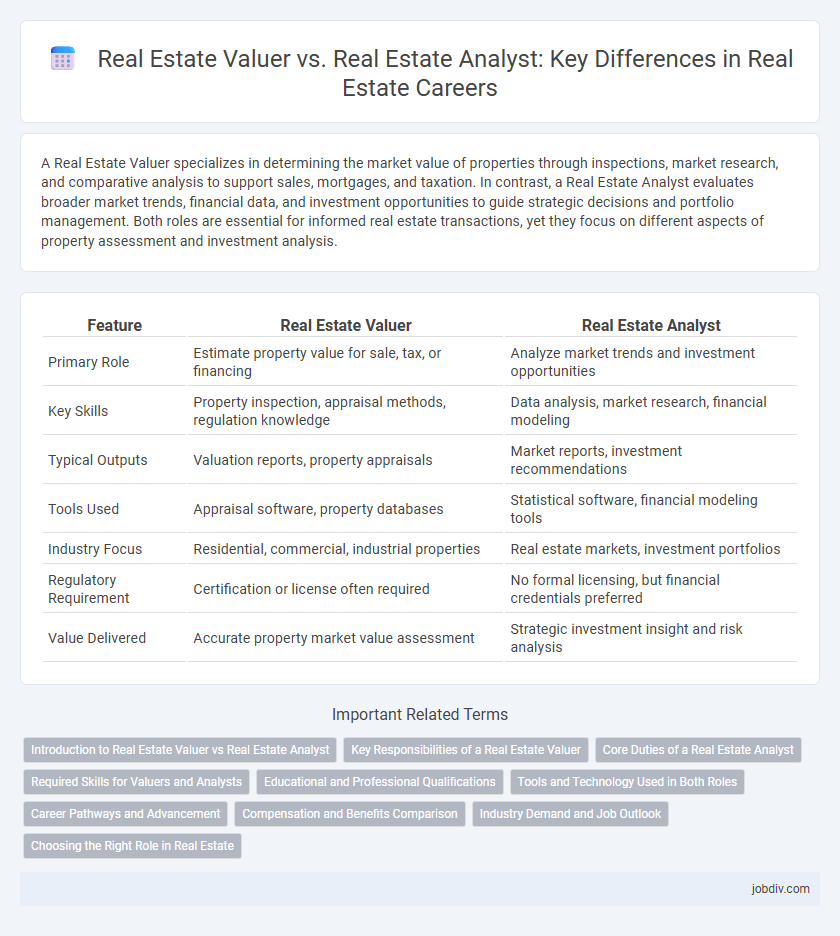
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Real Estate Valuer | Real Estate Analyst |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Estimate property value for sale, tax, or financing | Analyze market trends and investment opportunities |
| Key Skills | Property inspection, appraisal methods, regulation knowledge | Data analysis, market research, financial modeling |
| Typical Outputs | Valuation reports, property appraisals | Market reports, investment recommendations |
| Tools Used | Appraisal software, property databases | Statistical software, financial modeling tools |
| Industry Focus | Residential, commercial, industrial properties | Real estate markets, investment portfolios |
| Regulatory Requirement | Certification or license often required | No formal licensing, but financial credentials preferred |
| Value Delivered | Accurate property market value assessment | Strategic investment insight and risk analysis |
Introduction to Real Estate Valuer vs Real Estate Analyst
Real estate valuers specialize in determining the market value of properties by conducting physical inspections, analyzing comparable sales, and applying valuation methods such as the sales comparison or income approaches. Real estate analysts focus on market trends, financial modeling, and investment performance to provide insights for portfolio management and strategic decision-making. Both roles require strong knowledge of real estate markets but serve distinct purposes: valuers provide property-specific valuations while analysts deliver broader market and investment analyses.
Key Responsibilities of a Real Estate Valuer
A Real Estate Valuer is primarily responsible for determining the market value of properties by conducting detailed inspections and analyzing factors such as location, condition, and comparable sales data. They prepare comprehensive valuation reports used by buyers, sellers, lenders, and insurers for decision-making. Their expertise ensures accurate property appraisals essential for accurate pricing, mortgage approvals, and investment assessments.
