Heavy equipment repair demands specialized knowledge of complex hydraulic and mechanical systems, often requiring advanced diagnostic tools and substantial physical labor to maintain large machinery used in construction and farming. Small engine repair focuses on compact, simpler engines found in lawn mowers, chainsaws, and generators, emphasizing precision work with carburetors, spark plugs, and fuel systems. Both require technical skills, but heavy equipment repair involves larger scale operations and heavier components, while small engine repair prioritizes accessibility and fine-tuning.
Table of Comparison
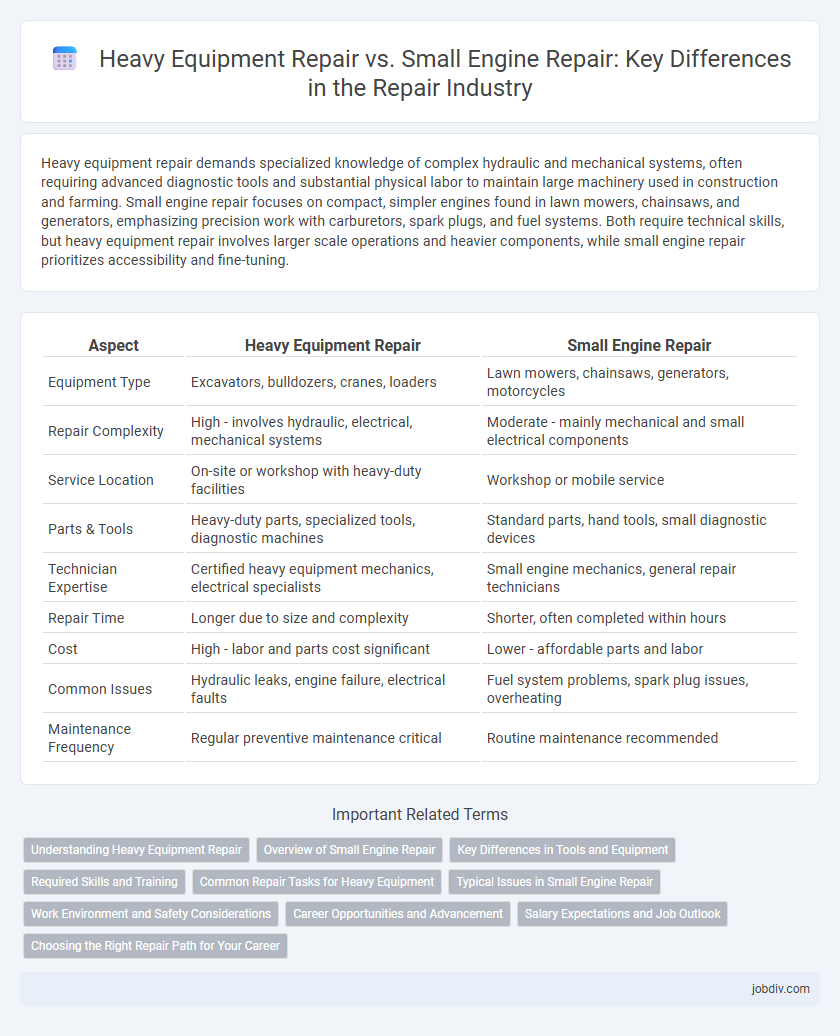
| Aspect | Heavy Equipment Repair | Small Engine Repair |
|---|---|---|
| Equipment Type | Excavators, bulldozers, cranes, loaders | Lawn mowers, chainsaws, generators, motorcycles |
| Repair Complexity | High - involves hydraulic, electrical, mechanical systems | Moderate - mainly mechanical and small electrical components |
| Service Location | On-site or workshop with heavy-duty facilities | Workshop or mobile service |
| Parts & Tools | Heavy-duty parts, specialized tools, diagnostic machines | Standard parts, hand tools, small diagnostic devices |
| Technician Expertise | Certified heavy equipment mechanics, electrical specialists | Small engine mechanics, general repair technicians |
| Repair Time | Longer due to size and complexity | Shorter, often completed within hours |
| Cost | High - labor and parts cost significant | Lower - affordable parts and labor |
| Common Issues | Hydraulic leaks, engine failure, electrical faults | Fuel system problems, spark plug issues, overheating |
| Maintenance Frequency | Regular preventive maintenance critical | Routine maintenance recommended |
Understanding Heavy Equipment Repair
Heavy equipment repair involves servicing large machinery used in construction, mining, and agriculture, requiring specialized skills in hydraulics, diesel engines, and electrical systems. Technicians must diagnose complex mechanical failures and perform repairs on components like transmissions, engines, and hydraulic pumps to ensure optimal performance. Understanding heavy equipment repair is crucial for maintaining operational efficiency and preventing costly downtime on job sites.
