Aircraft structures repair involves the restoration and maintenance of the physical framework of an aircraft, including the fuselage, wings, and landing gear, ensuring structural integrity and safety. Avionics repair focuses on the electronic systems used for communication, navigation, and monitoring, requiring specialized equipment and expertise to troubleshoot and fix complex circuitry. Both repair types are critical for overall aircraft functionality but demand distinct skills and tools tailored to mechanical or electronic components.
Table of Comparison
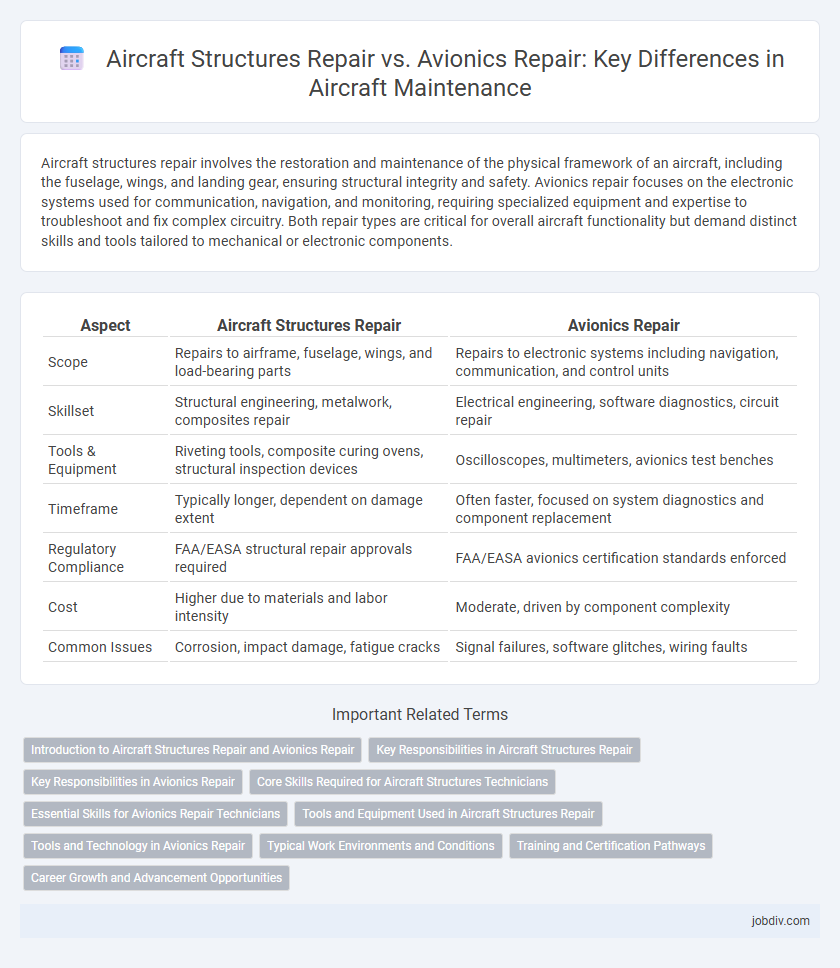
| Aspect | Aircraft Structures Repair | Avionics Repair |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Repairs to airframe, fuselage, wings, and load-bearing parts | Repairs to electronic systems including navigation, communication, and control units |
| Skillset | Structural engineering, metalwork, composites repair | Electrical engineering, software diagnostics, circuit repair |
| Tools & Equipment | Riveting tools, composite curing ovens, structural inspection devices | Oscilloscopes, multimeters, avionics test benches |
| Timeframe | Typically longer, dependent on damage extent | Often faster, focused on system diagnostics and component replacement |
| Regulatory Compliance | FAA/EASA structural repair approvals required | FAA/EASA avionics certification standards enforced |
| Cost | Higher due to materials and labor intensity | Moderate, driven by component complexity |
| Common Issues | Corrosion, impact damage, fatigue cracks | Signal failures, software glitches, wiring faults |
Introduction to Aircraft Structures Repair and Avionics Repair
Aircraft structures repair involves maintenance and restoration of the airframe, including the fuselage, wings, and control surfaces, ensuring structural integrity and airworthiness. Avionics repair focuses on diagnosing and fixing electronic systems such as navigation, communication, and flight control instruments essential for safe flight operations. Both types of repair require specialized skills but target fundamentally different components of an aircraft's functionality and safety.