Core Duties of a Real Estate Analyst
A Real Estate Analyst specializes in evaluating market trends, conducting financial modeling, and forecasting property investment returns to support strategic decision-making. They analyze data such as rental yields, occupancy rates, and comparable sales to assess asset performance and market potential. Their core duties include preparing detailed reports, advising stakeholders on investment risks, and identifying opportunities for portfolio optimization.
Required Skills for Valuers and Analysts
Real estate valuers require strong expertise in property appraisal methods, market trends analysis, and regulatory compliance to accurately assess property value. Real estate analysts need advanced skills in data interpretation, financial modeling, and market forecasting to evaluate investment opportunities and market conditions. Both roles demand proficiency in industry-specific software and a deep understanding of local real estate markets.
Educational and Professional Qualifications
A Real Estate Valuer typically holds certifications such as a Certified Residential Appraiser or Professional Valuer designation, often requiring specialized training in property appraisal and adherence to regulatory standards. In contrast, a Real Estate Analyst usually possesses a degree in finance, economics, or real estate and focuses on market research, financial modeling, and investment analysis. Both professions demand strong analytical skills, but the valuer emphasizes legal and regulatory knowledge while the analyst prioritizes financial and market data expertise.
Tools and Technology Used in Both Roles
Real Estate Valuers rely heavily on traditional appraisal software such as a la mode and Argus to conduct market comparisons and property inspections, integrating geographic information systems (GIS) for precise location analysis. Real Estate Analysts utilize advanced data analytics platforms like CoStar and REoptimizer to evaluate market trends, financial modeling, and investment performance, leveraging big data and predictive algorithms for strategic decision-making. Both roles increasingly incorporate artificial intelligence and machine learning tools to enhance accuracy and efficiency in property valuation and market analysis.
Career Pathways and Advancement
Real estate valuers specialize in property appraisal, focusing on determining market value for sales, taxation, and investment purposes, often advancing to senior valuer or consultancy roles. Real estate analysts concentrate on market trends, investment analysis, and financial modeling, with career progression leading to portfolio management, investment advisory, or market research director positions. Both career paths offer opportunities for specialization and leadership within real estate firms, financial institutions, and government agencies.
Compensation and Benefits Comparison
Real Estate Valuers typically earn a base salary ranging from $50,000 to $90,000 annually, with additional income from project-based fees and performance bonuses, while Real Estate Analysts usually have a salary range of $60,000 to $95,000, often complemented by bonuses tied to investment performance and market analysis accuracy. Valuers benefit from professional certifications such as the Appraisal Institute's MAI designation, which can significantly enhance earning potential, whereas Analysts often receive specialized training in financial modeling and market analytics that boosts their compensation packages. Both roles may receive benefits like health insurance, retirement plans, and continuing education allowances, but Analysts more frequently access stock options or profit-sharing in investment firms.
Industry Demand and Job Outlook
Real estate valuers specialize in assessing property values for sales, taxation, and investment purposes, with demand driven by market fluctuations and regulatory requirements. Real estate analysts focus on market trends, financial modeling, and investment strategies, experiencing strong growth due to increased real estate investment and data-driven decision-making. Industry projections indicate sustained job growth for both roles, with valuers needed for accurate property assessments and analysts essential for strategic investment insights.
Choosing the Right Role in Real Estate
Choosing between a Real Estate Valuer and a Real Estate Analyst depends on your career goals and skill set, as valuers focus on property appraisal and market value estimation while analysts specialize in data interpretation and investment forecasting. Real Estate Valuers must be proficient in property inspection, legal regulations, and valuation methods like the sales comparison or income approach. Real Estate Analysts require strong financial modeling, market trend analysis, and risk assessment capabilities to guide investment decisions and portfolio management.
Real Estate Valuer vs Real Estate Analyst Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com