Overview of Small Engine Repair
Small engine repair involves the maintenance and fixing of engines typically found in lawn mowers, chainsaws, generators, and other portable equipment, focusing on engines under 25 horsepower. This type of repair requires specialized knowledge of carburetor adjustments, ignition systems, fuel lines, and basic engine diagnostics to ensure optimal performance. Compared to heavy equipment repair, small engine repair emphasizes precision work on compact components and troubleshooting common issues like starting failures, fuel contamination, and wear of small internal parts.
Key Differences in Tools and Equipment
Heavy equipment repair requires specialized tools such as hydraulic lifts, large torque wrenches, and diagnostic systems designed for engines exceeding 100 horsepower, whereas small engine repair often involves handheld diagnostic devices, spark plug testers, and compact torque tools suitable for engines under 25 horsepower. The scale and complexity of machinery dictate the use of heavy-duty cranes, engine hoists, and computerized diagnostic software in heavy equipment repair, contrasting with the manual, portable toolkits used in small engine maintenance for lawn mowers or motorcycles. Equipment size, power output, and operational demands directly influence the types of repair tools, making heavy equipment repair tasks more reliant on industrial-grade apparatus and small engine repair more focused on precision and portability.
Required Skills and Training
Heavy equipment repair demands specialized training in hydraulic systems, diesel engines, and electronic controls for large machinery, requiring certifications such as ASE or manufacturer-specific programs. Small engine repair focuses on gasoline-powered engines under 25 horsepower, emphasizing skills in carburetor adjustments, spark plug maintenance, and fuel system diagnostics, often gained through technical schools or apprenticeships. Both fields require mechanical aptitude and problem-solving abilities, but heavy equipment repair involves more advanced diagnostics and adherence to safety regulations due to the complexity and size of the machinery.
Common Repair Tasks for Heavy Equipment
Common repair tasks for heavy equipment include hydraulic system maintenance, engine overhauls, and track or tire replacements. Technicians frequently address issues such as hydraulic leaks, engine malfunctions, and wear on undercarriage components. Proper calibration and alignment of heavy machinery are critical to ensure optimal performance and prevent costly downtime.
Typical Issues in Small Engine Repair
Small engine repair commonly involves addressing issues such as carburetor clogs, spark plug failures, and fuel line blockages that reduce engine performance. These repairs often require precise adjustments and replacements to restore efficient combustion and power output. Unlike heavy equipment repair, which deals with complex hydraulic and structural systems, small engine repair focuses on fine-tuning mechanical and electrical components for reliable operation.
Work Environment and Safety Considerations
Heavy equipment repair typically occurs outdoors or in large, industrial workshops where technicians handle machinery weighing several tons, necessitating strict adherence to safety protocols such as using heavy-duty personal protective equipment (PPE) and following machinery lockout/tagout procedures. In contrast, small engine repair is often performed indoors in smaller workshops with controlled environments, focusing on precision tasks requiring hand tools and moderate safety measures like eye protection and proper ventilation to mitigate exposure to fumes. Both work environments demand rigorous safety training, but the scale and type of hazards differ significantly, influencing the specific safety strategies employed.
Career Opportunities and Advancement
Heavy equipment repair offers expansive career opportunities in industries such as construction, mining, and agriculture, with higher earning potential due to the complexity and scale of machinery involved. Small engine repair careers are often found in automotive, landscaping, and recreational equipment sectors, providing faster entry-level roles but with limited advancement compared to heavy equipment technicians. Specializing in heavy equipment repair typically leads to advanced positions like fleet maintenance supervisor or technical trainer, reflecting its greater demand for specialized skills and ongoing professional development.
Salary Expectations and Job Outlook
Heavy equipment repair technicians typically earn between $50,000 and $75,000 annually, reflecting the specialized skills required to maintain and fix large machinery in industries like construction and mining. Small engine repair specialists, focusing on engines for lawn mowers, motorcycles, and generators, generally have salary expectations ranging from $30,000 to $45,000, with steady demand due to widespread use in residential and commercial maintenance. Job outlook for heavy equipment repair is projected to grow faster than average at about 6%, driven by infrastructure development, while small engine repair jobs experience modest growth around 3%, supported by consistent consumer needs.
Choosing the Right Repair Path for Your Career
Specializing in heavy equipment repair offers career opportunities in industries like construction, mining, and agriculture, requiring proficiency in hydraulic systems, diesel engines, and large mechanical components. Small engine repair emphasizes maintenance and troubleshooting of smaller engines found in lawnmowers, motorcycles, and generators, demanding skills in carburetors, spark plugs, and electrical systems. Selecting the right repair path depends on your interest in equipment scale, industry focus, and preferred complexity of mechanical challenges.
Heavy Equipment Repair vs Small Engine Repair Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com