Key Responsibilities in Aircraft Structures Repair
Aircraft structures repair primarily involves inspecting, restoring, and reinforcing the airframe, fuselage, wings, and control surfaces to maintain structural integrity and flight safety. Key responsibilities include identifying corrosion, repairing cracks or damage using approved materials and techniques, and ensuring compliance with FAA regulations and aerospace standards. Technicians also perform non-destructive testing, replace damaged components, and document all maintenance activities to uphold aircraft airworthiness.
Key Responsibilities in Avionics Repair
Avionics repair primarily involves diagnosing, troubleshooting, and maintaining the aircraft's electronic systems, including navigation, communication, and flight control instruments. Technicians are responsible for calibrating avionics equipment to ensure compliance with FAA regulations and maintaining software updates and hardware integrity. Precise testing and documentation of all repairs play a crucial role in ensuring flight safety and system reliability.
Core Skills Required for Aircraft Structures Technicians
Aircraft structures technicians must possess expertise in metalworking, composite materials, and structural integrity assessments to effectively repair fuselage, wings, and control surfaces. Proficiency in reading and interpreting technical blueprints and adherence to stringent aerospace safety standards ensures precise restoration of aircraft performance. These core skills distinguish structural repairs from avionics maintenance, which centers on electronic systems troubleshooting and software diagnostics.
Essential Skills for Avionics Repair Technicians
Avionics repair technicians must possess strong knowledge of electronic systems, circuit analysis, and aerospace communication protocols to effectively diagnose and repair aircraft avionics. Precision soldering, troubleshooting with oscilloscopes, and proficiency in software updates are critical skills distinguishing avionics repair from mechanical aircraft structures repair. Mastery of Digital Multiplexing (ARINC 429, MIL-STD-1553) and avionics test equipment ensures compliance with aerospace safety standards and enhances repair accuracy.
Tools and Equipment Used in Aircraft Structures Repair
Aircraft structures repair primarily involves heavy-duty tools such as hydraulic jacks, rivet guns, and precision measuring instruments to restore the airframe's integrity. Specialized equipment like non-destructive testing (NDT) devices, including ultrasonic and eddy current testers, ensure structural defects are accurately identified and repaired. These tools differ significantly from avionics repair equipment, which focuses on electronic diagnostic and calibration instruments.
Tools and Technology in Avionics Repair
Avionics repair relies heavily on advanced diagnostic tools such as oscilloscopes, signal analyzers, and specialized software for fault detection and system calibration. These technologies enable precise troubleshooting of complex electronic components and systems within aircraft, ensuring safety and compliance with aviation standards. In contrast to structural repairs that focus on physical materials and fabrication tools, avionics repair demands continuous updates in technology to address evolving electronic systems.
Typical Work Environments and Conditions
Aircraft structures repair typically occurs in hangars, maintenance bays, or on airfields where technicians work with large metal components and composite materials under varied weather conditions. Avionics repair takes place in controlled indoor environments such as specialized labs or workshops equipped with diagnostic tools for sensitive electronic systems. Both environments demand strict adherence to safety protocols and precision, but avionics repair requires more protection from static discharge and contamination.
Training and Certification Pathways
Aircraft structures repair requires specialized training in material sciences, welding techniques, and structural integrity assessment, with certification pathways governed by organizations like the FAA under Part 147 Aviation Maintenance Technician Schools. Avionics repair demands proficiency in electronic systems, circuit diagnostics, and software troubleshooting, often necessitating certifications such as the FAA's Airframe and Powerplant (A&P) with an avionics endorsement or manufacturer-specific programs. Both fields emphasize recurrent training to stay current with regulatory changes and technological advancements, ensuring compliance and safety in aviation operations.
Career Growth and Advancement Opportunities
Aircraft structures repair offers robust career growth through specialized skills in metalwork, composites, and structural integrity assessment, leading to advanced roles such as structural engineer or maintenance supervisor. Avionics repair focuses on electronic systems diagnostics, software updates, and avionics integration, providing advancement opportunities toward avionics systems specialist or avionics lead technician. Both fields demand continuous technical training and certification, but avionics repair often aligns with emerging technologies, boosting long-term career advancement in aerospace innovation.
Aircraft Structures Repair vs Avionics Repair Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com